Question
2. Two blocks move across a frictionless table due to a constant force of 8 N applied down as shown in the figure. Assume that the rope and pulley are massless and frictionless. What force is applied by block A on B?
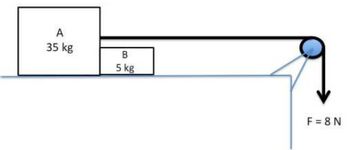
Transcribed Image Text:A
35 kg
B
5 kg
F = 8 N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- An empty elevator car of a building has a mass of 1 metric ton. It has a counterweight with a mass of 1.2 metric tons. What force must the motor of the elevator pull on the counterweight to make the elevator car go down with an acceleration of 0.5 m/se/sec? a. 12000 N b. 3057 N c. 11171 N d. 10310 Narrow_forwardF-H Only! Pleasearrow_forward8. Two 14-kg blocks are connected with a light rope pand the system is accelerating at 1.8 m/s°[Right]. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the blocks and the floor is 0.35. A F. a) Calculate the magnitude of the applied force, F,. b) Calculate the tension in the rope between block B and A.arrow_forward
- Two blocks are connected via a pulley, both blocks have a mass of 10.kg. One block rests on a horizontal surface and the other one hangs freely by a cord which passes over a pulley. Assume the cord does not stretch, ignore mass of pulley and cord, therefore acceleration is the same for both blocks and tension is the same for both blocks. The hanging block moves down so the block lying on the horizontal surface moves to the right. b. A 10.0 kg box slides down a 30.0 degrees incline at a rate of 0.40 m/s^2. What is the coefficient of kinetic frictionarrow_forwardThe net external force on the 25.5kg mower is 48.0N. If the force of friction is 22.5N. a. What force F in newtons is the person exerting on the mower? b.Suppose the mower is moving 1.10 m/s when the force F is removed. How fat will the mower go before stopping?arrow_forwarda. What is the mass of a book that weighs 3.2 N at a point where g = 9.80 m/ s2? b.At the same location, what is the weightof a dog whose mass is 14.0 Kg ?arrow_forward
- A force 450 N pushes on a 30.7 kg box at an angle of 50° from the horizontal. Starting from rest , the box achieves a velocity of 16.37 m/s in a time of 3.7 s. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the floor. a. 0.24 b. 0.45 c. 0.51 d. 0.35 A child on a sled has been given a push so that he is moving up a hill. The hill is covered with icy snow and can be treated as frictionless. The child has a mass of 22.7 kg; the sled has a 3.18 kg. How far will he go before coming to a stop if his speed is 2.44 m/s when he starts at the bottom of the hill? He holds on tightly and so does not fall off the sled, and the hill makes an angle of 25.50 with the horizontal. a. 0.29 m b. 1.14 m c. 1.41 m d. 0.70 marrow_forward7. A bowling ball and a feather are dropped from a height of 100 ft. The bowling ball weighs 12 Ibs and the feather weighs 3 ounces. a. What is the Force (in Newtons) of both objects? b. The value of g is varies depending on what planet you are on. Bigger planets have a larger value of g. The value of g on the moon is 1.62 m/s2. Calculate the forces of these objects falling on the moon.arrow_forwardA 2.00-kg object B is connected with a string to a 3.00-kgobject A, which is connected with a second string over a massless, frictionless pulley to a 8.00-kg object C. The strings have negligible mass and do not stretch, and the level tabletop is frictionless. Calculate the tension ?1. ?1= N Calculate the tension ?2. ?2= N Calculate the acceleration ? of the system. ?= m/s2arrow_forward
- A 2.0 kg box is at rest on a flat horizontal surface. A continuously applied force is then exertedon the box. When the applied force just exceeds 5.0N the box then begins to move. Q1. Construct a free-body diagram for the box at the moment when the applied force is 5.0N. Q2. Determine the magnitude of the peak static friction force and the corresponding coefficientof static friction.arrow_forward18. A child sits on a sled at the top of a hill, the hill makes an angle of 20° with the horizontal. The child's mass is 40kg. Use us = .1 and 4.03 a. b. Draw a free body diagram for this system. Does the child accelerate down the hill? *i.e., check that the coefficient of static friction is vercome by the component of the childs weight in the direction the child would accelerate. If they do, what is their acceleration? *use coefficient of kinetic friction in sum of the forces balance if the child moves.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios