
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Two blocks are joined by an inextensible cable as shown. The mass of block A is 192.4 kg and the mass of block B is 260.3 kg. If the system is released from rest, determine the acceleration (in m/s2 ) of block B. Assume that the coefficient of friction between block A and the plane is μk = 0.22 and that the pulley is weightless and frictionless.
Round off only on the final answer expressed in 3 decimal places. Use g = 9.81 m/s2
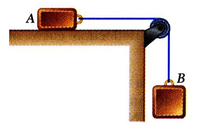
Transcribed Image Text:A
В
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Learning Goal: To apply the principle of angular impulse and momentum to find final speed and the time to reach a given speed. M B As shown, ball B, having a mass of 10.0 kg, is attached to the end of a rod whose mass can be neglected. Part A - Finding the final speed of the ball If the rod is 0.550 m long and subjected to a torque M = (2.45t² + 4.45) N-m, where t is in seconds, determine the speed of the ball when t= 3.10 s. The ball has a speed of v = 2.80 m/s when t = 0. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardUnder the man's pushing force P= 30.8 lb, the uniform cabinet is sliding on the ground with a constant acceleration of a. If the uniform cabinet has weight of 150 lb, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the cabinet and the ground is Uk 0.14, determine acceleration a in ft/s2. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g = 32.2 ft/s². -1 ft→1 ft→ P G 4 ft 3.5 ft В Your Answer: Answerarrow_forwardi need the answer quicklyarrow_forward
- The uniform 52-kg slender bar is initially at rest on a smooth horizontal plane when the forces are applied. If P₁ = 20 N and P₂ = 86 N, they are constant and are always perpendicular to the slender bar, determine angle (in degree) when time t = 0.40 s has passed. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. 0.75 m P₁ Your Answer: Answer 1.75 m 0.5 m P₂arrow_forward3. Blocks AA and BB of mass 10 kg and 4 kg respectively, are placed on the inclined plane and released. The coefficients of kinetic friction between the blocks and the inclined plane are μAμAmuA = 0.1 and μBμBmuB = 0.5. Neglect the mass of the linkarrow_forwardQ22. As shown in the image below, the force acting on the 5-kg crate is a function of time. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the surface is uk = 0.15. Determine the magnitude of the horizontal impulse (in N-s) done by all external forces to the crate during the period from t = 0 to t= 2.3 s. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s2. %3D F = (201² +30) N (t in second) F = F. 30 V1 Your Answer: Answerarrow_forward
- 7arrow_forwardA 100-kg box is towed to move horizontally from rest by a constant force P=200 N. The kinetic friction is μk =0.1. The angle of the force P is θ=30° with respect to the horizontal direction. The acceleration due to gravity is g=9.81 m/s2. (3) Select the expression of the friction force F. ___________ A. F=μN B. F=μP C. F=μmg D. F=0arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY