Question
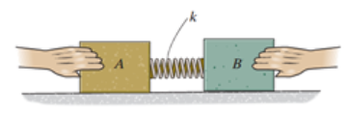
Two blocks A of mass mA and B of mass mB are connected to each other by a spring of length L, spring constant k, and negligible mass. The two blocks are released from rest on a smooth floor (negligible friction) when the spring is compressed by half of the springs’ length. The blocks move away from each other with speeds that can be related using the conservation of combined momentum of the two blocks. Which of the following best describes the relationship between the speeds of the two blocks?
A. vA = (mB/mA)vB
B. vA = (mA/mB)vB
C. vA = vB (mB/(mA+ mB))
D. vA = vB
Transcribed Image Text:34
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A box of mass 2.0 kg is hit with an arrow of mass 0.030 kg. The box then slides 24 cm before coming to rest. The coefficient of friction between the box and table is 0.30. What was the speed of the arrow when it hit the box?arrow_forwardA car of mass 1,907 kg collides with a wall. The initial speed of the car is 18.2 m/s. After collision, the car bounced in the opposite direction at a speed of 2.9 m/s. If the collision lasted for 172 ms, what was the average force in newtons exerted on the car by the wall? Express your answer in two decimal places with units of Newton.arrow_forwardBlock A (with mass 10 kg) slides along a frictionless floor with a speed of 0.75 m/s and collides with Block B (with mass 12 kg) which was at rest and is attached to a spring with spring constant 24 N/m. The blocks stick together after the collision; what is the maximum compression of the spring?arrow_forward
- A toy rocket operates by having a spring-loaded tube which ejects a small model rocket when released. The spring inside has a spring constant k = 625N/m, the rocket has a mass of 0.100 kg, and the maximum compression of the spring is 0.18 m. Consider the system of the rocket, spring, and the earth. Consider the interval of time between t1, when the rocket is released from the point of maximum spring compression, and t2, the moment when the spring is fully released and the rocket leaves the launcher. List below the types of energy that are changing during this interval and whether the changes are positive or negative. Please explain how you know.arrow_forwardWhen some cars are advertised, they quote a "stopping distance" from some speed to zero. The mass of the car and this value of "some speed" give a measure of initial motion, but we aren't necessarily told the mass. Using the stopping distance, one can directly calculate what physical quantity provided by the brakes? A impulse B chemical potential energy C power D kinetic energy E force F velocity G work H acceleration I massarrow_forwardA bullet of mass mb is fired horizontally with speed vi at a wooden block of mass mw resting on a frictionless table. The bullet hits the block and becomes completely embedded within it. After the bullet has come to rest relative to the block, the block, with the bullet in it, is traveling at speed uf. (Figure 1) Figure Before collision mb mw 1 of 1 After collision ▼ Part A Which of the following best describes this collision? View Available Hint(s) Operfectly elastic O partially inelastic Operfectly inelastic Submit Part B Which of the following quantities, if any, are conserved during this collision? ►View Available Hint(s) Okinetic energy only O momentum only Okinetic energy and momentum Oneither momentum nor kinetic energy Submit P Pearsonarrow_forward
- In a system with two moving objects, when a collision occurs between the objects: the total kinetic energy is always conserved. the total momentum is always conserved. neither the kinetic energy nor the momentum is conserved. the total kinetic energy and total momentum are always conserved.arrow_forwardDoing some physics homework and am kind of stumped here!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios