
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Two blocks A and B meet in
contact as shown in the figure. If he
coefficients of static friction for all
the surfaces in contact is 0.2,
Determine whether the 50-lb force moves the
block A up, keep balance,
or move block A down,
shifting block B to the right.
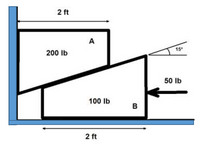
Transcribed Image Text:2 ft
A
15
200 Ib
50 lb
100 lb
B
2 ft
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- give upvote for right answerarrow_forwardHello good evening, Permission, i have a question in my homework. The following bellow is question. Please advice. Thank you Regards,Irfan A 132-lb cabinet is mounted on casters that can be locked to preventtheir rotation. The coefficient of static friction between the floor and each caster is 0.30. Assuming that the casters at both A and B are locked, determine :(a) the force P required to move the cabinet to the right, (b) the largest allowable value of h if the cabinet is not to tip over.arrow_forwardQ3 - Blocks A and B have a mass of 7 kg and 10 kg, respectively, and there are pulleys at C and D. Using the coefficients of static friction indicated, determine the following: 1- The smallest force P which can be applied to the cord that causes impending motion. 2- Does block B spill, flip over, or nothing happen? Prove that. 400 mm D B 500 mm HAB=0.1 A P MA=0.3arrow_forward
- The uniform 20-lb ladder rests on the rough floor forwhich the coefficient of static friction is s = 0.45 andagainst the smooth wall at B. Determine the horizontalforce P the man must exert on the ladder in order tocause it to move. Answer: P = _____________arrow_forwardUsing the definition of the static friction and the first condition of equilibrium, show that the coefficient of static friction in Method A is the ratio of the weight of the pan plus its contents to the weight of the carrier of the pan plus its contents to the weight of the carrier plus its content. Note: Show your free body diagrams.arrow_forwardgive upvote for right answerarrow_forward
- 1. The two 890 N blocks are pushed apart by the 150 wedge of negligible weight. The angle of static friction is 12° at all surfaces. Determine the force P required to start the blocks moving. 890N 890Narrow_forwardCalculate the horizontal force P on the light 14° wedge necessary to initiate movement of the 49-kg cylinder. The coefficient of static friction for both pairs of contacting surfaces is 0.40. Also determine the friction force FB at point B. (Caution: Check carefully your assumption of where slipping occurs.) P Answers: P= FB = i i 49 kg B N N Aarrow_forwardi need the answer quicklyarrow_forward
- Calculate the horizontal force Pon the light 11° wedge necessary to initiate movement of the 36-kg cylinder. The coefficient of static friction for both pairs of contacting surfaces is 0.40. Also determine the friction force Fg at point B. (Caution: Check carefully your assumption of where slipping occurs.) 36 kg A B P > 119 Answers: P = 108 N FB = i 27.1 Narrow_forwardCalculate the horizontal force P on the light 14° wedge necessary to initiate movement of the 49-kg cylinder. The coefficient of static friction for both pairs of contacting surfaces is 0.40. Also determine the friction force FB at point B. (Caution: Check carefully your assumption of where slipping occurs.) P Answers: P = FB = i i 4.87e+2 3.09e+2 49 kg B N A Narrow_forwardThe coefficient of static friction for both wedge surfaces is 0.37 and that between the 27-kg concrete block and the 28° incline is 0.70. Determine the minimum value of the force P required to begin moving the block up the incline. Neglect the weight of the wedge. Answer: P- -27 kg 28¹ Narrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY