
Trigonometry (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134217437
Author: Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie Daniels
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
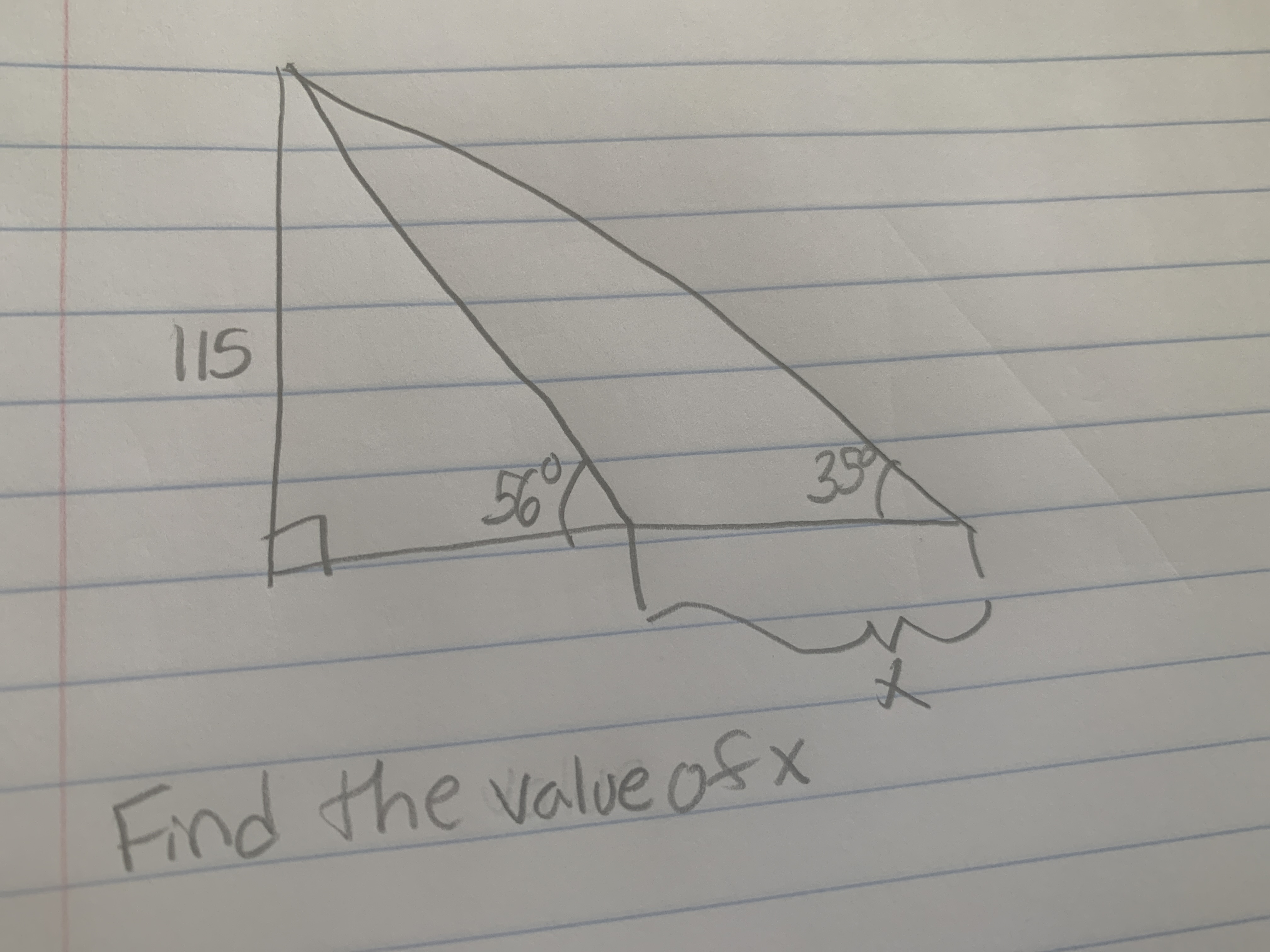
Transcribed Image Text:**Title: Solving for the Value of x in a Triangle**
**Introduction:**
This problem involves finding the value of the variable \( x \) in a geometric setup involving triangles. Understanding the relationship between the angles and sides of a triangle will be key in solving this problem.
**Diagram Explanation:**
We have a diagram of a right triangle with the following components:
- One angle is marked as \( 50^\circ \).
- Another angle is marked as \( 30^\circ \).
- There is a right angle at the base, denoted by the square corner.
- The side opposite the \( 30^\circ \) angle is labeled as \( x \).
- The adjacent side to the \( 30^\circ \) angle, parallel to the base, is given as \( 115 \).
**Problem Statement:**
Find the value of \( x \).
**Steps to Solve:**
1. Recognize that since the triangle is a right triangle, the angles must add up to \( 180^\circ \).
2. Use the fact that the sum of angles in a triangle is \( 180^\circ \) to find any missing angle.
3. Apply trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, or tangent) to solve for \( x \).
**Conclusion:**
Using the relationships between the triangle's angles and applying basic trigonometric identities, the value of \( x \) can be determined. This exercise provides practical experience in applying geometric principles and trigonometry to solve for unknown variables.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
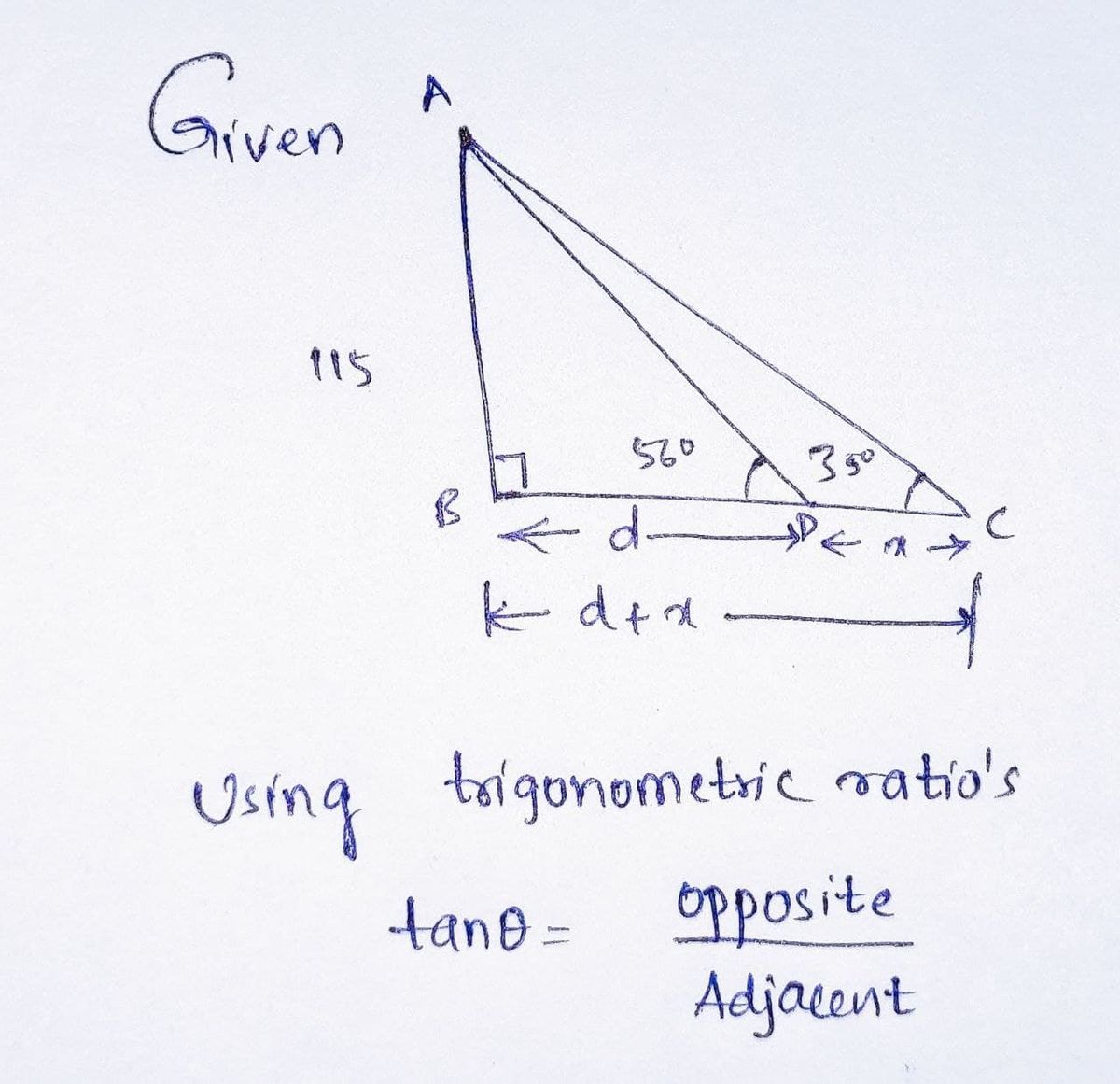
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Trigonometry (11th Edition)TrigonometryISBN:9780134217437Author:Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie DanielsPublisher:PEARSON
Trigonometry (11th Edition)TrigonometryISBN:9780134217437Author:Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie DanielsPublisher:PEARSON Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (11th Edition)
Trigonometry
ISBN:9780134217437
Author:Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie Daniels
Publisher:PEARSON

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:9781305652224
Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:9781337278461
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Cengage Learning