
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
identify test statistic
identify p-value
Construct a confidence interval suitable for testing the claim that the two samples are from populations with the same mean.__<μ1−μ2<__(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
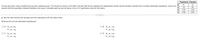
Transcribed Image Text:Treatment Placebo
lu
A study was done using a treatment group and a placebo group. The results are shown in the table. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations, and do not
In
H2
25
40
assume that the population standard deviations are equal. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. Use a 0.01 significance level for both parts.
2.35
2.63
0.94
0.65
a. Test the claim that the two samples are from populations with the same mean.
What are the null and alternative hypotheses?
O A. Ho: H1 µ2
H1: H1 <H2
O B. Ho: H1 < H2
H1: H1Z H2
OC. Ho: H1 = #2
O D. Ho: H1 = H2
H1: H1> H2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Hi could you answer whts in blankarrow_forwardDetermine the critical zz-values (z α/2 )(z α/2 ) corresponding to the confidence levels in the table below. Round answers to 3 decimal places for right tail areas and 2 decimal places for critical values Confidence Level Right Tail Area (α/2)(α/2) Critical Value (zα/2)(zα/2) 94% 86% 99% 82% 83%arrow_forwardR1arrow_forward
- R %24 X 021 6-3 Challenge Activities: Confide X 1zd zy Section 6.2- MAT 240: Applied S X https://learn.zybooks.com/zybook/MAT-240-J4452-OL-TRAD-UG.22EW4/chapter/6/section/2 1y library > MAT 240: Applied Statistics home > 6.2: Confidence intervals for population means E zyBooks catalog ? F CHALLENGE 6.2.2: Relating confidence intervals to hypothesis testing (one sample). ACTIVITY 389618.2548816.qx3zqy7 Jump to level1 A worker stands at the end of a production line for mint chocolate chip ice cream and uses warm water to melt the ice cream away from the chocolate. The amount of chocolate is then weighed. Each container should contain 4 ounces of chocolate. The results of a simple random sample of 12 containers is shown below. Assume the amount of chocolate added to the ice cream is normally distributed. 3. Chocolate 3.917 0.042 12 Mean Variance Observations Hypothesized Mean What condition is met for the use of a t-distribution? 1. -1.42 JP Pick t Stat P(T<=t) one-tail t Critical…arrow_forwardHow do I do this? Please helparrow_forward3) Estimating the Mean: Unknown Variance a) A student is working on his science fair project concerning the average height of a certain native plant, which he believes is normally distributed. He finds 25 mature plants and measures their heights, and determines the average height to be 10.2 cm (s = 1.2 cm). Construct a 96% confidence interval on the mean height of the plants. .<μ<.arrow_forward
- data: FieldA and Fields af- 34.751, p-value e.001292 alternative hypothesis: true difference in means is not equal to 0 95 percent conf dence interval: sample estimates: mean of x mean of 13.98803 11.02686 Q. Based on the summary statistics calculate the missing t test statistic from the R output: t statistic = 3.583 Q. Give the set up for the 95% confidence interval for the difference in averages. Use the degrees of freedom from the R output (round down). Estimate ± Critical Value × Standard Error - 14 2.042 0.701 Q. Make a conclusion based on the previous results. There is convincing evidence the average percent of water by volume in the soil between Field A and Field B differs. Based on the p-value, the test rejects * the null hypothesis. The 95% confidence interval and point estimate indicate the Field A has more average percent by volume than Field B.arrow_forwardTest the claim that for the population of statistics final exams, the mean score is 7676 using alternative hypothesis that the mean score is different from 76.76. Sample statistics include ?=21,n=21, ?⎯⎯⎯=78,x¯=78, and ?=11.s=11. Use a significance level of ?=0.05.α=0.05. (Assume normally distributed population.) The test statistic is The positive critical value is The negative critical value is The conclusion is A. There is sufficient evidence to reject the claim that the mean score is equal to 76. B. There is not sufficient evidence to reject the claim that the mean score is equal to 76.arrow_forwardcholesterol of all 20- to 29-year-old females. How many subjects are needed to estimate the mean HDL cholesterol within 2 points with 99% confidence assuming s=14.7 based on earlier studies? Suppose the doctor would be content with 95% confidence. How does the decrease in confidence affect the sample size required? A 99% confidence level requires ________ subjects. (Round up to the nearest subject.)arrow_forward
- n1=16 x‾1=124 s1=35 n2=12 x‾2=86 s2=31 Use this data to find the 98% confidence interval for the true difference between the population means. Assume that the population variances are not equal and that the two populations are normally distributed. Copy Data Step 2 of 3 : Find the margin of error to be used in constructing the confidence interval. Round your answer to six decimal places. Step 3 of 3 : Please also find the high and low endpoints and round to four decimal points.arrow_forwardImpact of the Population Standard Deviation on SE Compute the standard error for sample means from populations all with mean μ = 80 and with standard deviations o and o = 75 using a sample size of n = 90. Round your answers to two decimal places, if necessary. Standard Deviation o = 11: o = 40: o = 75: HI Standard Error = 11, o = 40,arrow_forwardjust the last part thank you!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman