
Toys Insane Inc. produces two goods: Glibber Gems (G) and Blubber Bricks (B). In order to produce Glibber Gems and Blubber Bricks, three input factors are necessary: Slime (S), Tran (T), and Gorilla Mucus (M). The following table summarizes how many input factors are necessary to produce one unit of each good and how many input factors are available in total:
|
|
Glibber Gems |
Blubber Bricks |
Total Units Available |
|
Slime Units |
1 |
2 |
14 |
|
Tran Units |
3 |
4 |
36 |
|
Gorilla Mucus Units |
9 |
6 |
90 |
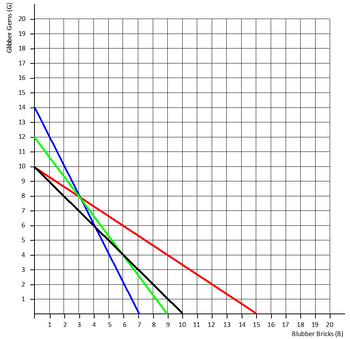
Below graph shows four lines: One for each constraint and an isoprofit line.
1: The slime constraint has which color?
| a |
Red |
| b |
Blue |
| c |
Green |
| d |
Black |
2: The tran constraint has which color?
| a |
Red |
| b |
Blue |
| c |
Green |
| d |
Black |
3: The gorilla mucus constraint has which color?
| a |
Blue |
| b |
Red |
| c |
Black |
| d |
Green |
4: The isoprofit line has which color?
| a |
Red |
| b |
Blue |
| c |
Green |
| d |
Black |
5: The slime constraint is represented by which equation?
| a |
G<=14-2B |
| b |
G<=10-1B |
| c |
G<=12-4/3B |
| d |
G<=10-2/3B |
6: The tran constraint is represented by which equation?
| a |
G<=10-1B |
| b |
G<=12-4/3B |
| c |
G<=14-2B |
| d |
G<=10-2/3B |
7: The gorilla mucus constraint is represented by which equation?
| a |
G<=14-2B |
| b |
G<=12-4/3B |
| c |
G<=10-2/3B |
| d |
G<=10-1B |
8:The isoprofit line is represented by which equation?
| a |
G=14-2B |
| b |
G=12-4/3B |
| c |
G=10-2/3B |
| d |
G=10-1B |
9: Given the constraints, what can be said about the combination of G=6 and B=6?
| a |
It is within the area of feasible production |
| b |
It is the profit maximizing production mix |
| c |
Both a. and b. |
| d |
None of the above |
10: Assuming that the unit profits for Glibber Gems and Blubber Bricks are each $5, what will be the profit maximizing production mix?
| a |
G=3, B=8 |
| b |
G=6, B=6 |
| c |
G=8, B=3 |
| d |
G=4, B=6 |
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

- Substitutions for goods cannot always be made. Which of the following is an example of a good that cannot be substituted with another good? gasoline jeans cow's milk cranberry juicearrow_forwarda) Explain by using an example why an MRS (Marginal Rate of Substitution) between two goods must equal the ratio of the price of the goods for the consumer to achieve maximum satisfaction?arrow_forwardGraphically show the effect of an increase in the cost of the tomato sauce on the equilibrium price and output in the market for pizza.arrow_forward
- Question #2 Consider the following demand function for frozen dinners where QD is the quantity of frozen dinners demanded per week, P is the price per frozen dinner, PF is the price per fast food meal, Y is the average yearly consumer income, and A is the number of advertisements for frozen dinners. Demand Function for Frozen Dinners: QD = 1,000 – 10P + 20PF – 0.01Y + A Suppose that a frozen dinner sells for $4, a fast food meal sells for $6, average yearly consumer income is $50,000, and that there are 20 advertisements for frozen dinners. Calculate and interpret the income elasticity of demand. Calculate and interpret the cross-price elasticity of demand with respect to fast food meals.arrow_forward(In this question we denote income by Y, not by W as in the lecture notes). The following figure shows the consumption of x and y for two market situations. We can conclude that: x is a normal good for all market situations. py is greater than px. It is not conclusive. x is an inferior good for some market situation. y is an inferior good for some market situation.arrow_forwardAyana is pitching an idea for a startup company that makes and sells solar-powered phonechargers (C). Her market research has found that consumer demand for this product can beexpressed as a function of the price of the charger itself (PC), the price of phones (PF), andthe consmer’s income (I). Consumer demand can be described by the function C(PC, PF, I) =(i−10PC)/ (PF) Suppose her chargers come in all different capacities to meet any quantity demanded, so youdon’t need to worry about restricting C to whole numbers for this problem. (a) Does this product satisfy the law of demand?Explain.arrow_forward
- Answer the question based on the following graph. Which of the following statements is entirely correct? Tom's monthly budget constraint 40 •D E nts 20 Number of hamburgers per month O Point E is unattainable and Point D is inefficient. O Both point D and E are unattainable. O Point E is inefficient and Point D is unattainable. O Point A is inefficient and Point E is unattainable. « Previous Next Number of hot dogs per montharrow_forwardPlease refer to the following information to answer the question (in bold) below: You enjoy consuming apples (A) and oranges (O). Suppose that your utility function over both goods is given by Your marginal utility function for apples is . Your marginal utility function for oranges is U (A, O) = AO³ MUA = 0³ MUO 3A0² . Currently, the price of apples is $10/peck, the price of oranges is $5/pound, and your income is $160. Assume that apples are your horizontal axis good and oranges are your vertical axis good. = When you set up the optimal decision rule for your consumer problem, which of the following statements best describes how much you will buy of apples and oranges at your consumer equilibrium? For each peck of apples, you will buy 1/3 pounds of oranges. For each peck of apples, you will buy 1 pounds of oranges. O For each peck of apples, you will buy 3 pounds of oranges. O For each peck of apples, you will buy 6 pounds of oranges.arrow_forwardPlease answer the question fully and completely else I will rate negative, thanks! Question 3 Consider an economy with two consumers, A and B, two goods called 1 and 2 and one firm. Consumers A and B are each endowed with a unit of each good. The utility functions of each consumer are: A: 13 4 4 u (x₁‚x2 ) = lnx₁ + Inx2 B:u ₁₂ (x, ‚ x 2 ) = x, x 2 The firm B 1 A 1 1 2 produces good 2 using good 1 as an input, according to the production function f(y) = y where y is the quantity of good 1. Consumer A is the sole shareholder of the firm and the firm operates to maximize profit. Page 2 If P₁ and P2 determine the utility maximizing demand of consumer are the per unit prices of goods 1 and 2, . B for each good as a function of p, and P2 · If P₁ P 2 1 and are the per unit prices of goods 1 and 2, determine the profit maximizing demand of the firm for good 1 as a function of p₁ and p2. Ifp, and p2 are the per unit 1 prices of goods 1 and 2, determine the utility maximizing demand of consumer…arrow_forward
- 25. A firm produces the output y using two inputs x₁ and x2 in non-negative quantities through the production relationship: y = g(x1,x2)=xx₁₂ The firm obtains a price of py > 0 per unit of y that it sells. It has available an inventory of K₁ units of the input x₁ and K2 units of the input x2. More units of x₁ and x2 may be purchased from the market at the unit prices of p1 > 0 and p2 > 0, respectively. Alternatively, the firm can also sell any unused amount of its inputs to the market at these prices. 6 (a) Describe the firm's profit-maximization problem, and derive the equations that define the criti- cal points of the Lagrangean L. (b) Assuming py = P₁ = P2 = 1, K₁ = 4, and K₂ = 0, solve for the firm's optimal level of output y. (c) Assume again that py = p₁ = p2 = 1, but suppose now that the values of K₁ and K₂ are interchanged, i.e., we have K₁ = 0 and K₂ = 4. Is the firm's new optimal output level different from the old level? Why or why not?arrow_forward5arrow_forwardDon’t know what steps to take to be able to solve correctlyarrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





