
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Tom has a budget of $44 per week that he can spend on Ramen and/or steak burritos. Each burrito costs $10 and each bowl of Ramen is $6. Using the table below, what combination of these two goods will maximize Tom’s utility given his budget constraint?
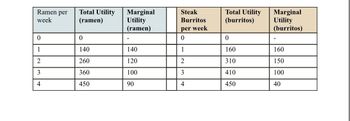
Transcribed Image Text:This table presents data on the utility derived from consuming ramen and steak burritos per week.
**Ramen Consumption:**
- **Ramen per week:** Indicates the number of ramen servings consumed weekly.
- **Total Utility (ramen):** Represents the total satisfaction or utility obtained from consuming ramen.
- **Marginal Utility (ramen):** Shows the additional utility gained from consuming one more serving of ramen.
**Data for Ramen:**
- 0 servings: Total Utility = 0, Marginal Utility = -
- 1 serving: Total Utility = 140, Marginal Utility = 140
- 2 servings: Total Utility = 260, Marginal Utility = 120
- 3 servings: Total Utility = 360, Marginal Utility = 100
- 4 servings: Total Utility = 450, Marginal Utility = 90
**Steak Burrito Consumption:**
- **Steak Burritos per week:** Indicates the number of steak burritos consumed weekly.
- **Total Utility (burritos):** Represents the total satisfaction or utility obtained from consuming burritos.
- **Marginal Utility (burritos):** Shows the additional utility gained from consuming one more burrito.
**Data for Steak Burritos:**
- 0 burritos: Total Utility = 0, Marginal Utility = -
- 1 burrito: Total Utility = 160, Marginal Utility = 160
- 2 burritos: Total Utility = 310, Marginal Utility = 150
- 3 burritos: Total Utility = 410, Marginal Utility = 100
- 4 burritos: Total Utility = 450, Marginal Utility = 40
This data illustrates the concept of diminishing marginal utility, where each additional unit consumed provides a decreasing amount of additional satisfaction.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Jesse has a budget of $16 to spend on either ice cream or cookies at the movie theater. A scoop of ice cream costs $4 while cookies costs $2. Use the table below to identify the utility maximizing quantity of ice cream and cookies given Jesse’s budget constraint. HINT: Use utility maximizing formula, MU1/P1 = MU2/P2 Ice cream (Quantity) Total Utility Cookies (Quantity) Total Utility 1 8 1 20 2 12 2 35 3 24 3 56 4 30 4 60 5 32 5 62 6 35 6 68 Group of answer choices 2 ice cream and 4 cookies 1 ice cream and 5 cookies 3 ice cream and 6 cookiesarrow_forwardThe tables show the utility Parker experienced from consuming varying quantities of waffles and pancakes. Assume that waffles cost $2.00 each, pancakes cost $1.00 each, and that Parker has $8.00 to spend on these two goods. Since Parker cannot afford more than four waffles or eight pancakes, the utility is given only for quantities smaller than these. Quantity of waffles Total utility of waffles Marginal utility of waffles 1 100 100 2 180 80 3 240 60 4 270 30 Quantity of pancakes Total utility of pancakes Marginal utility of pancakes 1 40 40 2 70 30 3 90 20 4 105 15 5 115 10 6 120 5 7 123 3 8 125 2 Given his budget constraint, determine what quantities of waffles and pancakes Parker will consume to maximize utility. quantity of waffles: waffleswaffles quantity of pancakes: pancakesarrow_forwardRick eats only french fries and burgers at his office cafeteria. His weekly lunch budget is $48. Each burger costs $6 and each order of fries costs $3. When deciding how much of each good to buy, Rick knows that 2 burgers and 4 orders of french fries will give him a utility of 8. At his utility-maximizing point, Rick's utility is:arrow_forward
- Please see the attached question.arrow_forwardam. 113.arrow_forwardI am trying to figure out how to finsih the table and answer question number 3. I am having a hard time understanding the total utility and figuring out on how to get the correct numbers. Above the graph it states that Kim has $20 per week in her entertainment budget. She splits her time between going to the movies and yoga classes. Each movie costs $8 while each yoga class costs $4. The total utility from each of these activities is set out in the table below.arrow_forward
- Refer to the table below. If the subscription price for a sports app is $2 per week, the subscription price of a game app is $1 per week, and a student has $9 per week to spend, what quantities will she purchase at a consumer optimum? Quantity of Sports Apps per week Marginal Utility (utils) Quantity of Game Apps per Week Marginal Utility (utils) 1 1,200 1 1,700 2 1,000 2 1,400 3 800 3 1,100 4 600 4 800 5 400 5 500 6 100 6 200arrow_forwardMr. Rational has $27 that he plans to spend purchasing 5 units of good X (priced at $3 per unit) and 6 units of good Y (priced at $2 per unit). The marginal utility of the fifth unit of X is 30, and the marginal utility of the sixth unit of Y is 18. If Mr. Rational is a utility maximizer, he should: buy less of X and more of Y. buy X and Y in the quantities indicated. buy more of X and less of Y. not buy anything. buy less of X and even lesser than that of Y.arrow_forward7. MRS and utility maximization Suppose your classmate Felix loves to eat dessert-so much so that he allocates his entire weekly budget to apple crisp and pie. The price of one bowl of apple crisp is $1.75, and the price of a piece of coconut crème pie is $7.00. At his current level of consumption, Felix's marginal rate of substitution (MRS) of apple crisp for pie is 5. In other words, Felix is willing to sacrifice five bowls of apple crisp for one piece of pie per week. Does Felix's current consumption bundle maximize his utility? That is, does it make him as well off as possible? If not, how should he change it to maximize his utility? Felix could increase his utility by buying more apple crisp and less pie per week. Felix could increase his utility by buying less apple crisp and more pie per week. Felix's current bundle maximizes his utility, and he should keep it unchanged.arrow_forward
- Caroline has a $10 dessert budget that she uses to buy pie and cake. Assume the price of pie (Pp) is fixed at $2. Table A shows Caroline's marginal MU utility (MU) and marginal utility per dollar () she receives from the first through fifth slices of pie she buys each week. Table B shows the same information for cake when the price of a slice of cake (Pc) is either $4 or $2. Assume that Caroline is rational consumer who wants to maximize her utility. Table A MU/P (If P=2) Pie MU (Slices) (Utils) 30 15 1 24 12 20 10 14 7 Table B Cake MU MU/P (Slices) (Utils) (If P=$4) (If P=$2) 40 10 20 32 8 16 2 24 12 16 4 8 4 1 2. 96 4. 4 5 1.arrow_forwardGabriella obtains utility from consuming granola bars and cappuccino. The following table shows the total utility (TU) she obtains from consuming different amounts of the two goods. The price of a granola bar is $3 and the price of a cup of cappuccino is $2. She has allocated $9 to spend on granola bars and cappuccino. 1. Complete the table by calculating the marginal utility (MU) and the MU per dollar spent on each granola bar and cup of cappuccino. 2. What is Gabriella’s optimal consumption bundle of granola bars and cups of cappuccino?arrow_forwardEthan has $17 per week in his food budget. He splits his choices between pizzas and hot dogs. Each slice of pizza costs $2 while each hot dog costs $3. The total utility (TU) from each of these choices is set out in the table below. Marginal utility for pizza and hotdog (MU/$) for TU MU MU pizza hotdog Units TU pizza pizza hotdog 1 10 5 2 18 9 3 20 12 4 22 15 5 23 17 1. Complete the table calculating marginal utility (MU) and marginal utility per dollar (MU/$) for both choices. Remember to show your work for at least one unit! 2. What is Ethan's utility maximizing choice? Justify your answer by showing your work! HINT: use the budget constraint equation to show the optimal choice! (MU/$) for hotdogarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education