Question
thumb_up100%
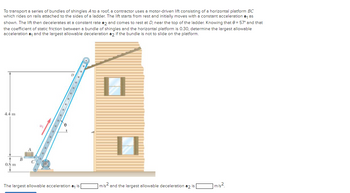
Transcribed Image Text:To transport a series of bundles of shingles A to a roof, a contractor uses a motor-driven lift consisting of a horizontal platform BC
which rides on rails attached to the sides of a ladder. The lift starts from rest and initially moves with a constant acceleration a₁ as
shown. The lift then decelerates at a constant rate a2 and comes to rest at D, near the top of the ladder. Knowing that 0 = 57° and that
the coefficient of static friction between a bundle of shingles and the horizontal platform is 0.30, determine the largest allowable
acceleration a₁ and the largest allowable deceleration a2 if the bundle is not to slide on the platform.
4.4 m
0.8 m
B
C
aj
8
The largest allowable acceleration a₁ is
m/s and the largest allowable deceleration a2 is
1 m/s²
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Friction Force:
It can be defined as the resistive force that acts between the surfaces of two objects which are in contact and which move relative to each other. It is given as,
where is the normal force and is the coefficient of friction.
The direction of the friction force is always opposite to the direction of the relative motion of the object with respect to the surface.
Newton's Second Law: According to this law, the net force acting on an object of constant mass is equal to the product of its mass with its net acceleration.
Step by stepSolved in 8 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- m A person is pushing a wooden crate of mass mo = 20 kg at a constant speed vo = 1.2– for Ax = 3 m along a rough horizontal floor that has a coefficient of friction µk = .4.arrow_forwardA block of mass 4.6 kg is sliding down a ramp with an initial speed of 1.5 m/s. The ramp is inclined from the horizontal by an angle theta = 34.9 degrees and the coefficient of kinetic friction is uk = 0.73. What is the magnitude of the displacement of the block along the ramp from the initial time until it stops?arrow_forwardA 35.0-kg child swings in a swing supported by two chains, each 2.98 m long. The tension in each chain at the lowest point is 440 N. (a) Find the child's speed at the lowest point.m/s(b) Find the force exerted by the seat on the child at the lowest point. (Ignore the mass of the seat.)N (upward)arrow_forward
- A 19.0 kg box is placed at the top of an inclined plane and released to either move freely or sit at rest. The plane is at an angle of 30° above the ground and has a total length of d = 2.80 m along the incline. The coefficient of static friction between the box and the plane is us = 0.40 and the coefficient of kinetic friction is pk = 0.30. What kind of friction does the box experience once it is released, and what is its magnitude? m d Kinetic, Fkf - 55.9 N Static, Fsf = 74.5 N Static, Fsf = 64.5 N Kinetic, Fkf = 48.4 Narrow_forwardTime left 0:20:32 An amusement park in Dubai has a ramp which is frictionless. A child drops a smooth object and it slides down the ramp and comes down through a height 4 m. What distance is necessary to stop the object on the flat track if the coefficient of friction is 0.4? h. Answer:arrow_forwardTwo crates of fruit are released from the top of a ramp inclined at 30 degrees from the horizontal and 4.5 meter long. The two crates consist of an apple crate of mass 20 kg that is placed in front of a watermelon crate of mass 80 kg. The apple crate has a coefficient of friction of 0.20 while the watermelon crate has a coefficient of friction of 0.15. How long does it take the apple crate to reach the bottom of the incline if it needs to travel a distance of 4.5 meters?arrow_forward
- B In the figure, block A has a mass of 9.06 kg. It rests on a smooth (assume frictionless) horizontal table and is connected by a very light horizontal string over an ideal pulley to block B, which has a mass of 2.80 kg. When block B is gently released from rest, how long does it take block B to travel 76.7 cm? Report your answer in seconds.arrow_forwardWhen an object slides on a surface, it encounters a resistance force called friction. This force has a magnitude of μN, where μ is the coefficient of kinetic friction and N is the magnitude of the normal force that the surface applies to the object. Suppose an object of mass 50 kg is released from the top of an inclined plane that is inclined 60° to the horizontal. Assume the gravitational force is constant, air resistance is negligible, and the coefficient of kinetic friction μ = 0.1. Determine the equation of motion for the object as it slides down the plane. If the top surface of the plane is 7 m long, what is the velocity of the object when it reaches the bottom? Assume that the acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/sec². Determine the equation of motion for the object as it slides down the plane. x(t) = mg sin 60° شت 60° N mg x(t) -KAN x(0) = 0 mg cos 60°arrow_forwardThe drawing shows a cube (mass=26.6kg), being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal surface P. A small cube (mass= 4.4kg) is in contact with the front surface of the large cube and will slide downward unless P is sufficiently large. The coefficient of static friction between the cubes is 0.710. What is the smallest magnitude that P can have in order to keep the small cube from sliding downward?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios