
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
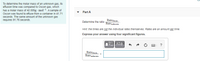
Transcribed Image Text:To determine the molar mass of an unknown gas, its
effusion time was compared to Oscon gas, which
has a molar mass of 42.005g - mol-1. Asample of
Oscon was found to effuse from a container in 41.71
Part A
seconds. The same amount of the unknown gas
requires 91.76 seconds.
Rateoscon
Rateunknown
Determine the ratio
Hint the times are not the individual rates themselves. Rates are an amount per time.
Express your answer using four significant figures.
?
RateOncon
Rateunknown
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Gases are different from solids and liquids. In a sample of gas, the molecules are far apart. The gas molecules also move around and collide with each other as well as with the walls of the container. These collisions generate pressure. The pressure of a gas can be measured in different units. One convenient unit of measure is called the atmosphere (atm) because it is based on atmospheric pressure. At sea level, the average pressure is 1 atm. As you get higher in altitude, the pressure steadily drops until you leave the atmosphere, where the pressure is very close to 0 atm. The table below shows the different commonly used units of measuring gas pressure. Use this table in the pressure unit conversions. Unit Abbreviation 1 atm equivalent FT atmosphere atm 1.00 atm (exact) millimeters of mercury mmHg 760 mmHg torr 760 torr inches of mercury in. Hg 29.9 in. Hg pounds per square lb/in.² 14.7 lb/in.² inch (psi) pascal torr Pa 101,325 Pa Part A Convert 1.20 atm of pressure to its equivalent…arrow_forwardEffusion is the process where a gas flows through a small hole in a container. Graham’s Law of Effusion says that the rate of effusion of a gas from a particular hole is inversely proportional to the square root of the MW of the gas (at constant temperature and pressure). Describe why normal balloons filled with He tend to go flat faster than the same balloons filled with air.arrow_forwardThe rate of effusion of NO2 gas through a porous barrier is observed to be 3.05 x 10-4 mol/h. Under the same conditions, the rate of effusion of CO₂ gas would be mol/h.arrow_forward
- At 287 K and 1.43*10^-2 atm, the density of a gas is 1.37*10^-5 g/cm^3. (a) Find the Vrms for the gas molecules. (b) Find the molar mass of the gas.arrow_forwardIn a 0.5 L container of gas at sea-level where the temperature is 298 K, the collision rate between molecules, Z, is 1.2 x 104 s. If the collision cross-section, o, of 9 × 10-19 m² remains unchanged, what is the change in collision rate if the temperature is cooled to 170 K? Note: the relative average speed is assumed to remain unchanged. 17arrow_forwardThe rate of effusion of CH_4 gas through a porous barrier is observed to be mol/h. 2.96 x 10^-4 Under the same conditions, the rate of effusion of Kr gas would bearrow_forward
- 6. On a certain day a laboratory barometer indicates that the atmospheric pressure is 786.2 torr. A sample of gas is placed in a flask attached to an open-end mercury manometer, and a meter stick is used to measure the height of the mercury in the two arms of the U tube. The height of the mercury in the open-end arm is 80.4 mm, and the height in the arm in contact with the gas in the flask is 123.5 mm. What is the pressure of the gas in the flask (a) in atmospheres, (b) in kilopascals?arrow_forwardA sample of O2 gas is observed to effuse through a porous barrier in 7.64 minutes. Under the same conditions, the same number of moles of an unknown gas requires 12.7 minutes to effuse through the same barrier. The molar mass of the unknown gas is g/mol.arrow_forwardImage from Pixabay: https://pixabay.com/photos/petrol-equipment-fire-extinguisher-3079094/ There is 17.0 g of carbon dioxide gas stored in a cylinder with a volume of 11.0. A pressure gauge shows the pressure to be 2.00 atm. R=0.0821 L-atm/(mol-K) In degrees Celsius, determine the temperature of the gas. Round your answer to a whole number. Answer: ____°Carrow_forward
- A sample of O3 gas is observed to effuse through a pourous barrier in 1.06 minutes. Under the same conditions, the same number of moles of an unknown gas requires 0.736 minutes to effuse through the same barrier. The molar mass of the unknown gas is g/mol.arrow_forwardFour 0.6 mol samples of xenon gas are described in the table below. Rank these samples in order of decreasing rate of collisions between atoms. That is, select "1" next to the sample with the most collisions per second between Xe atoms and the walls of the container. Select "2" next to the sample with the next most collisions per second between Xe atoms and the walls of the container, and so on. sample A C D volume 27. L 21. L 31 L 23 L temperature. -95 °C -69. °C -95, °C -95 °C X collisions per second 1 (most) 2 3 4 (least)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY