
Concept explainers
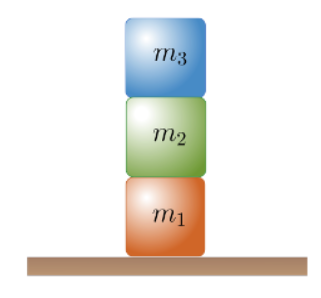
Three blocks are stacked on the floor. From the bottom of the stack to the top, their masses are m1, m2, and m3, respectively, as shown on the diagram. When referring to the various forces, the subscripts i=1,2,3 of the blocks will be used, and ff will be used to indicate the floor.
- Weights, if required, will be denoted with the corresponding subscript of the block as Fg,i, for i=1,2,3.
- The normal force exerted by object a on object b, if required, will be denoted as Fn,a→b for i=1,2,3, f, but a≠b.
- The force of kinetic friction exerted by object a on object b, if required, will be denoted as Fk,a→b for i=1,2,3,f, but a≠b.
- The
force of static friction exerted by object a� on object b�, if required, will be denoted as F⃗ s,a→b for i=1,2,3,f, but a≠b.
Form an expression for the magnitude of the force of the bottom-most block on the center block valid for any value of the vertical acceleration, ay, using only the parameters provided in the palette.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Enter an expression for the magnitude of the force of the bottom-most parcel on the center parcel valid for any value of the vertical acceleration, ay, using only the parameters provided in the palette
Enter an expression for the magnitude of the force of the bottom-most parcel on the center parcel valid for any value of the vertical acceleration, ay, using only the parameters provided in the palette
- Three forces of A, B & C act on a bolt as shown in the figure below. Where A = 3000 N, B = 2500 N and C = 2700 N. Find the resultant force magnitude and direction. (A 32 B 54° 35° C Resultant Force = 3670 N, Direction = 125° Resultant Force = 3870 N, Direction = 135° Resultant Force = 3550 N, Direction = 115° O Resultant Force = 3950 N, Direction = 105°arrow_forwardA block of mass m = 1.85 kg is pushed a distance d = 3.15 m along a frictionless horizontal table by a constant applied force of magnitude F = 16.0 N directed at an angle ? = 32.0° below the horizontal as shown in the figure below. A block labeled m is on a horizontal surface. An arrow labeled vector F points downward and to the right at an angle ? above the horizontal, and acts upon the upper left corner of the block. A faded image of the block is a distance d to the right of the block. (a) Determine the work done on the block by the applied force.(b) Determine the work done on the block by the normal force exerted by the table.(c) Determine the work done on the block by the force of gravity.(d) Determine the work done by the net force on the block.arrow_forwardWrite the solution on a paper and round to 4 decimal placesarrow_forward
- Workmen are trying to free an SUV stuck in the mud. To extricate the vehicle, they use three horizontal ropes, producing the force vectors shown in the figure.(Figure 1) Take F₁ = 864 NF2 = 784 N, and F3 = 384 N. Figure Part A F₂ 53° F3 32° F₁ Find the components of each of the three pulls. Enter your answer as three numbers, separated with commas. F1, F2, F32 = ΜΕ ΑΣΦ Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again Part B Find the y components of each of the three pulls. Enter your answer as three numbers, separated with commas. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ Fly, F2y, Fay = ? ? N N 1 of 1arrow_forwardA block of mass m = 2.90 kg is pushed a distance d = 7.80 m along a frictionless horizontal table by a constant applied force of magnitude F = 16.0 N directed at an angle ? = 24.0° below the horizontal as shown in the figure below. A block labeled m is on a horizontal surface. An arrow labeled vector F points downward and to the right at an angle ? above the horizontal, and acts upon the upper left corner of the block. A faded image of the block is a distance d to the right of the block. (a) Determine the work done on the block by the applied force. J(b) Determine the work done on the block by the normal force exerted by the table. J(c) Determine the work done on the block by the force of gravity. J(d) Determine the work done by the net force on the block.arrow_forwardF1 F2 Given that F1 825 N, F2 = 630 N, and a = 32° , determine the magnitude of the resultant force and its direction measured counterclockwise from the positive x axis. . The magnitude of the resultant force in N is (round to two decimal places) : N The direction of the resultant force in degrees is (round to two decimal places) : degreesarrow_forward
- A crate sits on a wooden horizontal surface (a wooden floor). The figure shows a top view of this looking down onto the crate (gravity would be acting into the page). Man one and man two apply forces F1 and F2, at angles of θ1 and θ2 respectively, with the goal of moving the crate in the x-direction. A resultant force of Fr = 30.5 lbs in the x-direction is required to accomplish this. All of the forces are in the xy plane. If man one applies a force of F1 = 21 lbs at an angle of θ1 = 16° from the positive x-axis, complete the following steps to determine the magnitude and angle of the force man two must apply. c) Combine these two equations to develop an expression for tan(θ2) in terms of Fr, F1, F2, and θ1. Remember that the crate does not move along the y-direction. d)Solve numerically for the value of θ2 in degrees. e)Using this value for θ2 and other known values, solve numerically for the value of F2 in lbs.arrow_forwardConnected objects with inclined plane problem. Consider the figure where you have two boxes connected by a string over a pulley. The smooth (frictionless) ramp is inclined to a an angle of 35° with the flat ground, and the box on the ramp has a mass of 6.40 kg. The mass of the 6.4 kg hanging box is m = 3.05 kg. You don't need to consider significant figures in your answer, but don't round excessively partway through your calculations. 35° Find (a) the direction and (b) the magnitude of the hanging box's acceleration.arrow_forwardThree force vectors act on a free body at the origin as shown. F1= 4 N F2=2.0 i + 3.1 J N F3= 6.3 N at 35° relative to positive x axis. a) Report the unit vector in the direction of F3 (in unit vector or i,j,k notation to 4 sig figs) b)Calculate the resultant force R, which is the sum of the three forces F1,F2, and F3 (in unit vector or i,j,k notation to 4 sig figs)arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





