
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
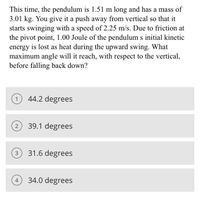
Transcribed Image Text:This time, the pendulum is 1.51 m long and has a mass of
3.01 kg. You give it a push away from vertical so that it
starts swinging with a speed of 2.25 m/s. Due to friction at
the pivot point, 1.00 Joule of the pendulum s initial kinetic
energy is lost as heat during the upward swing. What
maximum angle will it reach, with respect to the vertical,
before falling back down?
1
44.2 degrees
2
39.1 degrees
3 31.6 degrees
4
34.0 degrees
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 9. A helium balloon is released from the floor in a room at rest, then slowly rises and comes to rest touching the ceiling. During this process, the gravitational potential energy of the balloon has increased. Since energy is conserved, the energy of something else must have decreased during this process. Which of the following is the main contribution to this decrease? (A) The kinetic energy of the balloon decreased. (B) The elastic potential energy of the balloon decreased. (C) The thermal energy of the air in the balloon decreased. (D) The thermal energy of the air in the room decreased. (E) The gravitational potential energy of the air in the room decreased. 10. An archer takes aim at a target that is 100 m away. Assuming she holds the bow at the same height as the center of the target and shoots an arrow with velocity v = 100 m/s, at what angle above the horizontal should she aim the bow so that the arrow hits the center of the target? (A) arccos (1/5) 2 (B) arcsin (1/5) 2 (C)…arrow_forwardIn the winter activity of tubing, riders slide down snow covered slopes while sitting on large inflated rubber tubes. To get to the top of the slope, a 2.50 kg tube, is pulled at a constant speed by a tow rope that maintains a constant tension of 12.0 N along the direction of the slope. How much thermal energy is created in the slope and the tube during the ascent of a 6.10-m-high, 51.8-m-long slope, in Joule? Use g = 10.0 m/s2. Your answer needs to have 3 significant figures, including the negative sign in your answer if needed. Do not include the positive sign if the answer is positive. No unit is needed in your answer, it is already given in the question statement.arrow_forward1. A particle moves in one dimension and is subject to a conservative force, whose potential energy function is given by U(x), where a and b are positive constants. U ( x ) = a x 3 − b x a) Find the two equilibrium positions of the particle. b) For each of the two equilibrium positions, determine whether the equilibrium is stable or unstable.arrow_forward
- This time, the pendulum is 1.62 m long and has a mass of 4.59 kg. You give it a push away from vertical so that it starts swinging with a speed of 1.82 m/s. Due to friction at the pivot point, 1.00 Joule of the pendulum s initial kinetic energy is lost as heat during the upward swing. What maximum angle will it reach, with respect to the vertical, before falling back down? 29.5 degrees 28.0 degrees 24.6 degrees 26.4 degreesarrow_forward7.10arrow_forwardA 100 kg object is fired straight up with an initial speed of 200 m/s. Ignore air resistance and set the initial height of the object at zero. Use g = 10m/s/s. Find the total energy of the object. Find the height of the object when its speed is 100 m/s. Find the speed of the object when its height is 100 m. Find the maximum height of the object.arrow_forward
- Judy has started fast walking for half an hour each day in an effort to lose weight. Judy currently weighs 100 kg. She walks expending about 0.1 kcal per kg of body weight per minute. For a woman, we multiply the body weight in kg by 0.9 kcal/kg body weight/hour to calculate her BMR. What is Judy’s daily energy expenditure? (Ignore TEF due to its small portion)?arrow_forwardA 68.1-kg boy is surfing and catches a wave which gives him an initial speed of 1.60 m/s. He then drops through a height of 1.62 m, and ends with a speed of 8.51 m/s. How much nonconservative work (in kJ) was done on the boy? Answer______ kJarrow_forwardA box with mass 1.78 kg is being pulled across a rough surface with a coefficient of kinetic friction Hk = 0.398. The pulling force has a magnitude %D of 14.5 N and is directed at an angle 20.4 degrees above horizontal. If the box is dragged a distance of 10.8 m, what is the total energy lost to friction? (Hint: be sure to account for the upward component of the pulling force.) Image size: s ML Max F 9. m Dlogno ont mote oroarrow_forward
- This time, the pendulum is 1.55 m long and has a mass of 3.05 kg. You give it a push away from vertical so that it starts swinging with a speed of 1.27 m/s. Due to friction at the pivot point, 1.00 Joule of the pendulum s initial kinetic energy is lost as heat during the upward swing. What maximum angle will it reach, with respect to the vertical, before falling back down? 14.4 degrees 18.7 degrees 17.3 degrees 18.0 degreesarrow_forwardIn the figure, a 2.6 kg block is accelerated from rest by a compressed spring of spring constant 660 N/m. The block leaves the spring at the spring's relaxed length and then travels over a horizontal floor with a coefficient of kinetic friction -0.272. The frictional force stops the block in distance D 7.9 m. What are (a) the increase in the thermal energy of the block-floor system, (b) the maximum kinetic energy of the block, and (c) the original compression distance of the spring? DURRES No frictionarrow_forward1) A constant horizontal force of F = 200.0 N pushes a crate of mass m = 25.0 kg, initially at rest, along a rough horizontal surface. The crate travels a total distance of 8.00 m, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the surface is 0.250. a) What is the work done on the crate by the force F? b) How much does friction increase the internal energy of the crate-surface system ?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON