
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
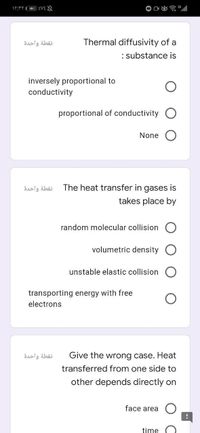
Transcribed Image Text:نقطة واحدة
Thermal diffusivity of a
: substance is
inversely proportional to
conductivity
proportional of conductivity O
None
نقطة واحدة
The heat transfer in gases is
takes place by
random molecular collision
volumetric density O
unstable elastic collision
transporting energy with free
electrons
نقطة واحدة
Give the wrong case. Heat
transferred from one side to
other depends directly on
face area
time
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following graph shows the thermal behavior of 2 kg of a material called Uniandesato undergoing a solid-liquid phase transition. In a container, thermally insulated from the outside, 20 kg of liquid water at a temperature of 80°C are placed. In addition to this, an unknown amount of Uniandesato in a 100% solid state at its melting temperature (10°C) is added. The specific heat of water is 4186 J/kg°C. a) If the system reaches an equilibrium temperature of 60°C, calculate the initial amount of Uniandesato added to the container. b) Calculate the change in entropy during this process and show that it is consistent with the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Hint: Extract the necessary information to solve this problem from the graph.arrow_forwardPlease provide the answers with appropriate images and stepsarrow_forwardd) Compare Young's modulus E (the stiffness property) and thermal conductivity (the heat transmission property) of aluminum alloys (a non-ferrous metal), alumina (a technical ceramic), polyethylene (a thermoplastic polymer) and neoprene (an elastomer). Which has the highest modulus Which has the lowest thermal conductivity? Lest you answer in a table Material 1- Young's modulus, E GPa T-conductivity . W/m.K 2. 3- 4-arrow_forward
- Which of the following statements are correct in the context of thermal conductivity? (Check all that apply.) Check All That Apply The thermal conductivity of gases is proportional to the square root of absolute temperature. The thermal conductivity of liquids is proportional to the square root of absolute temperature. The thermal conductivity of most liquids decreases with increasing temperature. The thermal conductivity of most liquids increases with increasing temperature.arrow_forwardInternal energy includes (choose all what apply) O Vibrational energy of particles energy in chemical bonds Rotational energy of particles Translational energy of particlesarrow_forward1) A 0.30-kg ball is attached at the end of a 0.90-m-long stick. The ball and stick rotate in a horizontal circle. Because of air resistance, a continual push must be exerted on the stick to keep the ball moving at a constant speed, causing a 0.036-Nm torque. Draw an extended force diagram showing the forces exerted on the ball and stick and use it to determine the magnitude of the resistive force that the air exerts on the ball opposite its motion. What assumptions did you make? Ability A14: Is able to construct an extended force diagram Needs Work Inadequate FD contains no errors in vectors or vector placement but lacks a key feature such as labels of forces with two subscripts or the location of the intended axis of rotation. FD is constructed but contains major errors such as incorrect or mislabeled force vectors, forces exerted from incorrect locations, or does not identify the axis of rotation. Ability D7: Is able to choose a productive mathematical procedure for solving the…arrow_forward
- By the sign convention, heat transfer is positive when a system receives energy from its surroundings in a process. True False 的00arrow_forwardPart A What is the capacitance of two square parallel plates 3.6 cm on a side that are separated by 2.1 mm of paraffin? Dielectric constant of paraffin is = 2.2 Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. Α Хь 919 . x.10"arrow_forwardI need the answer as soon as possiblearrow_forward
- What is the magnitude of only the x component of BG?arrow_forwardGlobal Consumption (2016) CO2 350 kg/MWh 260 kg/MWh 200 kg/MWh Type of Fuel Coal 44 billion MWh Oil 51 billion MWh Natural Gas 37 billion MWh Table 1: Global fossil fuel consumption, 2016 4. Globally, fossil fuel energy use was about 132 billion megawatt-hours (MWh) in 2016. Table 1 shows the individual estimates for coal, oil, and natural gas, as well as the carbon intensity of each fuel, given in kilograms of CO2 per MWh of energy consumed. For example, each MWh of coal that is burned releases about 350 kg of CO2. Use the table to estimate the total amount of CO2 (in kilograms, kg) that was emitted in 2016 from the burning of fossil fuels. Start by estimating the amount emitted for each fuel type. Then find the total. You may find it beneficial to use scientific notation. For example 44 billion MWh is 44 × 10° MWh (or 44E9, as entered into your calculator). Round to two significant digits in your final answer.arrow_forwardA heating element made of tungsten wire connected to a large battery that has negligible internal resistance. When the heating element reaches 80.0°C, it consumes electrical energy at a rate of 480 W. Assume that the temperature coefficient of resistivity has the value given in Table 25.2 in the textbook and that it is constant over the temperature range in this problem. In the equation R(T) = Ro [1 + a(T - To)] take To to be 20.0°C. Part A What is its power consumption when the temperature of the heating element is 110.0°C? Express your answer with the appropriate units. P = Submit Value Provide Feedback Request Answer Units ?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY