
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
There is a steam power cycle that uses water as the working fluid, where the condenser pressure is 20 kPa. The pressure in the boiler is 4 MPa. The steam that comes out of the boiler is saturated steam. The water enters the pump as a saturated liquid.The isentropic efficiencies of the pump and turbine are 87% and 97% respectively.
Determine
a) Real work on the pump
b) Heat transfer in theboiler
c) The real work on the turbine
d) The heat in the condenser
e) The thermal efficiency of the cycle
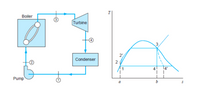
Transcribed Image Text:T
Boiler
Turbine
3
2',
Condenser
4
14'
Pump
a
2.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- don't copyarrow_forwardA heat exchanger has the objective of condensing 5 kg/s of water vapor and taking it from a pressure of 1.0 MPa and 300 °C to atmospheric pressure and 60 °C. Liquid water is used as refrigerant (Cp= 4.22 kJ/kgK), it enters at 1 °C and leaves the exchanger at 50 °C. a) What is the mass flow rate of the cold water stream? b) If the water is exchanged for another refrigerant substance whose specific heat is 2.0 kJ/kgK, what will be its outlet temperature if the same mass flow is maintained?arrow_forward3) Combined Cycle (CC) Natural Gas Power: Cheap natural gas (mostly fromfracking and similar extraction techniques) and CC gas plants are one of theprimary reasons that US carbon emissions peaked in ∼2010 and has been declining. Here, natural gas powers a Brayton cycle turbine, and the exhaustfrom that turbine is then fed into a steam generator to run a Rankine cycleturbine.a) The high temperature in the Brayton cycle turbine is 1500K. The exhaust for the Braytoncycle exits at about 850K. What is the maximum efficiency that you could expect from aheat engine operating between these two temperature extremes? b) A heat exchanger is able to deliver the Brayton cycle exhaust to a Rankine (steam) cycle.The the final outgoing temperature from this steam cycle is 325K. What is the maximumefficiency that you could expect to achieve operating between the high temperature fromthe Brayton cycle and the low temperature from the Rankine cycle? (That is, what is thetheoretical max efficiency of the…arrow_forward
- Figure on the right provides steady-state operatingdata for an ideal vapor-compression refrigeration cycle withRefrigerant 134a as the working fluid. The mass flow rate ofrefrigerant is 30.59 lb/min. Sketch the T–s diagram for thecycle and determinea) the compressor power, in horsepower.b) the rate of heat transfer, from the working fluid passingthrough the condenser, in Btu/min.c) the coefficient of performance.arrow_forwardA power plant uses steam flowing at 75kg/s to perform power cycle. Both the turbine and the pump operate adiabatically and without irreversibilities. a) find quality at the turbine exit b) find mass flow rate (kg/s) of cooling water through the condenser c) find efficiency of the cycle d) plot the cycle on a T-s diagram, indicate the saturation curve and each state of the working fluid.arrow_forwardWork is done on a system in (mark all): a) Refrigeration cycle b) Power cycle c) Heat pump cyclearrow_forward
- In a steam power plant operating according to the simple ideal Rankine cycle, steam enters the turbine at 10 MPa pressure and 600 ° C temperature and condenses at 30 kPa pressure. The isentropic efficiency of the turbine and the pump is 90%, the steam flow circulating in the cycle is 25 kg s. a) The power generated in the cycle, b) The heat thrown into the environment in the condenser c) Calculate the thermal efficiency.arrow_forwardiii) the exit area of the nozzle. Take Cp = 1.005 kJ/kg-K and R=287 J/kg-K Q.B3. A heat engine operates between two reservoirs at 400°C and 30°C. Half the power produced by the heat engine is used to drive a Carnot heat pump that removes heat from the cold surroundings at 2°C and transfers it to a house maintained at 27°C. The heat engine is absorbing heat at a rate of 5 kJ/s. i) Draw the complete schematic of the device ii) Determine the thermal efficiency of the heat engine iii) Determine the coefficient of performance of the heat pump iv) Determine the rate of heat loss from the house. v) Determine the minimum rate of heat extraction by the heat pump, and vi) the total rate of heat rejection.arrow_forwardThe following data for the R-12 refrigeration system as shown are as follows: Evaporator 1 0 OC 30 TOR Evaporator 2 -10OC 20 TOR Evaporator 3 -20OC 10 TOR Condenser 20OC Assume simple saturation and isentropic compression and determine the following: a) Draw the h-s diagram b) The refrigerant flow in each evaporator c) Total work of compression, WC in kW d) Heat rejected in the condenser, QR in kj/min e) Coefficient of performancearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY