
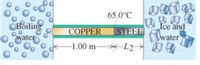
There is a long rod, insulated to avoid any heat loss on its sides, is in perfect thermal contact with the boiling water (at atm pressure) at of the one end and with the ice-water mixture. The rod has a 1.00 m section of copper (with one end in boiling water) connected and joined together end-to-end to a length, L2, of steel (with one end in the ice water). Both sections of the rod have cross-sectional areas = 4.00 cm2. The temperature of the copper-steel junction is 65.0 °C after a steady state has been met. How much heat per second flows from the boiling water to the ice-water mixture?
kCopper = 380 W/m*K
kStainless Steel = 50 W/m*K
A. How much heat per sec (watts) flows from boiling water to ice water mixture?
B. Find the length L2 of steel section in meters
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- How much much heat must be supplied to water at 180 degrees celcius to make 1 kg of wet steam at 9000 kpa , having a dryness fraction of 80% ? .arrow_forwardUse the Kedzierski (2003) refrigerant/lubricant mixture pool boiling model to predict the boiling heat transfer coefficient (hm) for a range of superheats (4T, = 8 K to 40 K) and Ts = 277.6 K: 5.9×107(1−x,)ph ATk, (1-e*) x, To Where 1₂ %₁ = = 9m T-T Г x Τσ PL-Pbx 5.9×107(1-x₂)ph AT 0.755lp₁ (1-x₁) _ 18.75õ₁ (1—x₁) _ 18.75×10¯¹º[m]p, (1-x₂) Xp Prv XpPrv XpPrv Assume that λ = 1.34 for xb=0.005 and that λ = 0.3 for Xb = 0.02. The properties of the refrigerant (R123) at the film temperature are: KL (W/mK) 0.139 R123 Or (N/m) 179692.3 0.01764 hfg (J/kg) The properties of the mineral oil (lubricant) are: PL (kg/m³) 917.8 York-C VL (cSt) 60 Prv (kg/m³) 2.701 VL (m²/s) 6 × 10-5 OL (N/m) 0.026 1.) Plot hm vs ATs and le vs ATs for two lubricant mass fractions: x = 0.005 (use 2 = 1.34 for Xb = = 0.005) and x = 0.02 (use λ = 0.3 for xb = 0.02). Compare the predicted ro for the two mass fraction cases. Provide a plausible reason for why the boiling heat transfer coefficient for a given AT's for…arrow_forwardOn a hot humid summer day, the air can be considered saturated steam at 950C. If you were to take an ice-cold beverage (40C) from the cooler, you would notice drop-wise condensation on the side of the can forming. What is the condensation heat transfer coefficient for the cold can? Assume the can is 12-cm tall and has a diameter of 8-cm.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





