
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
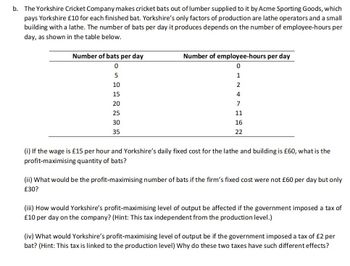
Transcribed Image Text:b. The Yorkshire Cricket Company makes cricket bats out of lumber supplied to it by Acme Sporting Goods, which
pays Yorkshire £10 for each finished bat. Yorkshire's only factors of production are lathe operators and a small
building with a lathe. The number of bats per day it produces depends on the number of employee-hours per
day, as shown in the table below.
Number of bats per day
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
Number of employee-hours per day
0
1
2
4
7
11
16
22
(i) If the wage is £15 per hour and Yorkshire's daily fixed cost for the lathe and building is £60, what is the
profit-maximising quantity of bats?
(ii) What would be the profit-maximising number of bats if the firm's fixed cost were not £60 per day but only
£30?
(iii) How would Yorkshire's profit-maximising level of output be affected if the government imposed a tax of
£10 per day on the company? (Hint: This tax independent from the production level.)
(iv) What would Yorkshire's profit-maximising level of output be if the government imposed a tax of £2 per
bat? (Hint: This tax is linked to the production level) Why do these two taxes have such different effects?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Can you assist in filling out this chart?arrow_forward2-49) A refinisher of antiques named Constance has been so successful with her small business that she is planning to expand her shop. She is going to start enlarging her shop by purchasing the following equipment. Assume the prices for the equipment that Constance wants to replace have not been constant. Use the cost index data for each piece of equipment to update the costs to the price that would be paid today. What would be the net cost to Constance to obtain this equipment? Assume that she can trade the old equipment in for 15% of its original cost. Equipment Varnish bath Power scraper Paint booth Original Size 50 gal % hp 3 ft³ Cost of Original Equipment Power- Sizing Exponent $3500 0.80 $250 0.22 $3000 0.6 New Equipment Size 75 gal 1.5 hp 12 ft³ Original Cost Index 154 780 49 Cost Index Today 171 900 76arrow_forwardSuppose a company incurs the following costs: labor, $2,000; equipment, $600; and materials, $200. The company owns the building, so it doesn't have to pay the usual $900 in rent. Instructions: Enter your responses as a whole number. a. What is the total accounting cost? $ b. What is the total economic cost? $ c. If the company sold the building and then leased it back, what would be the change in 1. accounting costs? $ 2. economic costs? $ Q Search L O of e <arrow_forward
- Practice Question 1 If the price of the product is GH¢2.00 and cost per unit of labour is GH¢10.00, Complete the table below. Labour unit Marginal Marginal Revenue Tetal Total Average Product Total TRP-TLC MRP-MLC Marginal Labour Cost Labour Cost Product Product Revenue Product Product 10 10 20 25 30 45 40 60 50 70 60 75 70 78 80 80 00:15 1 2 3 4 56 70arrow_forwardThe following table shows a company's total cost of production at various production quantities. Fill in the remaining cells of the table. (Note: If a value is a decimal, round to the nearest integer.) Average Fixed Cost Average Total Cost Fixed Variable Total Marginal Average Variable Quantity Cost Cost Cost Cost Cost (Pairs) (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars per pair) (Dollars per pair) 150 150 1 150 60 210 2 150 105 255 3 150 135 285 4 150 150 300 150 180 330 6. 150 240 390 7 150 345 495 150 495 645 9. 150 675 825 On the following graph, plot the company's average total cost (ATC) curve using the green points (triangle symbol). Next, plot its average variable cost (AVC) curve using the purple points (diamond symbol). Finally, plot its marginal cost (MC) curve using the orange points (square symbol). (Hint: For ATC and AVC, plot the points on the integer: For example, the average total cost of producing one pair of boots is $210, so you should start your…arrow_forwardSay that the last tonne of steel produced by a steel company imposes three types of costs: labour costs of $25, additional equipment costs of $10, and the cost of additional “crud” dumped into the air of $15. What costs will the steel company consider in deciding whether to produce another tonne of steel?arrow_forward
- 7. Costs in the short run versus in the long run Ike's Bikes is a major manufacturer of bicycles. Currently, the company produces bikes using only one factory. However, it is considering expanding production to two or even three factories. The following table shows the company's short-run average total cost each month for various levels of production if it uses one, two, or three factories. (Note: Q equals the total quantity of bikes produced by all factories.) Number of Factories Q = 100 440 580 720 1 2 3 Q = 200 320 400 480 Average Total Cost (Dollars per bike) Q = 300 Q = 400 240 320 240 240 320 240 Q = 500 480 400 320 Q = 600 720 580 440 Suppose Ike's Bikes is currently producing 600 bikes per month in its only factory. Its short-run average total cost is $ per bike. Suppose Ike's Bikes is expecting to produce 600 bikes per month for several years. In this case, in the long run, it would choose to produce bikes using On the following graph, plot the three short-run average total…arrow_forwardThe cost structure of a manufacturer of micro- chips is described in the table that follows. The firm's fixed costs equal $10,000 per day. Calculate the average variable cost, average fixed cost, and average total cost at each output level. Output (microchips per day) Total Cost of Output ($ thousands) 10 25 60 50 95 75 150 100 220 125 325 150 465arrow_forwardWhat is the marginal product and average product of employing 3rd labor- (1) Total Labor Units Product (Employees) (Sandwiches per Hour) 0 1. 2 3 15, 10 5, 12.5 5, 10 (2) 10, 10 0 10 25 30arrow_forward
- The maximum number of workers that a firm would hire isarrow_forwardUse the following information to answer question 22-23. Number of Workers Hired 4 5 6 7 8 Question 22 Diminishing marginal returns set in when the process.... a) fourth b) sixth c) seventh d) eighth Number of Meals Sold 300 320 worker is added to the production Question 23 Average product will fall above marginal product when the a) fourth b) sixth c) seventh d) eigth worker is hired.arrow_forwardHand written solutions are strictly prohibitedarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education