
ECON MICRO
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781337000536
Author: William A. McEachern
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
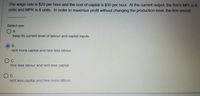
Transcribed Image Text:The wage rate is $20 per hour and the cost of capital is $30 per hour. At the current output, the firm's MPL is 6
units and MPK is 8 units. In order to maximize profit without changing the production level, the firm should
Select one:
OA.
keep its current level of labour and capital inputs.
В.
rent more capital and hire less labour
c.
hire less labour and rent less capital
O D.
rent less capital and hire more labour
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the difference between a fixed input and a variable input?arrow_forwardA common name for fixed cost is overhead. If you divide fixed cost by the quantity of output produced, you get average fixed cost. Supposed fixed cost is 1,000. What does the average fixed cost curve look like? Use your response to explain what spreading the overhead means.arrow_forwardWhat is the difference between economies of scale, constant returns to scale, and diseconomies of scale?arrow_forward
- Automobile manufacturing is an industry subject to significant economies of scale. Suppose there are four domestic auto manufacturers, but the demand for domestic autos is no more than 2.5 times the quantity produced at the bottom of the long-run average cost curve. What do you expect will happen to the domestic auto industry in the long run?arrow_forwardUsing the graph on the right, determine how the firm should change the quantity of the production factors in order to reduce the costs. The firm that is producing at point A can reduce its costs for producing 900 units by employing A. same capital and more labour. B. more capital and more labour. O C. less capital and more labour. D. more capital and less labour. E. less capital and the same labour. OO ỗ Q=1800 Q = 900 Isocost line OUarrow_forwarddo fast all answer.arrow_forward
- If capital and labour are perfect complements then the marginal products of capital and labour are undefined A True Faise Question 16 A firm uses 10 units of labour and 20 units of capital to produce 10 units of output. The marginal product of labour is 0.5. If there are constant returns to scale the marginal product of labour must be 0.25 True B False Question 17 Afirm uses 10 units of labour and 30 units of capital to produce 10 units of output. The marginal product of labour is 05. If there are constant returns to scale the marginal product of labout must be 0.25 A True Falsearrow_forwardQUESTION 24 Which of the following is most likely to be a fixed input for Peter's Country Fresh Pies? Oa ovens Ob berries c. milk Od. flour Oe. eggs QUESTION 25 The short run is a period of time: O a during which all resources are fixed. Ob during which at least one resource is fixed. OC. less than or equal to six months. d. during which profits are always positive. Oe during which all resources are variable. QUESTION 26 The long run is a period of time: Oa during which all resources are fixed. Ob. less than one year. c. during which all resources are variable. d. during which profits are always negative e that is the same for all industries. QUESTION 27 Increasing marginal returns to the variable factor of production are generally the result of a falling wagesarrow_forward3. The Chipper Cookie Company's output is given by the Cobb-Douglas Production function P = 120L0.7 K0.3, where P is the number of units produced when Lis the amount spent on labor and K is the amount spent on capital. a. What is the production if L = 600 and K = 600? b. Find the marginal productivities. c. Evaluate the marginal productivities with L= 600 and K = 600. d. Interpret the meanings of the marginal productivities found in part c. e. If their budget is $1200 then there is a constraint L+ K = 1200. Use Lagrange multipliers (^) to find the values of L and K that will maximize production and find the maximum production f. Find and interpret 2 for this problem. only need part e and f!arrow_forward
- 2. The Acme Anvil Company's output is given by the Cobb-Douglas Production function P = 60L2/3K1/3, where P is the number of anvils produced when L is the amount spent on labor and K is the amount spent on capital. a. What is the production if L = 150 and K = 150? b. Find the marginal productivities. c. Evaluate the marginal productivities with L = 150 and K = 150. d. Interpret the meanings of the marginal productivities found in part c. e. If their budget is $300 then there is a constraint L+ K = 300. Use Lagrange multipliers (2) to find the values of L and K that will maximize production and find the maximum production f. Find 2. 12| is called the marginal productivity of money and will give the number additional units produced for each dollar increase in the budget. Interpret 2 for this problem. Only need paVAS e and flarrow_forwardwhich of the following best describes marginal product?A.)Left over output- the loaves a bakery makes but does not sell that goes unused. B.) The total number of loaves a bakery can create with 5 workers and a fixed amount of capital. C.) The loaves made by a bakery using a substandard quality flour that ultimately harms business profits. D.) When the number of bakery staff increases from 2 to 3 bakers, 5 additional loaves are made.arrow_forward1.Suppose a chair manufacturer is producing in the short run (with its existing plant andequipment). The manufacturer has observed the following levels of production correspondingto different numbers of workers:Number of Workers Number ofChairs 1 10 2 18 3 24 4 28 5 30 6 28 7 25a. Calculate the marginal and average product of labor for this production function.b. Does this production function exhibit diminishing returns to labor? Explain.c. Explain intuitively what might cause the marginal product of labor to becomenegative.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax


Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:9781544336329
Author:Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:SAGE Publications, Inc

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337091992
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...
Economics
ISBN:9781305506893
Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...
Economics
ISBN:9781305506725
Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:OpenStax