
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:An engineer wanted to determine how the weight of a car affects gas mileage. The accompanying data represent the weights of various domestic cars and their gas mileages in the city for a certain model year. Complete parts (a)
through (d) below.
Click here to view the car data.
Click here to view the table of critical values of the correlation coefficient
(a) Determine which variable is the likely explanatory variable and which is the likely response variable. Choose the correct answer below.
The explanatory variable is the weight and the response variable is the miles per gallon.
The explanatory variable is the miles per gallon and the response variable is the weight.
(b) Draw a scatter diagram of the data. Choose the correct graph below.
O A.
Weight (lbs)
r=
4100-
3300-
2500+
15 23 31
Miles per Gallon
N
B.
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Miles per Gallon
31-
23-
(c) Compute the linear correlation coefficient between the weight of a car and its miles per gallon.
15+
2500 3300 4100
Weight (lbs)
O C.
Weight (lbs)
4100-
3300-
2500-
15 23 31
Miles per Gallon
U
D.
Miles per Gallon
31-
23
15-
2500 3300
Weight (lbs)
4100
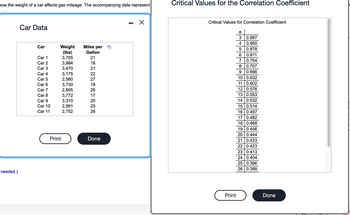
Transcribed Image Text:how the weight of a car affects gas mileage. The accompanying data represent
needed.)
Car Data
Car
Car 1
Car 2
Car 3
Car 4
Car 5
Car 6
Car 7
Car 8
Car 9
Car 10
Car 11
Weight
(lbs)
3,755
3,984
3,470
3,175
2,580
3,730
2,605
Print
3,772
3,310
2,991
2,752
Miles per
Gallon
21
18
21
22
27
18
26
17
20
25
26
Done
X
Critical Values for the Correlation Coefficient
Critical Values for Correlation Coefficient
Print
n
3
0.997
4 0.950
5
0.878
6
0.811
7
0.754
8
0.707
9 0.666
10 0.632
11 0.602
12
0.576
13 0.553
14 0.532
15 0.514
16 0.497
17 0.482
18 0.468
19 0.456
20 0.444
21 0.433
22 0.42
23 0.413
24 0.404
25 0.396
26 0.388
Done
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
The variables weight of a car and its miles per gallon are ( pick one - negatively, not, or positively) associated because r is ( pick one - zero, negative or positive) and the absolute value of the correlation coefficient is ( pick one - less or greater) the critical value (enter your response here.)
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
The variables weight of a car and its miles per gallon are ( pick one - negatively, not, or positively) associated because r is ( pick one - zero, negative or positive) and the absolute value of the correlation coefficient is ( pick one - less or greater) the critical value (enter your response here.)
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Listed below are annual data for various years. The data are weights (metric tons) of imported lemons and car crash fatality rates per 100,000 population. Construct a scatterplot, find the value of the linear correlation coefficient r, and find the P-value using a =0.05. Is there sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a linear correlation between lemon imports and crash fatality rates? Do the results suggest that imported lemons cause car fatalities? 228 Lemon Imports Crash Fatality Rate 266 358 484 531 15.8 15.7 15.5 15.2 14.8 O C. Ho: p=0 YD. Ho: p=0 H,:p>0 H1: p#0 Construct a scatterplot. Choose the correct graph below. O A. В. Oc. C. OD. Ay 17- Ay 174 Ay 17- Ay 17- 16- 16- 16- 16- 15- 15- 15- 15- 14- 14- 14+ 14- -> 600 -> 200 400 600 200 400 600 200 400 200 400 600 The linear correlation coefficient is r= -0.971. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) The test statistic is t= - 7.036 . (Round to three decimal places as needed.) The P-value is (Round to three decimal…arrow_forwardPLEASE SHOW AN EXPLANATION FOR EACH PARTarrow_forwardClick this Video for Finding Correlation Coefficient by Using Formula. Yessica thought that there was a correlation between the amount of time students slept the evening before their final exam and their final exam grade. She took an SRS of 5 students in her class and recorded the sleep time the evening before their final exam, and their final exam score. Let the sleep time the evening before the final exam represents the explanatory variable, and the final exam score be the response variable. Below is a sample data set. x (hour) 8 9 3 9 1 2 3 4 5 Calculate the sample correlation coefficient (r) to three decimal places. r= 9 Why would we expect the correlation coefficient to be positive? As the sleep time increases, exam score increases As the sleep time increases, exam score decreases As the sleep time decreases, exam score increases There is no change in exam score to sleep time C E y (score) 91 94 51 100 90 C Aarrow_forward
- A survey was taken in 2018 that asked people about their saving habits. Researchers wanted to know if people who saved more also spent less. The scatterplot below shows their results when comparing two variables: the amount people reported that they put into savings each month, and the amount they reported that they spent on clothes. The researchers found the correlation coefficient for this data to be -0.239. Which of the following is true about these variables? a. There is no relationship between savings and money spent on clothes each month.b. There is a weak, positive linear relationship between savings and money spent on clothes each month.c. There is a perfect, negative linear relationship between savings and money spent on clothes each month.d. There is a weak, negative linear relationship between savings and money spent on clothes each month.arrow_forwardSusan, a personal trainer, was interested in whether or not there was a linear relationship between the number of visits her clients made to the gym each week and the average amount of time her clients exercised per visit. She took the following data. Client 1 2 3 4 5 6 Number of visits per week 1 3 4 2 3 5 Average time spent exercising per visit (hours) 2 1.5 1 2 2 0.30 Is the correlation coefficient significant? Group of answer choices No Yes Perhaps Insufficient Information to make a decisionarrow_forwardThe price drivers pay for gasoline often varies a great deal across regions throughout the United States. The following data show the price per gallon for regular gasoline for a random sample of gasoline service stations for three major brands of gasoline (Shell, BP, and Marathon) located in eleven metropolitan areas across the upper Midwest region (OhioGasPrices.com website, March 18, 2012). Click on the datafile logo to reference the data. DATA file Shell BP Metropolitan Area Marathon Akron, Ohio Cincinnati, Ohio Cleveland, Ohio Columbus, Ohio Ft. Wayne, Indiana Indianapolis, Indiana Lansing, Michigan Lexington, Kentucky Louisville, Kentucky Muncie, Indiana Toledo, Ohio 3.77 3.72 3.87 3.76 3.78 3.87 3.89 3.79 3.83 3.83 3.85 3.77 3.83 3.85 3.93 3.84 3.84 4.04 3.87 3.87 3.99 3.79 3.78 3.81 3.69 3.78 3.84 3.84 3.83 3.79 3.79 3.86 3.86 Use a = .05 to test for any significant difference in the mean price of gasoline for the three brands. Round SS to 6 decimals, MS to 6 decimals, F to 2…arrow_forward
- A researcher measures GPA and height for a group of high school students. What kind of correlation is likely to be obtained for these two variables?arrow_forwardA random sample of college students was surveyed about how they spend their time each week. The scatterplot below displays the relationship between the number of hours each student typically works per week at a part- or full-time job and the number of hours of television each student typically watches per week. The correlation between these variables is r = –0.63, and the equation we would use to predict hours spent watching TV based on hours spent working is as follows: Predicted hours spent watching TV = 17.21 – 0.23(hours spent working) Since we are using hours spent working to help us predict hours spent watching TV, we’d call hours spent working a(n) __________________ variable and hours spent watching TV a(n) __________________ variable. The correlation coefficient, along with what we see in the scatterplot, tells us that the relationship between the variables has a direction that is _________________ and a strength that is ______________________. According to the…arrow_forwardFor the following research topics, what is the independent variable and what is the dependent variable? Examining the effect of IQ on Grades Gender and Self-Esteem Age and Political Views Race and level of educationarrow_forward
- Fully explain the issues and problems with the below correlational data. Focus on the data in the highlighted box versus the rest of the data. Do not try to explain the data, but rather focus on the statistical issues and problems. IF YOU CAN'T SEE THE IMAGE HERE. PLEASE GO TO THIS LINK Linke 10 6. 8. 7. 5. 4. 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Age Enjoyment of Hip-Hoparrow_forwardFor a data set of chest sizes (distance around chest in inches) and weights (pounds) of twelve anesthetized bears that were measured, the linear correlation coefficient is r= 0.276. Use the table available below to find the critical values of r. Based on a comparison of the linear correlation coefficient r and the critical values, what do you conclude about a linear correlation? Click the icon to view the table of critical values of r. The critical values are Table of Critical Values of r IT Number of Pairs of Data n Critical Value of r 4 0.950 0.878 0.811 7 0.754 0.707 0.666 10 0.632 11 0.602 12 0.576arrow_forwardSelect the most appropriate response. If the correlation between a person’s age and annual income is 0.60, then the coefficient of determination tells us that: 36% of the variation in a person’s annual income can be explained by the predictor variable age. 36% of a person’s annual income can be explained by their age 60% of the variation in a person’s annual income can be explained by the predictor variable age 60% of a person’s annual income can be explained by their agearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman