
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
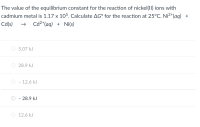
Transcribed Image Text:The value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction of nickel(11) ions with
cadmium metal is 1.17 x 105. Calculate AG° for the reaction at 25°C. Ni2+(aq) +
Cd(s)
Cd2*(aq) + Ni(s)
O 5.07 kJ
28.9 kJ
- 12.6 kJ
- 28.9 kJ
O 12.6 kJ
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine the equilibrium constant at 25 ºC for the dissolution of magnesium hydroxide in acidic solution: Mg(OH)2 (s) + 2H + (aq) ⇌ Mg 2+ (aq) + 2H2O (l)arrow_forward18.5arrow_forwardWhich of the following is true for the cell below? Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq) ‖ Cr3+ (aq) | Cr(s) * The cations flow from the cathode to the anode. * The electrons flow from the anode to the cathode. * The chromium is oxidized. * The anions flow from the anode to the cathode. * The zinc is reduced.arrow_forward
- Calculate AG for the following reaction from the equilibrium constant at the temperature given. 2SO, (g) + Oz (g) --→ 2SO, (3) T=500°C Kp =48.2 O 24.9 kJ 0-24.9 kJ O 16.1 kJ 0 16.1 kJarrow_forwardCalculate ΔG° for the following balanced redox reaction and determine if the reaction is spontaneous. (values are made-up) 2 Na+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) → 2 Na(s) + Cl2(s) Na+(aq) + e⁻ → Na(s) E° = +0.362 V Cl2(s) + 2 e⁻ → 2 Cl-(aq) E° = +0.789 V use this equation: Δ G ° = − n F E cell °arrow_forwardGiven the following information: F1- (aq): ΔGf° = -276.48 kJ/mol Na1+ (aq): ΔGf° = -261.87 kJ/mol 2 Na (s) + F2 (g) → 2 NaF (aq) a) Find ΔG° for this reaction using the above numbers. b) Write the expression for Qeq. (Note that NaF is a strong electrolyte!) c) Find ΔG at 325.0 K for 0.01500 atm F2 and 3.065 M NaF.arrow_forward
- Consider the following reaction at 298K.2 Cu2+ (aq) + Co (s) 2 Cu+ (aq) + Co2+ (aq)Which of the following statements are correct?Choose all that apply. K < 1 n = 4 mol electrons The reaction is product-favored. Eocell > 0 delta Go > 0arrow_forwardFor the following redox reaction calculate the Ecell and K at 298 K. 2Na+(aq) + Ca(s)→2Na(s) + Ca2+(aq) Half Reaction E(V) Na+(aq) + e- → Na(s) -2.71 Ca2+(aq) + 2e- → Ca(s) -2.87arrow_forwardConsider the following reductions. Cr2+(aq) + 2 e- ⟶⟶ Cr(s) Eored = - 0.910 V Co2+(aq) + 2 e- ⟶⟶ Co(s) Eored = - 0.280 V Which element is the better oxidizing agent? Explain your answer.arrow_forward
- Calculate the K and AG for the following reaction at 25 °C: Zn(s) + CuSO₂(aq) → ZnSO₂(aq) + Cu (s) Note: Reference the Standard reduction potentials at 25 °C and Fundamental constants tables for additional information. Part 1 of 2 Round your answer to 3 significant digits. Bo = Part 2 of 2 AGⓇ ☐x10 = Round your answer to 4 significant digits. X kJ mol 0x10 3 X Śarrow_forwardThe free energy change for the following reaction at 25 °C, when [Cu2+] = 2.57x10-³ M and [I₂] = 1.10 M, is 88.8 kJ: 2Cu²+(2.57x10-3 M) + 2.001 (aq)—2Cu+ (aq) + 1₂(1.10 M) AG= 88.8 kJ What is the cell potential for the reaction as written under these conditions? Answer: V Would this reaction be spontaneous in the forward or the reverse direction?arrow_forwardUse standard reduction potentials to calculate the standard free energy change in kJ for the reaction: 2H+ (aq) + Hg(1)→ H₂(g) + Hg²+ (aq) 2H+ (aq) + 2e¯ → H₂(g) Fº red 2+ Hg2 (aq) + 2e¯ → Hg(1) AGO = || kJ K for this reaction would be Eº red = 0.000 V = = 0.855 V than one.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY