
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The upper leg muscle (quadriceps) exerts a force of 1270 N, which is carried by a tendon over the kneecap (the patella) at the angles shown in Figure 5.43. Find the magnitude and direction of the force exerted by the kneecap on the upper leg bone (the femur).
Answer in N
Answer in ° (counter-clockwise from an axis directed to the left)
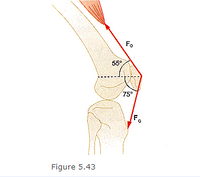
Transcribed Image Text:Fo
55°
75°
Figure 5.43
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A uniform plank of length 2.00 m and mass 29.5 kg is supported by three ropes, as indicated by the blue vectors in the figure below. Find the tension in each rope when a 685–N person is d = 0.500 m from the left end. magnitude of T1 = magnitude of T2 = magnitude of T3 =arrow_forwardA uniform plank of length 2.00 m and mass 29.5 kg is supported by three ropes, as indicated by the blue vectors in the figure below. Find the tension in each rope when a 705-N person is d-0.500 m from the left end. magnitude of T magnitude of T magnitude of N T. 2000 Qarrow_forwardThe figure below shows a bird feeder that weighs 101.1 N. The feeder is supported by a vertical wire, which is in turn tied to two wires, each of which is attached to a horizontal support. The left wire makes a 60° angle with the support, while the right wire makes a 30° angle. What is the tension in each wire (in N)? A bird feeder is suspended from a vertical wire. The top of the wire is tied to two other wires. The left and right wires go up and to the left and up and to the right, respectively, from the connection point to a horizontal support. The left wire makes an angle of 60° with the support. The right wire makes an angle of 30° with the support. left wire Nright wire Nbottom wire Narrow_forward
- The block shown in (Figure 1) has a mass of m = 100 kg, a height H = 1.4 m, and width L = 2 m. It is resting on a ramp that makes an angle = 38 ° with the horizontal. A force P is applied parallel to the surface of the ramp at the top of the block. What is the maximum force that can be applied without causing the block to move? The coefficient of static friction is μ = 0.38, and the center of mass of the block is at the center of the rectangle. Figure Att P H ( y N F x 2 of 2 Part D Use the free-body diagram shown in (Figure 2) and write the equilibrium equation for the moments about the point of contact. Express your answer in terms of one or more of P, W, H, L, N, F, and 0. Σ Μo = 0 = Submit Part E Ptip= Submit Part F What is the maximum magnitude of P that can be applied before tipping would occur, assuming the block does not slip? Express your answer to three significant figures with appropriate units. CHA Pmax = IVE ΑΣΦΠ 1 Submit Request Answer Value Provide Feedback Request…arrow_forwardThree forces of A, B & C act on a bolt as shown in the figure below. Where A = 3000 N, B = 2500 N and C = 2700 N. Find the resultant force magnitude and direction. (A 32 B 54° 35° C Resultant Force = 3670 N, Direction = 125° Resultant Force = 3870 N, Direction = 135° Resultant Force = 3550 N, Direction = 115° O Resultant Force = 3950 N, Direction = 105°arrow_forwardThe large quadriceps muscle in the upper leg terminates at its lower end in a tendon attached to the upper end of the tibia (see Figure a). The forces on the lower leg when the leg is extended are modeled as in Figure b, where T is the force of tension in the tendon, w is the force of gravity acting on the lower leg, and F is the force of gravity acting on the foot. Find T when the tendon is at an angle of 25.0° with the tibia, assuming that w = 29.0 N, F = 12.3 N, and the leg is extended at an angle ? of 40.0° with the vertical. Assume that the center of gravity of the lower leg is at its center and that the tendon attaches to the lower leg at a point one-fifth of the way down the leg. (Give the magnitude.)arrow_forward
- Forces F₁, F₂, and F 2 3 act on the structure shown below, at an overhead view. We wish to put the structure in equilibrium by applying a fourth force, at a point such as P. The fourth force has vector components an We are given that a = 2.9 m, b = 3.4 m, c = 1.3 m, F₁ = 21 N, and F F2= 12 N, and F3 = 6.4 N. (a) Find F 47 F (b) Find F. (c) Find d. N N E a Varrow_forwardA 1,175 N dowel is held in place by a light cord at an angle ? = 31.0° to the horizontal as shown in the figure. The dowel is attached to a pivot at the bottom, and a mass of weight w = 2,100 N hangs from its top. The dowel makes an angle of ? = 59.0° with the horizontal. Assume the dowel is uniform. Find the tension in the supporting cord (in kN). kN (b) Find the components of the reaction force (in kN) exerted by the floor on the dowel. horizontal component:magnitude kNdirection vertical component:magnitude kNdirectionarrow_forwardThe upper leg muscle (quadriceps) exerts a force of FQ = 1180 N, which is carried by a tendon over the kneecap (the patella) at the angles shown in the figure below. 55° 75° Find the magnitude in newtons and direction in degrees counter-clockwise from an axis directed to the left of the force exerted by the kneecap on the upper leg bone (the femur). magnitude direction N ° counter-clockwise from an axis directed to the leftarrow_forward
- A uniform plank of length 2.00 m and mass 26.0 kg is supported by three ropes, as indicated by the blue vectors in the figure below. Find the tension in each rope when a 710–N person is d = 0.500 m from the left end. Answer the 3 boxes below:arrow_forward20° 60° 2. A 10,000 N weight is supported by a cable attached to a massless beam, 4 m long, that can pivot at its base. The beam is stabilized by a second cable attached to a wall. It settles in the position shown on the left, where the weighted cable is vertical, the second cable is 20⁰ from horizontal, and the beam is 60° from horizontal. Find the tension in the second cable and the horizontal and vertical reaction forces at the W base of the beam.arrow_forwardThree main forces that act on the patella, and are shown on the diagram below. These forces are the quadriceps muscle force (FQ), the patella ligament force (FPL), and the patellofemoral joint reaction force (FPF). The angles a and ẞ are with respect to a line that is perpendicular to FPF. Assuming a = 10°, ẞ = 30°, and FQ = 4000 N, use the equations for static equilibrium to calculate the FPL in Newtons. Round to an integer, such there is no need for a decimal. FQ FPF FP Barrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON