
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
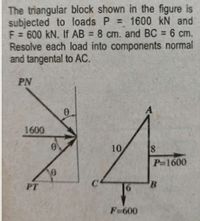
Transcribed Image Text:The triangular block shown in the figure is
subjected to loads P = 1600 N and
F = 600 kN. If AB = 8 cm. and BC = 6 cm.
Resolve each load into components normal
and tangental to AC.
PN
0.
A
1600
10
P-1600
PT
B
F=600
8.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Hide bla Clear my choice A rigid beam is supported by a pin at A and two metallic wires at B and C. Determine the force P that causes the point C to displace downward by 0.3 mm. Given: E (wire B) = 70 Gpa, E (wire C) = 200 Gpa and both wires have a diameter D = 4 mm. Consider a linear elastic behavior. |-1 2 m 1.5 m A 3 m 2 m 2 m Select one: 11:49 PM A G d) ENG Barrow_forwardThe cantilever beam consists of a rectangular structural steel tube shape [E = 29,000 ksi; | = 1960 in.4]. For the loading shown, determine: (a) the beam deflection at point A. (b) the beam deflection at point B. Assume MA = 160 kip-ft, P = 17 kips, LAB = 6.4 ft, LBC = 9.6 ft. AP MA A B C LAB LBC Answer: (a) VA = in. (b) VB = in.arrow_forwardpls help! Write the complete solutions and legibly. Answer in 2 decimal places. UPVOTE WILL BE GIVEN! MECHANICS OF DEFORMABLE BODIES Let Q = 0 and T = 8 (Example: 12Q°C = 120°C). Just substitute the number in letter. Thank you! For the frame shown, a 4QQT-N load is acting on member ABD at D. If the allowable material shear stress for is 4Q MPa, determine the required diameter (rounded off to the nearest 2.5 mm) of the pins at C and D. Pin C and pin D are subjected to double shear and single shear, respectively. If the thickness of member BC is 12 mm and that of member DE is 16 mm, determine the maximum bearing stress at C.arrow_forward
- PROBLEM No. 2 The rigid bar ABCD of negligible weight is initially horizontal, and the steel rods attached at A and C are stress-free. If a 20-kip load is applied, determine the vertical displacement in the bar at A and C that will cause a stress in the rod at C to be 50 ksi. Indicate the direction of movement. Use E = 29x106 psi for steel. (Provide FBD and movement diagram in your computation). A = 0.5 in.? 3 ft | A B D | 20 kips te 2 ft -→-- 2 ft -→l 4 ft 4 ft A = 0.75 in.²arrow_forwardThe cantilever beam consists of a rectangular structural steel tube shape [E = 29,000 ksi; I = 1500 in.“]. For the loading shown, determine: (a) the beam deflection at point A. (b) the beam deflection at point B. Assume MA = 150 kip-ft, P = 26 kips, LAB = 6.1 ft, LBC = 9.2 ft. MA A LAB LBCarrow_forwardA portal frame shown in figure (not drawn to scalé) has a hinge support at joint P and a roller support at joint R. A point load of 50 kN is acting at joint R in the horizontal direction. The flexural rigidity. El, of each member is 106 kNm². Under the applied load, the horizontal displacement (in mm, round off to 1 decimal place) of joint R would be 5 m Q El El 10 m 50 kNarrow_forward
- Identify the equation for the deflection at point C.arrow_forwardThe cantilever beam consists of a rectangular structural steel tube shape [E = 29,000 ksi; / = 1990 in.“]. For the loading shown determine: (a) the beam deflection at point A. (b) the beam deflection at point B. Assume MA = 150 kip-ft, P = 30 kips, LAB = 4.9 ft, LBc = 7.4 ft. MA A B LAB LBC Answer: (a) VA = in. (b) VB = in.arrow_forwardSolve correctly please and ny hand solvearrow_forward
- 2. A rectangular beam with b = 250 mm and d = 460 mm is reinforced for tension only with 3-25 mm bars. The beam is simply supported over a span of 6 m and carries a uniform dead load of 0. 680 KN/m including its own weight. Use fy=276.50 MPa and fc'=20.70 MPa. The value of omega "w" is. O 0.171 O 0.128 O 0.085 0.212 0.294 O 0.337arrow_forward02) The cantilever beam is subjected to the load shown Below. Determine 1. the actual stresses acting at point A. (Hint: Tmax = 1936x(0.5). 2. IfG =30 GPa find the angle of twist at the free end of beam. Y 10 kN 25 NA 120 mm 15 500 mm Good Luck and be Greenarrow_forwardA rectangular steel block is 4 inches long in the x direction, 3 inches longin the y direction, and 4 inches long in the z direction. The block issubjected to a triaxial loading of three uniformly distributed forces asfollows: 48 kips tension in the x direction, 60 kips compression in the ydirection, and 54 kips tension in the z direction. If ν = 0.30 and E = 29 ×106 psi, determine the single uniformly distributed load in the x directionthat would produce the same deformation in the y direction as the originalloading. Note provide a diagram/figure. -Draw and label the diagram correctly, No diagram in the solution will be marked wrong. -Shortcut solution will be marked wrong.- Direction of the assumption of the equilibrium equation must be shown, no direction will be marked wrong.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning