
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
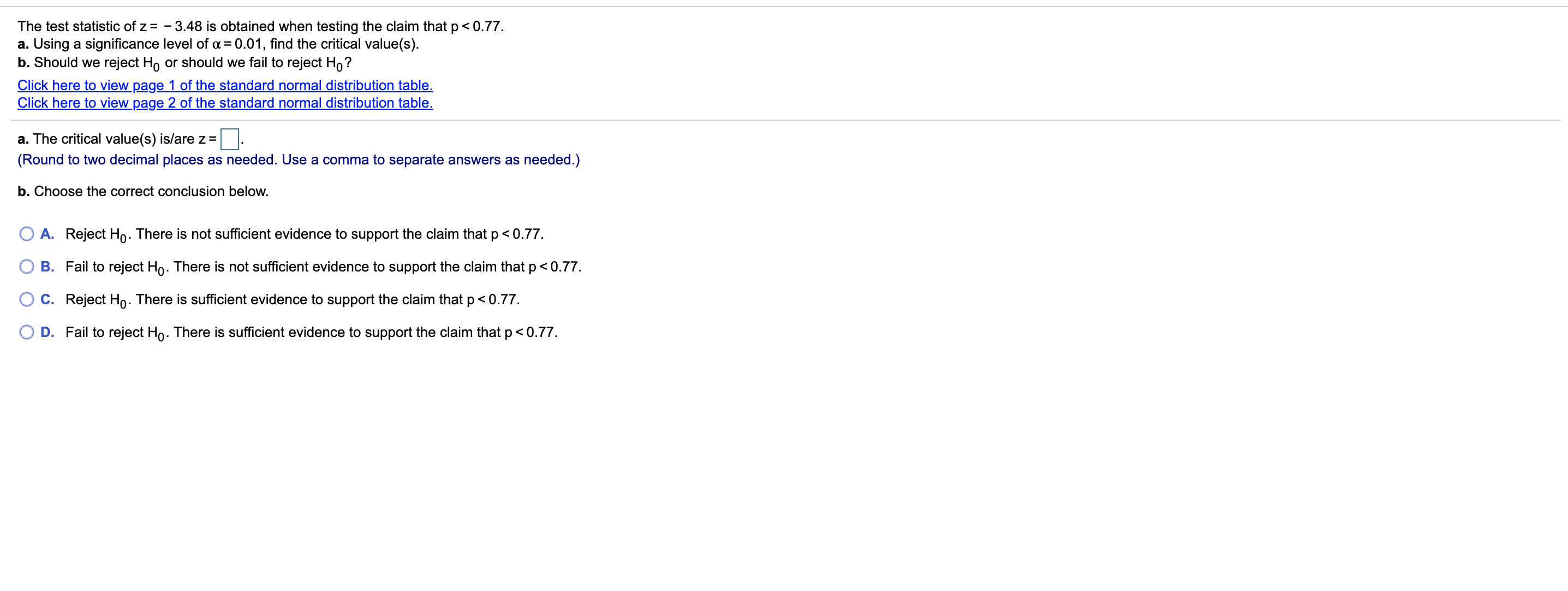
Transcribed Image Text:The test statistic of z= - 3.48 is obtained when testing the claim that p< 0.77.
a. Using a significance level of a = 0.01, find the critical value(s).
b. Should we reject Ho or should we fail to reject Ho?
Click here to view page 1 of the standard normal distribution table.
Click here to view page 2 of the standard normal distribution table.
a. The critical value(s) is/are z =
(Round to two decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)
b. Choose the correct conclusion below.
A. Reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that p<0.77.
B. Fail to reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that p< 0.77.
C. Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that p< 0.77.
D. Fail to reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that p<0.77.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 4 The test statistic of z= -1.54 is obtained when testing the claim that p<. This is a left-tailed test. Using a 0.05 significance level, complete parts (a) and (b). Click here to view the standard normal distribution table for negative z scores. Click here to view the standard normal distribution table for positive z scores. a. Find the critical value(s). Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box(es) within your choice. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) O A. There is one critical value; the critical value is OB. There are two critical values; the lower critical value is and the upper critical value isarrow_forwardThe test statistic of z = 1.68 is obtained when testing the claim that p 0.302. a. Identify the hypothesis test as being two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed. b. Find the P-value. c. Using a significance level of a = 0.01, should we reject Ho or should we fail to reject Ho? Click here to view page 1 of the standard normal distribution table. Click here to view page 2 of the standard normal distribution table. a. This is a test.arrow_forwardIs memory ability before a meal the same as after a meal? Ten people were given memory tests before their meal and then again after their meal. The data is shown below. A higher score indicates a better memory ability. Ho: Select an answer H₁: Select an answer ✓ Before a Meal After a Meal Assume a Normal distribution. What can be concluded at the the a = 0.01 level of significance? For this study, we should use Select an answer a. The null and alternative hypotheses would be: b. The test statistic ? ✓ = Score on the Memory Test 67 44 71 77 63 76 53 50 71 82 76 54 71 86 75 88 58 49 89 83 Select an answer Select an answer V c. The p-value d. The p-value is ? ✓ a e. Based on this, we should f. Thus, the final conclusion is that ... Select an answer Select an answer (please enter a decimal) (Please enter a decimal) (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.) Select an answer the null hypothesis.arrow_forward
- 1 The test statistic of z = 1.88 is obtained when testing the claim that p>0.41. This is a right-tailed test. Using a 0.01 significance level, complete parts (a) and (b). Click here to view the standard normal distribution table for negative z scores. Click here to view the standard normal distribution table for positive z scores. a. Find the critical value(s). Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box(es) within your choice. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) O A. There is one critical value; the critical value is OB. There are two critical values; the lower critical value is b. Should we reject Ho or should we fail to reject Ho? and the upper critical value is O A. Ho should not be rejected, since the test statistic is in the critical region. OB. Ho should be rejected, since the test statistic is in the critical region. O C. Ho should not be rejected, since the test statistic is not in the critical region. O D. Ho should be rejected, since the test statistic is…arrow_forwardThe test statistic of z= - 1.46 is obtained when testing the claim that p = 1/6. a. Using a significance level of a = 0.05, find the critical value(s). b. Should we reject Ho or should we fail to reject Ho? Click here to view page 1 of the standard normal distribution table. Click here to view page 2 of the standard normal distribution table. a. The critical value(s) is/are z= (Round to two decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)arrow_forwardComplete parts (a) and (b) below. Click here to view Page 1 of the table of areas under the standard normal curve. Click here to view Page 2 of the table of areas under the standard normal curve. a. The test statistic in a right-tailed test is z= 1.71. Determine the P-value and decide whether, at the 5% significance level, the data provide sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis. The P-value is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) This P-value V sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis because it is V the significance level. b. The test statistic in a right-tailed test is z= - 0.82. Determine the P-value and decide whether, at the 5% significance level, the data provide sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis. The P-value is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) This P-value sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis in…arrow_forward
- 6 The test statistic of z = -2.47 is obtained when testing the claim that p<7. This is a left-tailed test. Using a 0.01 significance level, complete parts (a) and (b). Click here to view the standard normal distribution table for negative z scores. Click here to view the standard normal distribution table for positive z scores. a. Find the critical value(s). Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box(es) within your choice. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) O A. There are two critical values; the lower critical value is OB. There is one critical value; the critical value is b. Should we reject Ho or should we fail to reject Ho? and the upper critical value is O A. Ho should be rejected, since the test statistic is in the critical region. O B. Ho should not be rejected, since the test statistic is not in the critical region. O C. Ho should be rejected, since the test statistic is not in the critical region. O D. Ho should not be rejected, since the test statistic…arrow_forwardThe test statistic of z= -3.23 is obtained when testing the claim that p <0.31. a. Using a significance level of x = 0.01, find the critical value(s). b. Should we reject Ho or should we fail to reject Ho? Click here to view page 1 of the standard normal distribution table. Click here to view page 2 of the standard normal distribution table. a. The critical value(s) is/are z = 0. (Round to two decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) b. Choose the correct conclusion below. O A. Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that p <0.31. B. Fail to reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that p <0.31. OC. Fail to reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that p<0.31. O D. Reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that p<0.31. 484arrow_forwardRed Blood Cell Count: A simple random sample of 300 adult males is taken to measure the red blood cell count (in cells per microliter). Use a significance level of 0.01 to test the claim that the sample has a mean less than the population mean (μ = 5.4 million cells per microliter). Does the sample have a normal distribution? Explain why. Does the result suggest that the male sample has a red blood cell count below 5.4 million cells per microliter? Determine the descriptive statistics of the sample. State the statistical hypotheses: H0 and HA. Determine the α Is this test one or two tailed? What statistical conclusion did you reach regarding the question being evaluated? RED 4.80 4.73 4.47 4.32 4.95 3.95 4.68 4.60 4.09 5.47 4.44 4.15 5.07 4.38 5.22 4.22 4.32 4.30 6.34 5.60 4.93 5.18 3.54 4.61 4.22 4.99 5.23 4.01 4.07 5.06 4.30 4.28 4.76 4.14 4.61 4.67 4.36 4.28 4.59 4.77 3.86 5.38 5.03 4.60…arrow_forward
- The test statistic of z = 2.55 is obtained when testing the claim that p = 0.269. a. Identify the hypothesis test as being two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed. b. Find the P-value. c. Using a significance level of α = 0.10, should we reject Ho or should we fail to reject Ho? Click here to view page 1 of the standard normal distribution table. Click here to view page 2 of the standard normal distribution table. a. This is a two-tailed test. b. P-value= (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardThe test statistic of z = 0.81 is obtained when testing the claim that p > 0.2. a. Identify the hypothesis test as being two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed. b. Find the P-value. c. Using a significance level of α = 0.10, should we reject Ho or should we fail to reject Ho? Click here to view page 1 of the standard normal distribution table. Click here to view page 2 of the standard normal distribution table. a. This is a test. 4 b. P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) c. Choose the correct conclusion below. ⒸA. Fail to reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that p > 0.2 OB. Reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that p > 0.2. O C. Fail to reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that p > 0.2. O D. Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that p > 0.2.arrow_forwardLet x be a random variable representing dividend yield of Australian bank stocks. We may assume that x has a normal distribution with s.d.= 2.3% . A random sample of 12 Australian bank stocks has a sample mean of x=6.16% . For the entire Australian stock market, the mean dividend yield is 7.2%. Do these data indicate that the dividend yield of all Australian bank stocks is higher than 7.2%? Find (or estimate) the P-value. Round your answer to three decimal places.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman