
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:K
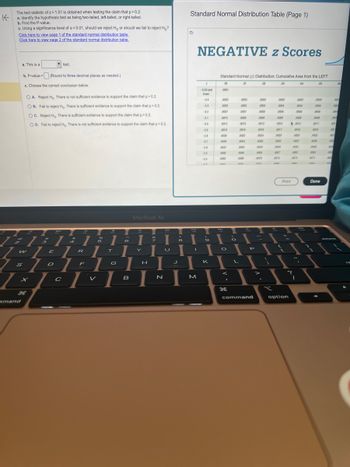
The test statistic of z= 1.51 is obtained when testing the claim that p>0.2.
a. Identify the hypothesis test as being two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed.
b. Find the P-value.
c. Using a significance level of a = 0.01, should we reject H, or should we fail to reject Ho?
Click here to view page 1 of the standard normal distribution table.
Click here to view page 2 of the standard normal distribution table.
7
a. This is a
b. P-value =
c. Choose the correct conclusion below.
S
z
7 s
1
mand
1
OA. Reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that p>0.2.
OB. Fail to reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that p>0.2.
OC. Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that p>0.2.
OD. Fail to reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that p>0.2.
w
H
test.
5
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
TEL
ZOE
D
C
1
1:1
4
R
F
I
V
%
5
1
T
G
A
6
B
MacBook Air
|
9
||
Lu
I
N
H
J
8
Standard Normal Distribution Table (Page 1)
O
1
M
NEGATIVE z Scores
2
-3.50 and
lower
-34
-33
-3.2
-30
-2.9
-2.8
-27
-24
S
K
Standard Normal (2) Distribution: Cumulative Area from the LEFT
.00
01
03
04
05
0001
0003
0005
0007
0010
0013
0019
0006
0005
0047
0082
-
O
g
F
0003
0005
0007
0009
0013
0018
0025
0004
0045
0060
0080
asna
L
P
command
0003
0005
0006
www
0009
0013
0018
0024
0033
0044
0069
0078
as
-
;
0003
.0004
0006
0009
0012
0017
0023
0032
0043
0067
0075
area
Print
?
option
0003
0004
0006
0008
0012
0016
0023
0031
0041
0066
.0073
I
0003
.0004
.0006
0008
.0011
.0016
0022
0000
0040
0054
0071
mar
Done
.000
001
001
.000
002
.002
.000
.000
000
0062
006
na
06
Transcribed Image Text:The test statistic of z= 1.51 is obtained when testing the claim that p>0.2.
a. Identify the hypothesis test as being two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed.
b. Find the P-value.
c. Using a significance level of a = 0.01, should we reject Ho or should we fail to reject Ho?
Click here to view page 1 of the standard normal distribution table.
Click here to view page 2 of the standard normal distribution table.
a. This is a
2
@
b. P-value=
c. Choose the correct conclusion below.
S
OA. Reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that p>0.2.
OB. Fail to reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that p>0.2.
12
W
OC. Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that p > 0.2.
OD. Fail to reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that p>0.2.
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
X
test.
#
3
E
D
с
$
4
a
R
F
%
5
V
FR
T
G
MacBook Air
6
Y
B
&
7
H
U
N
00*
8
J
(
9
8
K
M
O
O
L
<
1
Time Remaining: 01:08
D
P
^
command
{
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A manufacturer of MP3 players conducts a set of comprehensive tests on the electrical functions of its product. All MP3 players must pass all tests prior to being sold. Of a random sample of 700 MP3 players, 28 failed one or more tests. Find a 90% confidence interval for the proportion of MP3 players from the population that pass all tests. Click here to view page 1 of the standard normal distribution table. Click here to view page 2 of the standard normal distribution table. The 90% confidence interval isarrow_forwardSolve and show work.arrow_forwardThe test statistic of z = 2.03 is obtained when testing the claim that p#0.874. a. Identify the hypothesis test as being two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed. b. Find the P-value. c. Using a significance level of a = 0.01, should we reject Ho or should we fail to reject Ho? Click here to view page 1 of the standard normal distribution table. Click here to view page 2 of the standard normal distribution table. a. This is a two-tailed test. b. P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
- The test statistic of z = 1.41 is obtained when testing the claim that p> 0.9. a. Identify the hypothesis test as being two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed. b. Find the P-value. c. Using a significance level of a = 0.01, should we reject H, or should we fail to reject H,? Click here to view page 1 of the standard normal distribution table. Click here to view page 2 of the standard normal distribution table. ..... a. This is a test. b. P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) c. Choose the correct conclusion below. A. Fail to reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that p> 0.9. B. Reject Ho: There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that p> 0.9. O c. Fail to reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that p> 0.9. D. Reject Ho: There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that p>0.9.arrow_forwardThe test statistic of z = 1.30 is obtained when testing the claim that p> 0.2. a. Identify the hypothesis test as being two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed. b. Find the P-value. c. Using a significance level of a = 0.01, should we reject Ho or should we fail to reject Ho? Click here to view page 1 of the standard normal distribution table. Click here to view page 2 of the standard normal distribution table. a. This is a right-tailed test. b. P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardThe test statistic of z= 1.07 is obtained when testing the claim that p #0.587. a. Identify the hypothesis test as being two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed. b. Find the P-value. c. Using a significance level of α = 0.10, should we reject Ho or should we fail to reject Ho? viow page 1 of the standard normal distribution table.arrow_forward
- A 0.05 significance level is used for a hypothesis test of the claim that when parents use a particular method of gender selection, the proportion of baby girls is different from 0.5. Assume that sample data consists of 66 girls in 144 births, so the sample statistic of 1124 results in a z score that is 1 standard deviation below 0. Complete parts (a) through (h) below.Click here to view page 1 of the Normal table. LOADING... Click here to view page 2 of the Normal table. LOADING...Question content area bottomPart 1a. Identify the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis. Choose the correct answer below.A.H0: p=0.5H1: p>0.5B.H0: p≠0.5H1: p=0.5C.H0: p=0.5H1: p≠0.5D.H0: p=0.5H1: p<0.5Part 2b. What is the value of α?α=0.050.05 (Type an integer or a decimal.)Part 3c. What is the sampling distribution of the sample statistic? Student (t) distribution Normal distribution χ2Part 4d. Is the test two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed? Left-tailed Two-tailed…arrow_forwardThe test statistic of z = 1.52 is obtained when testing the claim that p> 0.7. a. Identify the hypothesis test as being two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed. b. Find the P-value. c. Using a significance level of a = 0.01, should we reject Ho or should we fail to reject H,? Click here to view page 1 of the standard normal distribution table. Click here to view page 2 of the standard normal distribution table) a. This is a two-tailed test. b. P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) c. Choose the correct conclusion below. O A. Reject Ho - There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that p> 0.7. O B. Fail to reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that p> 0.7. OC. Fail to reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that p> 0.7. O D. Reject Ho- There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that p > 0.7.arrow_forwardThe test statistic of z= 2.45 is obtained when testing the claim that p #0.854. a. Identify the hypothesis test as being two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed. b. Find the P-value. c. Using a significance level of a = 0.05, should we reject Ho or should we fail to reject Ho? Click here to view page 1 of the standard normal distribution table. Click here to view page 2 of the standard normal distribution table. a. This is a test. ***arrow_forward
- The test statistic of z = 0.69 is obtained when testing the claim that p> 0.3. a. Identify the hypothesis test as being two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed. b. Find the P-value. c. Using a significance level of a = 0.05, should we reject H, or should we fail to reject H,? Click here to view page 1 of the standard normal distribution table. Click here to view page 2 of the standard normal distribution table. a. This is a test. b. P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) c. Choose the correct conclusion below. A. Fail to reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that p> 0.3. B. Reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that p> 0.3. O C. Fail to reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that p > 0.3. D. Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that p> 0.3.arrow_forwardThe test statistic of z = 2.00 is obtained when testing the claim that p #0.438. a. Identify the hypothesis test as being two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed. b. Find the P-value. c. Using a significance level of α = 0.01, should we reject Ho or should we fail to reject Ho? Click here to view page 1 of the standard normal distribution table. Click here to view page 2 of the standard normal distribution table. a. This is a ▼test. b. P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) c. Choose the correct conclusion below. A. Reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that p *0.438. B. Fail to reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that p # 0.438. C. Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that p = 0.438. D. Fail to reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that p #0.438. 0 0 Standard Normal (z) Distribution: Cumulative Area from the LEFT .04 .5160 .5557 .5948 .6331 .6700 .7054 .7389 .7704…arrow_forwardThe test statistic of z = 1.68 is obtained when testing the claim that p 0.302. a. Identify the hypothesis test as being two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed. b. Find the P-value. c. Using a significance level of a = 0.01, should we reject Ho or should we fail to reject Ho? Click here to view page 1 of the standard normal distribution table. Click here to view page 2 of the standard normal distribution table. a. This is a test.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman