
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
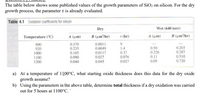
Transcribed Image Text:The table below shows some published values of the growth parameters of SiO2 on silicon. For the dry
growth process, the parameter t is already evaluated.
Table 4.1 Oxidation coefficients for silicon
Dry
Wet (640 torr)
Temperature ("C)
A (µm)
B (um'/hr)
T (hr)
A (um)
B (um'/hr)
0.370
0.235
0.165
0.0011
800
920
0.50
0.203
1.4
0.37
0.0049
0.0117
0.027
0.226
0.11
0.05
0.287
0.510
0.720
1000
0.076
1100
1200
0.090
0.040
0.045
0.027
a) At a temperature of 1100°C, what starting oxide thickness does this data for the dry oxide
growth assume?
b) Using the parameters in the above table, determine total thickness if a dry oxidation was carried
out for 5 hours at 1100°C. "
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (References) TUTOR Balance Redox Reactions in Acidic Solution Balance the reaction between Ag and MnO, to form Agt and Mn2+ in acidic solution. When you have balanced the equation using the smallest integers possible, enter the coefficients of the species shown. Enter "1" if the coefficient is "1." Ag+ MnO4 Ag* + Mn2+ Water appears in the balanced equation as a (reactant, product, neither) with a coefficient of . (Enter 0 for neither.) How many electrons are transferred in this reaction? Submit Show Approach Show Tutor Steps Submit Answer Try Another Version 6 item attempts remaining Previous Email Instructorarrow_forwardHow many moles of Oz gas are produced at 1 atm pressure and 25 °C by the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of NaySO4 if 0.500 A is passed through the solution for 75.0 minutes? Here is the oxygen reduction reaction. Oz (g) + 4 H+ (ag) + 4 € - 2 H20(1) Report your answer in moles to three significant figures. Do NOT use scientific notation. Do NOT put units in the answer box.arrow_forwardUsing the equation 2Mn(OH)2(s)+O2(aq)->2MnO(OH)2(s), Determine the number of moles of MnO(OH)2 Formed for every one mole of O2 consumed. Show work.arrow_forward
- (27) What is the value of the equilibrium constant (Keq) when the following redox reaction takes place at 727°C? Mn (s) + Sn¹+ (aq) → Mn²+ (aq) + Sn²+ (aq) (A) 2.55 x 10¹3 (B) 2.76 x 10¹8 (C) 7.62 x 1036 (D) 5.23 x 10-15 (E) 3.62 x 10-1⁹ The most convenient form of the equation for this one might not be on your note sheet. I suggest using: RT ECELL -In K nF (28) An archaeologist claims that a bone in her collection is from a saber-toothed tiger that is believed to have the carbon-1arrow_forwardWhat volume of oxygen gas at STP must be consumed to produce the corrosion of 200 g of iron? Hint. Fe- Fe2+ +2e (one mole of Fe produces 2 moles of electrons) 40H 02+2H20+4e (42 mole O2 = 1 mole Fe) V=nRT/p =(8.314J/mol)arrow_forwardCalculate AG for the formation of one mole of N₂O4 from its elements using AH and ASfº for N₂O4. Use data in the table below: Substance Ag(s) AgCl(s) Al(s) Al₂O3(s) C(s) (graphite) (8) CO₂(g) CH₂(g) CH₂Cl(g) CH₂OH(1) C₂H₂(g) C₂H4(g) C₂H6(g) C8H18 (7) C₂H₂OH(1) Ca(s) CaCO3(s) CaCl₂(s) 197.9 213.6 186.2 234.2 126.8 CO(NH,),(s) 104.6 CO(NH,),(aq) 173.8 200.8 219.8 229.5 466.9 161 CO(g) CO₂(g) CH4(g) Substance Ag(s) AgBr(s) AgCl(s) Al(s) Al₂O3(s) C(s) (graphite) Standard Entropies of Some Typical Substances at 298.15 K Sº (J mol-¹ K-¹) 40 76.1 107 C₂H₂(g) C₂H4(g) C₂H6(g) C₂H,OH(1) Ca(s) CaBr₂(s) CaCO3(s) CaCl₂(s) CaO(s) Cl₂(g) Fe(s) Sᵒ (J mol-¹ K-¹) Fe₂O3(s) H₂(g) H₂O(g) H₂O(1) AGO = CH₂Cl(g) CH₂I(g) CH₂OH(1) CO(NH₂)2(s) (urea) CO(NH,),(aq) kJ mol-1 42.55 96.2 28.3 51.0 Ca(OH)₂(s) CaSO4(s) CaSO4 H₂O(s) CaSO4-2H₂O(s) 5.69 41.4 92.9 114 Substance CaO(s) Ca(OH)₂(s) CaSO4(s) CaSO4+H₂O(s) 131 CaSO4-2H₂O(s) 194.0 223.0 27 Cl₂(g) Fe(s) Fe₂O3(s) H₂(g) H₂O(g) H₂O(1) HCI(g) HNO3(1) H₂SO4(1)…arrow_forward
- Which among the following metals has the most tendency to form oxide layers on surface implants? TABLE II.4.4.5 Electrochemical Series Metal Potential (V) Gold 1.43 1.20 Platinum Mercury 0.80 Silver 0.79 0.34 Copper Hydrogen Lead Tin Molybdenum Nickel Cobalt Cadmium Iron Chromium Zinc Aluminum Titanium Magnesium Sodium Lithium titanium iron tin aluminum 0 -0.13 -0.14 -0.20 -0.25 -0.28 -0.40 -0.44 -0.73 -0.76 -1.33 -1.63 -2.03 -2.71 -3.05arrow_forward= oft C W Write balanced half-reactions for the following redox reaction: Erosoft Microsoft 5.52.210.. O ELECTROCHEMISTRY Writing the half-reactions of a complex redox reaction in acidic ... esc 2+ Zn (aq)+Bi (aq)+6OH(aq) ► Zn(s)+BiO3(aq)+ 3 H₂O(1) reduction: oxidation: 0 Explanation < 3+ Check 0217 Q 103 SEV ♫ MacBook Pro ©20arrow_forwardAssuming an efficiency of 49.10%,49.10%, calculate the actual yield of magnesium nitrate formed from 117.8 g117.8 g of magnesium and excess copper(II) nitrate. Mg+Cu(NO3)2⟶Mg(NO3)2+CuMg+Cu(NO3)2⟶Mg(NO3)2+Cu actual yield:arrow_forward
- What is Eocell in volts? In (s) | In(OH)3 (s) || SbO2- (aq) | Sb (s) In(OH) 3 (s) + 3 e-⟶In (s) + 3 OH- Eo = -1.00 VSbO2- (aq) + 2 H2O (l) + 3 e-⟶ Sb (s) + 4 OH- (aq) Eo = -0.66 V Group of answer choices +1.66 +0.34 -0.34 +1.98 -1. 66arrow_forwardStandard Reduction (Electrode) Potentials at 25 Half-Cell Reaction * (volts) F2(8) + 2 e2F (aq) 287 Ce* (aq) +e Ce (aq) 1.61 Mn0, (aq) + BH'(aq) +5e Mn"( "(aq) + 4 H20(1) 1.51 Cla(g) +2e -2 C (aq) 1.36 Cr20, (aq) + 14 H'(aq) - 6e2 Cr*"(aq) + 7 H20() 1.33 Oz() + 4 H'(aq) + 4e2 H20(1) 1.229 Br20) + 2 e2 Br (aq) 1.08 NO3 (aq) + 4 H'(aq) + 3eNO(g) + 2 H20() Hg"(aq) 0.96 2 Hg (aq) + 2e 0.920 Hg"(aq) + 2 e- Hg(1) 0.855 Ag (aq) +e Ag(s) 0.799 Hg2" (aq) - 2e-2 Hg(1) 0.789 Fe" (aq) +e Fe"(ag) 0.771 12(s) + 2e 21 (aq) 0.535 Fe(CN)"(aq) + e Fe(CN), (aq) 0.48 Cu (aq) + 2eCu(s) 0.337 Cu"(aq) +e- Cu (aq) 0.153 S(s) + 2 H'(aq) + 2 e H2S(aq) 0.14 2H'(aq) + 2e-H2(8) 0.0000 Pb (aq) + 2e- Ph(s) -0126 Sn (aq) + 2 e Sn(s) -014 Ni (aq) + 2 e- Ni(s) -0.25 Co (aq) + 2 e Co(s) -0.28 "(aq) + 2e Cd(s) -0.403 Cr"(aq) +e "(aq) -041 Fe"(aq) + 2 e Fe(s) -044 Cr"(aq) +3e-Cr(s) -0.74 Zn"(aq) +2 e- Zn(s) -0.763 2 H20() +2e Hz(z) + 2 OH (aq) -0.83 Mn"(aq) + 2e - Mn(s) -1.18 A" (aq) + 3e- Al(s) -1.66 Mg (aq) + 2 e- Mg(s)…arrow_forwardQuestion 21 of 26 What is the change in enthalpy in joules when 5.44 x 10-4 mol of AgCI dissolves in water according to the following chemical equation: AgCI(s) – Ag*(aq) + Cl-(aq) AH = 65.5 kJ STARTING AMOUNT ADD FACTOR ANSWER RESET *( ) 1 1000 0.001 3.56 х 10° 0.0356 35.6 0.00831 65.5 6.022 x 1023 5.44 x 10-4 g Ag+ J g Cl- mol Ag* kJ mol AgCI g A9CI mol Cl-arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY