
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
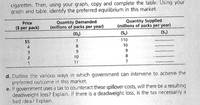
Transcribed Image Text:cigarettes. Then, using your graph, copy and complete the table. Using your
graph and table, identify the preferred equilibrium in this market.
Quantity Demanded
(millions of packs per year)
Quantity Supplied
(millions of packs per year)
Price
($ per pack)
(D)
(S,)
(S,)
$5
7
110
10
4
3
10
8
11
7
1
d. Outline the various ways in which government can intervene to achieve the
preferred outcome in this market.
e. If government uses a tax to counteract these spillover costs, will there be a resulting
deadweight loss? Explain. If there is a deadweight loss, is the tax necessarily a
bad idea? Explain.

Transcribed Image Text:2. The table below shows hypothetical demand and supply schedules for cigarettes
in the absence of government intervention.
a. Draw a diagram showing demand (Do), supply (S,), and equilibrium price and
quantity in the market before government intervention.
b. Government policy-makers estimate that the spillover costs associated with
cigarette smoking are an extra $2 for each pack sold. Outline the nature of
these spillover costs in the case of cigarette smoking.
c. Using the estimate from part b, draw a new supply curve (S,) on your graph
that incorporates both private and public costs of producing and consuming
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following graphs illustrate how positive externalities can be generated by both the production (supply) and consumption (demand) of the vaccine. Dead Weight Loss Supply Marginal Cost P Market Social Quantity Optimum D2 Marginal Social Benefit Positive Externality D₁- Marginal Private Benefit ■FIGURE 5-4 Price of Marginal benefit, MB Underproduction S-PMC SMC = PMC-MB -Deadweight loss D= PMB = SMB Market Failure Due to Positive Production Externality in the Oil Exploration Market Expenditures on oil exploration by any company have a positive externality because they offer more profitable opportuni- ties for other companies. This leads to a social marginal cost that is below the private marginal cost, and a social optimum quantity (Q₂) that is greater than the competitive market equilibri um quantity (Q). There is underpro- duction of Q-Q, with an associated deadweight loss of area ABC. Quantity of oil Positive Externality- Demand Please review the following on the foundations of…arrow_forwardThis is from my microeconomics class, Mankiw Chapter 12. It is one question broken up into two parts. 1) A Culinary Conundrum Assume that Georgetown University President John DeGioia is interested in encouraging healthier eating habits on the part of Georgetownstudents. Assume further that Georgetown Students have two options for their meals: they can eat in the cafeteria on campus or at one of the fancy restaurants in the surrounding neighborhood. Meals on campus are healthier than most off-campus options, so President DeGioia would like to encourage students to eat on campus more often. However, students think it’s fun to go off campus for their meals when they can afford to do so. Thus,you should consider on-campus meals to be inferior good standoff-campus meals to be normal goods. a.) True, false, or uncertain: if President De Gioia orders the cafeteria to lower the price of its meals, students will eat on campus more often. Explain your answer. b.) True, false, or…arrow_forwardWhat would likely be the impact on health care costs if a government implements price controls on pharmaceuticals? A. Health care costs would increase due to higher administrative overhead. B. Health care costs would decrease as drug prices are directly reduced. C. Health care costs would remain unchanged, as other expenses would rise to offset drug cost savings. D. Health care costs would initially decrease but eventually lead to shortages and higher costs in the long term.arrow_forward
- The four categories present potential responses to environmental problems. Place each response in the category that best matches it. It is possible that a category may end up with more than one scenario or none at all. Command‑and‑control regulation (e.g., environmental standards) Marketable or tradable pollution permits (e.g., cap‑and‑trade) Pollution or emissions tax Well‑defined property rights The government requires that auto manufacturers limit pollution to a specified threshold. An auto manufacture is charged a fee per unit of pollution emitted into a river. Auto manufactures are allowed to pollute as much as they wish, provided that they have purchased a sufficient number of pollution vouchers. The government requires that auto manufacturers use new, cleaner technology in producing cars. A steel mill pays nearby homeowners to compensate them for the noise they must put up with as a result of the steel manufacturing process.arrow_forwardA. Economic profit is an indication that consumers are willing to pay more for a good or service being offered. True False B. An advantage of tradable permits over emission taxes is that no knowledge of marginal abatement costs is needed to ensure that the tax rate is optimal. the regulator sets the price of permits. the regulator does not have to determine how much to reduce pollution levels. the regulator must set the optimal tax rate.arrow_forward1. For the demand function Qd = a - bP and the supply fuction Qs = dP - c, using Cramer's rule determine the equilbrium price and equilibrium quantity. 2. In calm waters, the oil spilling from the ruptured hull of a grounded tanker spreads in all directions. Assuming that the area polluted is a circle and that its radius is increasing at a rate of 2ft/sec, determine how fast the area is increasing when the radius of the circle is 40ft. 3. A firms production function is Q(L) is 15L2 - 0.1L3, where output (Q) is a fuction of a single input labour (L) I. Find the number of workers required to maximize total product. II. For what number of workers is average product maximumarrow_forward
- Discuss how rationing impure public goods would limit consumption of the following (USE PROPER DIAGRAM) : i. Roads : ii. Healthcare iii. Public recreational parksarrow_forwardScenario 10-1 The demand curve for gasoline slopes downward and the supply curve for gasoline slopes upward. The production of the 1,000th gallon of gasoline entails the following: a private cost of $3.10 • a social cost of $3-55 a value to consumers of $3.70 Refer to Scenario 10-1. Suppose the equilibrium quantity of gasoline is 1,150 gallons; that is, QMARKET = 1,150. Then the equilibrium price of a gallon could be a. $3.30. b. $3.80. c. $3.00. d. $2.80.arrow_forwardg. State the definition of spillover benefits. h. Give two examples of a spillover benefit situation and explain why your examples are correct. Be specific. i. Explain in detail, the economic effects of spillover benefits. Explain why the market demand curve understates true demand and what happens next leading to the market failure. Explain the nature of the market failure. j. Thoroughly and completely explain how spillover benefits are corrected and the economic implications of the corrections. Explain the two approaches used to solve the spillover benefit problem and how they work to solve the problem.arrow_forward
- Please drag and drop the markers 1 through 5 below to denote the appropriate position on the diagram that answers the question. a) Show with marker 1 the efficient level of marginal abatement costs. b) Show with marker 2 the marginal abatement costs if each produce must reduce pollution to 7.5 units. c) Denote with marker 3 the area that measures total abatement costs for each polluter. d) Show with marker 4 the marginal abatement costs if sources 1 and 2 merged and were constrained to a maximum total emissions of 15 units. e) Show with marker 5 the total abatement costs if both sources merged and were constrained to a maximum total emissions of 15 units. Marginal Cost (in dollars) MC MC, Quantity of Emissions Reduced A Source 1 10 5 4 13 14 15 15 14 13 12 11 10 8 O Source 2 5arrow_forwardDescribe briefly, the hedonic price method of estimating benefits. Use an environmental example to illustrate your answer. Explain why this valutationarrow_forwardplease draw the social cost line Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education