
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
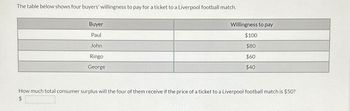
Transcribed Image Text:The table below shows four buyers' willingness to pay for a ticket to a Liverpool football match.
Buyer
Paul
John
Ringo
George
Willingness to pay
$100
$80
$60
$40
How much total consumer surplus will the four of them receive if the price of a ticket to a Liverpool football match is $50?
$
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the market for a pair of shoes, Jena is willing to pay $75 for a pair while Jane is willing to pay $85 for a pair. The actual price that each must pay for a pair of shoes is $65. What is the combined amount of consumer surplus of Jena and Jane? Multiple Choice $10 $160 $30 $20arrow_forwardPrice (dollars per unit) Price (dollars per unit) D Quantity (units per month) Figure B Quantity (units per month) Figure A Price (dollars per unit) Price (dollars per unit) D Quantity (units per month) Quantity (units per month) Figure C Figure D The above figure shows the demand curves in four different markets. If each of the markets has an identical upward sloping supply curve and the same tax is levied on suppliers, which market would produce the largest amount of deadweight loss? A) B B) C C) A D) Darrow_forwardAssume that a price floor of $320 has been implemented and there are no wasteful quality improvements. What are the total gains from trade (total surplus) with a price floor of $320? Hint: enter your answer as a number only with no $ sign Example: if the answer is $10,000, enter 10,000 2,400arrow_forward
- What is the value of deadweight loss if the market price is $15? Group of answer choices: $20 $5 $15 $10arrow_forwardSuppose Home is a small exporter of wheat. At the world price of 100 US dollars per tonne, Home growers export 20 tons of wheat. Now suppose the Home government decides to support its domestic producers with an specific export subsidy of 40 US dollars per tonne. Use Figure 1 to answer the following questions: Figure 1: Supply and Demand for Wheat at Home Home price 140 100 X 10 20 40 50 Supply Demand Quantity (a) Explain why consumer and producer surplus can be used to gauge the change in welfare caused by the export subsidy on individuals and firms.arrow_forwardMultiple Choice $1,562.5 $6,250 $4,687.5 $3,125arrow_forward
- 1.2 Consider the following customers of a Japanese sushi restaurant. Their total benefit (TB) measured in terms of the maximum amount of money they are willing to pay for n dishes are given below. Dish of sushi 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Customer A 0 60 90 Total Benefit ($) 115 125 120 110 95 70 Customer B 0 30 50 60 55 50 40 25 5 As postulated in economics, customers are maximizing their economic surpluses. One can decide not to dine in this Japanese restaurant and can get zero economic surplus. (a) The sushi restaurant is now charging customers $20 per dish. How many dishes do these two customers choose to buy under this pricing arrangement respectively? Use both total and marginal approach to solve the problem. Show your steps. (b) Now, the sushi restaurant changes its pricing policy. Now they charge each customer $100 and let them order as many as they want. Will the customers continue to dine in this restaurant? If so, how many dishes would they choose to buy? Again, solve this using both…arrow_forwardSuppose the following graph shows the demand for, and supply of, apartments in New York City. Use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the equilibrium monthly rent and quantity of apartments in the absence of price controls. Then use the green point (triangle symbol) to fill the area representing consumers' surplus, and use the purple point (diamond symbol) to fill the area representing producers' surplus. MONTHLY RENT (Dollars per apartment) 2800 2600 2400 2200 2000 1800 0 Demand Supply 0.8 3.2 QUANTITY OF APARTMENTS (Millions per month) 1.6 2.4 4.0 Equilibrium A CS PS ?arrow_forwardWhich of the following pairs of company profits and consumer surplus maximize welfare (or efficiency)? Question 8 options: Producer surplus = 90, Consumer surplus = 30 Producer surplus = 70, Consumer surplus = 70 Producer surplus = 100, Consumer surplus = 10 Producer surplus = 80, Consumer surplus = 50arrow_forward
- Matthew and Victoria are shopping for a new pair of running shoes. Victoria is willing to pay $200 and Matthew is willing to pay $110 for a new pair of shoes. What is the total gain in surplus when the price of then shoes decreases from $160 to $100?arrow_forwardIllustrate using an appropriate diagram [see sample below] where the Crocs online store in Australia [https://www.crocsaustralia.com.au/] sets the average price of a pair of Classic Clog to maximise profit. And within that diagram, explain ‘Gains from trade’ and ‘Deadweight Loss’. In your diagram, assume at the profit-maximising point, the average price of the Classic Clog is $60, and the unit cost is $35. Determine whether the PED is more elastic or inelastic Use hypothetical values (rough guesses) relying on intuition for quantities sold (Q) per month Once your diagram is complete (and properly labelled), explain ‘Gains from trade’ and ‘Deadweight Loss’ associated with your diagram.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education