
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
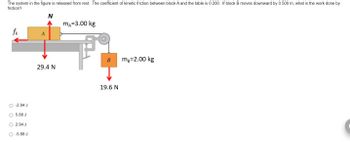
Transcribed Image Text:The system in the figure is released from rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction between block A and the table is 0.200. If block B moves downward by 0.500 m, what is the work done by
friction?
N
mA=3.00 kg
fk
A
B mg=2.00 kg
29.4 N
-2.94 J
O 5.88 J
O 2.94 J
O -5.88 J
19.6 N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the figure, a constant external force P = 300 N is applied to a 20.0 kg box, which is on a rough horizontal surface. While the force pushes the box a distance of 8.00 m, the speed changes from 0.500 m/s to 2.60 m/s. The work done by friction during this process is closest to P 30° 20 kg -8.0 m O A. +2209 J ОВ.-1948 J OC.-2013 J O D.+1948 J O E. +2013 Jarrow_forwarda 40 N horizontal force is applied to a 6.0 kg box. Friction is negligible. The box moves a horizontal distance of 4.0 meters. The work done by the 40 N force is A. 160 J B. 10 J C. 80 J D. 92 Jarrow_forwardA child throws a stone upwards. While the stone is moving upwards the gravitational force does positive work on it and the gravitational potential energy increases. the gravitational force does positive work on it and the gravitational potential energy decreases. the gravitational force does negative work on it and the gravitational potential energy increases. O the gravitational force does negative work on it and the gravitational potential energy decreases.arrow_forward
- An object is acted on by the force shown in the figure(Figure 1). What is the final position of the object if its initial position is x = 0.40 mm and the work done on it is equal to 0.21 J? Express your answer using two significant figures.arrow_forwardThe two ropes shown in the bird's-eye view of the figure are used to drag a crate 5.8 m across the floor. How much work is done by the force fk→?Express your answer with the appropriate units. How much work is done by the force T1→?Express your answer with the appropriate units. How much work is done by the force T2→?Express your answer with the appropriate units.arrow_forwardOn a horizontal surface, an object slides from point P to point Q along a straight line, then slides back from Q to P along a semicircle. If P and Q are a distance L apart, how much work did the force of kinetic friction do during the entire process? The magnitude of fk is fk.arrow_forward
- A system of two objects has AKtot = 7 J and AUint = -4 J. Part A How much work is done by interaction forces? Express your answer in joules. IVE ΑΣΦ Wint = Submit Part B How much work is done by external forces? Express your answer in joules. V—| ΑΣΦ Wext= = Request Answer Submit Request Answer ? ? J Jarrow_forwardThe figure shows a block of mass 10 Kg. Determine what work will be done by the force F that will lift said block with constant speed to a height of 18 m. µ = 0.3 a. 2931 J b. 4870 J c. 61 J d. 37 J e. 1262 Jarrow_forward0 Question 3 A block of mass m = 1 kg is sliding on a horizontal surface with initial velocity vo = 2 m/s. The block is brought to a stop by kinetic friction in a distance of 4 m. What is the work done by the force of friction acting on the block? 2J O-0.5 J O-2 J 08 J 0.5 J O-8 J 1 pts Question 4 1 ptsarrow_forward
- Starting from rest, a 6.2-kg block slides 3.2 m down a rough 37-degree incline. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the incline is μk = 0.55. a) Determine the work done by the friction force between block and incline. b) Determine the work done by the normal force. c) Determine the net work done on the block.arrow_forwardplease help.arrow_forwardThe object is being pulled in a straight line along the ground by a 50-N force directed 60° above the horizontal. How much work does the force do in pulling the object 5 m? O 530 J O 125 J 0.55 J O 125 kJ O 53 Jarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON