
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
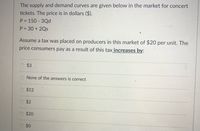
Transcribed Image Text:The supply and demand curves are given below in the market for concert
tickets. The price is in dollars ($).
P = 150 3Qd
P = 30 + 2Qs
Assume a tax was placed on producers in this market of $20 per unit. The
price consumers pay as a result of this tax increases by:
$3
None of the answers is correct
$12
$2
$20
$0
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The consumer surplus for John is $10 and his maximum willingness to pay for the product is $30 What would have been the market price?arrow_forwardA small province is planning to levy a hotel room tax of $20 per night on hotel owners to recover some of the costs of government services associated with nonresidents. The average price of a standard hotel room in this province before the implementation of the tax is $150 per night. Market analysts predict that the average price of a hotel room will increase to $155 per night after the tax. a) Use the supply and demand model to illustrate and explain how the proposed tax on hotel operators will impact the market for hotels. Clearly show in your diagram and explain in words the impact on price and quantity of hotel rooms as well as the revenue raised and any deadweight loss caused by the tax. b) Discuss how tax incidence is shared between buyers and sellers. What share of this tax is paid for by buyers, and what share is paid for by sellers? c) What do your findings in part b tell you about the price elasticity of demand for hotel rooms compared to the price elasticity of supply?…arrow_forwardPrice (dollars per gallon of ice cream) 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 Quantity (thousands of gallons of ice cream) The above figure shows the market for gourmet ice cream. In effort to reduce obesity, government places a $2 tax per gallon on suppliers in this market, shifting the supply curve from So to S1. The tax incidence is A) split equally between consumers and producers, each paying $1 per gallon. B) such that consumers pay $2 per gallon and producers pay $1 per gallon. C) split equally between consumers and producers, each paying $2 per gallon.arrow_forward
- Can you help me with this please? Can you explain how to factor in consumer and producer surpluses With substitute and complement goods? arrow_forwardA $1 tax per unit levied on consumers of good is equivalent to Question 2 options: A price floor that raises the price by $1 per unit A price floor ceiling that raises the good's price by $1 All other answers are incorrect A $1 per unit tax levied on producers of the goodarrow_forwardRefer to the graph shown. With an effective price ceiling at $3, total surplus is reduced by: Please see attached image.arrow_forward
- on Consider the market for tablets depicted below (think iPad or Microsoft Surface). If a price ceiling is adopted at $600, then there will be a shortage of units. P $800 $600 0 75 100 125 S₁ D₁arrow_forwardA binding price floor in this market might be set at: $Price Supply P3 P2 P1 Demand Q1 Q2 Q3 Quantity Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. a P3, which results in a market surplus equal to the distance from Q1 to Q3. b P3, which results in a makret surplus equal to the distance from Q1 to Q2. C P1, which results in a market shortage equal to the distance from Q1 to Q3. d P1, which results in a market shortage equal to the distance from Q1 to Q2.arrow_forwardThe government decides that the sugar price support program is getting too expensive. It abandons the support price program and instead assigns a marketing quota to each sugar producer. This quota gives the holder the right to sell sugar on the market and can be transferred to other producers. Altogether the quotas allocate to sugar growers add up to 9 million cwt. Please grab this problem, indicating clearly the market price and quantity. Not sure if this is necessary for the question but given is demand for sugar: Q= 20 - P Supply for sugar: Q = 2 + P quantities are in million hundredweight (cwt) and price is dollars per cwt. picture is of previous question that goes along to help answer with this one. I am needing help with number 3 that is picturedarrow_forward
- Calculate the producers' surplus for the supply equation at the indicated unit price p. (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) p = 90 + q; p = 225 $ Note: Hand written not allowedarrow_forwardComsumer Surplus Study The goal of this assignment is to apply Calculus to analyze consumer and producer surplus. This activity is based off the economical principles discussed in Section 3.1 of "Principle of Economics" and Section 7 of Chapter 3 in the Business Calculus book. The table below shows how supply and demand of gasoliine vary depending on the price: Price ($/gal) Demand (million of gal.) Supply (million of gal.) 753 513 550 1.2 700 1.4 640 600 1.6 580 639 1.8 543 660 2.2 450 680 2.4 430 700 2.6 420 720 2.8 390 735 3. 367 763 Note: there is some randomization in the above data to account for price fluctuations. Make sure to check that you input the correct data in your device. Perform the following work • Assume that Supply has a quadratic relationship with the price. Find this relationship (the help buttons contain an article to compute trend-lines in Excel): S(p) = Round your answer to 3 decimal places %3D • Assume that the Demand has a quadratic relationship with the…arrow_forwardThe supply curve for product X is given by QXS = -300 + 10PX .a. Find the inverse supply curve.P = ___ + ___ Qb. How much surplus do producers receive when Qx = 300? When Qx = 800?When QX = 300: $ ___When QX = 800: $ ___arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education