
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
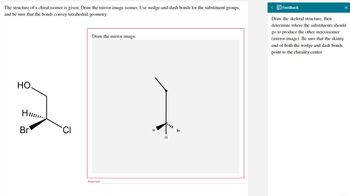
Transcribed Image Text:The structure of a chiral isomer is given. Draw the mirror image isomer. Use wedge-and-dash bonds for the substituent groups,
and be sure that the bonds convey tetrahedral geometry.
Draw the mirror image.
HO.
2
H
Br
Incorrect
H
•
CL
Br
<
Feedback
Draw the skeletal structure, then
determine where the substituents should
go to produce the other stereoisomer
(mirror image). Be sure that the skinny
end of both the wedge and dash bonds
point to the chirality center.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Using the drawing space below, draw the mirror image of the following molecule: CI H OH Br Once you have drawn the mirror image, decide whether your mirror image is an enantiomer of the molecule above, and click the yes or no button under the drawing area. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Is your mirror image an enantiomer? O Yes Ο NO × × ●● Ś Śarrow_forward2. If a molecule has 3 asymmetric carbon centers, how many stereoisomers are there? Show work. ^.arrow_forwardPlease solve parts d and e!arrow_forward
- Click on all structures that are enantiomers of the first (leftmost). If no structure qualifies, submit your answer without selecting any structure. OCH 3 H₂CO H CH=CH₂ HI F CH=CH₂ Fill H CH=CH₂ OCH3 H₂C=CHI OCH3 Harrow_forwardUse flat representation of rings, not chair in the drawing. Determine the most and least stable. Consider the most stable chair for each of these isomers, and then draw the most stable and least stable isomer based on a comparison of the best chair for each one.arrow_forwardPlease type out your answer, cannot be hand-drawnarrow_forward
- Draw a structural formula of the R configuration of the compound shown below.arrow_forward4. For each of the following molecules, label each stereocenter as R or S. Label the molecules appropriately as chiral or meso. a. b. methionine NH₂ H d. но. OH c. D = 2H, T = ³H, isotopes of hydrogen. f.T. OH OH CI Y ОНarrow_forwardName: Expt. 4: Molecular Models: Stereoisomers Laboratory Work – Be sure and answer all questions embedded in the text. Shown below is a representation of 2-bromopropane. a. Draw the mirror image of this representation. b. Build a model of each structure. Are the two structures superimposable? 1. 1o fro c. Look carefully at one of your models. Do you see a mirror plane of symmetry in the molecule? d. If so, draw where it is or describe in words what the plane is. er an steren somers H. CH3 . -Br CH3 mirror planearrow_forward
- Highlight each chiral center in the following molecule. If there are none, then check the box under the drawing area. HO There are no chiral centers. CI X 3arrow_forwardITEM #5 (Everyone should look at this question). Consider the two Fischer projections shown at right. They CH CH are NOT of the same molecule. H- -HO- HO In a short paragraph, explain why the molecules shown are NOT the same. OH но- H. HO. но In your explanation, describe how the groups of a Fischer projection are positioned in the ACTUAL molecule (Are the molecules flat in real life, or three-dimensional in real life? If three-dimensional, where exactly are the Hs and OHs positioned when one interprets these projections?) H- HO но H- CH,OH ČH;OH Also in your explanation, describe why the second molecule is not simply the first molecule flipped over (like a pancake).arrow_forwardAtomic #'s & Masses: Carbon: 6, 12.01g/mole Oxygen: 8, 16.00g/mole H: 1, 1.01g/mole 4. Answer questions for the following molecule: a. Circle any/all chiral centers. b. Is the molecule chiral or achiral. H H CH₂ CH₂ Br Brarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY