
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
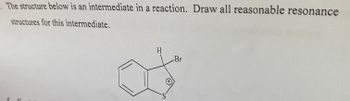
Transcribed Image Text:## Question: Resonance Structures
The structure below is an intermediate in a reaction. Draw all reasonable resonance structures for this intermediate.
### Provided Chemical Structure:
The given chemical structure consists of a benzene ring fused to a five-membered ring containing a sulfur atom (indicated as "S"). The five-membered ring also contains a carbon-bromine (C-Br) bond and a hydrogen (H) atom. The sulfur atom carries a positive charge.
Here is a detailed breakdown of the structure:
- A benzene ring (hexagonal ring with alternating double bonds).
- An attached five-membered ring containing:
- One sulfur atom (S) with a positive charge.
- One carbon atom bound to both a hydrogen (H) and a bromine (Br) atom.
### Graph/Diagram Explanation:
- **Benzene Ring**: Recognizable by its hexagonal shape with alternating double bonds.
- **Five-Membered Ring**: Fused to the benzene ring at two adjacent carbon atoms.
- **Sulfur Atom (S⁺)**: Located within the five-membered ring and marked with a positive charge.
- **Carbon-Bromine Bond**: One of the carbon atoms in the five-membered ring has a single bond to a bromine atom (Br).
- **Hydrogen Atom**: Attached to the same carbon atom as the bromine (C-H bond).
### Task: Drawing Resonance Structures
The goal is to draw all reasonable resonance structures for this intermediate. Resonance structures are different Lewis structures for the same molecule that show the delocalization of electrons. They involve the movement of lone pairs and/or π (pi) electrons to different positions while keeping the atom connectivity unchanged.
In this case, consider how the positive charge on the sulfur atom and the double bonds in the benzene ring can be rearranged to provide alternative resonance structures.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw resonance structures and draw out bonds of heteroatomsarrow_forwardWhich of the following species is a valid resonance structure of A? Use curved arrows to show how A is converted to any valid resonance structure. When a compound is not a valid resonance structure of A, explain why not.arrow_forwardDraw a resonance structure that places a pi bond in a different position. Include all lone pairs in your structure. :O: H Drawing Qarrow_forward
- Draw all possible resonance structures for the species belowarrow_forwardWhat are four contributing resonance structures for the following compound?arrow_forwardDirections: Read the following statements. Write your answer in a separate sheet of paper. Lewis dot ion after electron symbol of each ion if ionic bond is formed Charge of each Lewis dot Туре of Bond Atoms symbol of each atom Formula of the transfer if ionic involved Product bond is formed Na, O Са, N S, CIarrow_forward
- Draw one resonance structure of the following substance different from the given one. Interactive 3D display mode H3C O CH3arrow_forwardWhat would the resonance structure of these 2 compounds be? And which would be the major?arrow_forwardDraw an arrow pushing pattern represents the flow of electrons that converts the first resonance structure into the second resonance structure?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY