
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
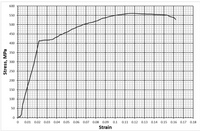
The stress-strain diagram of reinforcement steel having a cross-sectional diameter of 12 mm diameter and 100 mm gage length is determined after its tensile strength test as follows. Based on the stress-strain diagram determine the followings properties of the material (Poisson’s ratio of the material is 0.32)
a) Resilience
b) Shear modulus
c) Bulk modulus
d) Ductility as described by the percent change in length
Transcribed Image Text:600
550
500
450
400
350
300
250
200
150
100
50
0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09
0.1
0.11 0.12 0.13 0.14 0.15 0.16 0.17 0.18
Strain
Stress, MPa
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A steel component is subjected to alternate cyclical loading. The steel follows Basquin's law for high cycle fatigue, o, x N = C, (where the stress amplitude is in MPa). Ignore the geometric detail and assume that Marin's modifying factors are all equal to 1. You are given the minimum stress ain = -213 MPa, the maximum stress omax = 213 MPa. The material data are Tensile strength oUTS = 539 MPa, Basquin's constant c, = 875 MPa, Basquin's exponent a = 0.085. a) Calculate the stress ratio R, the stress amplitude o, in MPa and the mean stress am in MPa. The answers are acceptable with a tolerance of 0.01 for R and of 1 MPa the stresses. R: MPa MPа b) Calculate the corresponding life, in 10° cycles, (tolerance of 0.1 106 cycles) N :arrow_forwardDraw the stress-strain diagram for any ductile and brittle material and explain the following points: (a) Modulus of elasticity (b) Yield strength (c) Ultimate Strength (d) Ductility (e) Toughnessarrow_forwardThe composite bar is firmly attached to unyielding supports. The bar is stress-free at 50°F. Compute the stress in each material after the 80-kip force is applied and the temperature is increased to 100°F. Use a = 6.5 x106/°F for steel and a = 12.8 x106/°F for aluminum. Aluminum A = 2 in.² E = 10 x 106 psi 15 in. Steel A = 3 in.2 E = 29 × 106 psi 80 kips 10 in.arrow_forward
- #4 will upvote to anyone who will answerarrow_forward3-3. Data taken from a stress-strain test for a ceramic are given in the table. The curve is linear between the origin and the first point. Plot the diagram, and determine approximately the modulus of toughness. The rupture stress is or = 53.4 ksi.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning