
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
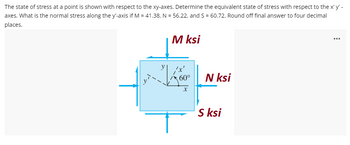
Transcribed Image Text:The state of stress at a point is shown with respect to the xy-axes. Determine the equivalent state of stress with respect to the x' y' -
axes. What is the normal stress along the y'-axis if M = 41.38, N = 56.22, and S = 60.72. Round off final answer to four decimal
places.
M ksi
60°
N ksi
X
S ksi
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the following structure, determine the stress in each bar. Indicate whether the stress is tensile or compressive. The area of each bar is indicated in this figure. Answ. AB = 8.33 ksi (C), BC = 8.33 ksi (C), DE = 25 ksi (T), AD = 16.6667 ksi (T), BE = 8.33 ksi (T), AE = 27.77 ksi (C)¸ CE = 10.41667 ksi (T).arrow_forwardPlease give me right solution a,b and c...arrow_forwardDetermine the equivalent state of stress on an element if it is oriented 50° counterclockwise from the element shown. Assume that σ = -13 ksi and Txy = -19 ksi. Solve the problem using ox Mohr's circle. σχ F Part A Determine the normal stress ox'. Express your answer in kilopounds per square inch to three significant figures. ANSWER: = Tap image to zoom ksi Part B Determine the normal stress Øy'. Express your answer in kilopounds per square inch to three significant figures. ANSWER:arrow_forward
- Rods AB and BC have diameters of 2.9 mm and 4.6 mm, respectively. A force F = 2.4 kN is applied to the ring at B, as shown. (Figure 1) Determine the angle so that the average normal stress in each rod is equivalent. Express your answer to three significant figures. What is this stress? Express your answer to three significant figures and include appropriate units.arrow_forwardMohr’s circle is shown for a point in a physical object that is subjected to plane stress. Each grid square is 600 psi in size. (a) Determine the stresses σx, σy, and the magnitude of τxy and show them on a stress element. (b) Determine the principal stresses and the magnitude of the maximum in-plane shear stress acting at the point and show these stresses on an appropriate sketch (e.g., see Figure 12.15 or Figure 12.16).arrow_forwardCalculate the design moment strength Mu for the following section. Take f'c = 40 MPa. Sketch the strain and stress distribution diagrams for each section and try to work out your solutions using equilibrium conditions. Yield stress for N bars is 500 MPa. 75 700 60 1500 T 4N28 450arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning