
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The state of in-plane stress at a point on an element of material is shown. Let |σx| = 370 MPa, |σy| = 130 MPa, and |τxy| = 85.0 MPa. Use this information to represent the state of stress of the same point that is rotated through an angle of θ = 25.0.
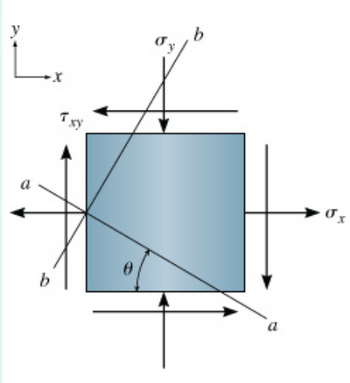
Transcribed Image Text:L₁
b
0
b
σ x
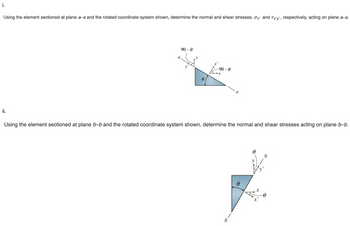
Transcribed Image Text:i.
Using the element sectioned at plane a-a and the rotated coordinate system shown, determine the normal and shear stresses, σ and Ta'y', respectively, acting on plane a-a.
ii.
a
90 - 0
⁹0
-90-0
x
Using the element sectioned at plane b-b and the rotated coordinate system shown, determine the normal and shear stresses acting on plane b-b.
0
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 3: The state of stress at a point in an elastic body is defined by the stress components, O11 = 2000; O22 = -2000; o12 = 1000; G23 = -400; 013 = 033 = 0. A plane that passes through the point has unit normal vector (1/5, 3/5, 3/V5) in relation to the x, y, z axes. (A) Find the stress vector components of the X, y, z axes acting on the plane. (B) Find the magnitude stress vector components of the x, y, z axes acting on the plane. (C) Find the magnitude of the normal stress acting on the plane. (D) Find the magnitude shear stress acting on the plane. (E) Construct the 3D Mohr's circle. (You can use the graphical paper to construct the circle and then take photo or by scanner to attach it with your answer). (F) Based on the Mohr's circle, determine the principal stresses and the maximum shear stress.arrow_forwardAn 6 mm diameter aluminum rod has lines scribed on it that are exactly 10 cm apart. After a 2.08 kN force has been applied, the separation between the lines has increased to l' = 10.009 cm. 30 cm 10 cm -F l' a. Calculate the stress and strain in the rod. (Express your answer for stress using two significant figures.) |MPa (Express your answer for strain using four decimal spaces.) E = b. To what total length has the rod stretched? (Express your answer using three decimal places.) L final cmarrow_forwardConsider the frame in (Figure 1). The crate weighs 400 lb. Follow the sign convention. Figure 4 ft A B 1.5 ft 1.5 ft 1.5 ft 1.5 ft F /C . E 0 D 0.4 ft < 1 of 1 ▼ Part D Determine the normal force at point E. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. NE = Submit Part E VE = Submit Determine the shear force at point E. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. Part F [5] 195| ΑΣΦ | 11 | vec 4 Request Answer ME = Π| ΑΣΦ I Request Answer vec Determine the moment at point E. Express your answer in pound-feet to three significant figures. [V=| ΑΣΦ www. vec ? ? ? lb lb lb-ftarrow_forward
- The square deforms into the position shown by the dashed lines in (Figure 1). The dimensions are S = 60 mm, S' = 65 mm, Ax₁ = 5 mm, and Ax₂ = 6 mm. Side D'B' remains horizontal. Figure 91.5° Ax₁ AX₂ < 1 of 1 Part A Determine the shear strain at A relative to the x, y axes. Express your answer in radians to three significant figures. 17 ΑΣΦ ↓↑ vec 6 (YA)zy = Submit Part B Request Answer Determine the shear strain at B relative to the x, y axes. Express your answer in radians to three significant figures. ? Review radarrow_forwardfill in the blank please Tensile normal stresses are considered positive in Mohr’s circle. For the specific stress element face, if the shear stress makes the element rotate clockwise, then the normal stress is drawn ( ) the σ axis.arrow_forwardThe solid rod is subjected to the loading shown. Take F = 100 kN, P = 10 kN. Determine the state of stress at point C. A) Determine the normal stress at point C. B) Determine the shear stress (τxy)C at point C. C) Determine the shear stress (τxz)C at point C.arrow_forward
- 1.40 Given a major principal strain of 600µ and strain invariants I, = 400µ and I, = - 4800µ, find the remaining principal strains. Find, in magnitude and direction, the octahedral normal and shear strains. Answer: (1u = 1 x 10 ) 200p.- 400u. 133µ, 822uarrow_forwardThe state of stress at a point in a member is shown on the element. Take σx= 98 MPa, σy= 50 MPa, τxy= 35 MPa in the directions shown. Solve the problem using the stress transformation equations. A) Determine the normal stress component acting on the inclined plane AB. B) Determine the shear stress component acting on the inclined plane AB.arrow_forwardThe 1900-NN load is applied along the centroidal axis of the member. (Figure 1) Determine the magnitude of the resultant internal normal force in the member section a-a. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. 2) Determine the magnitude of the resultant internal shear force in the member section a-a. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forward
- Determine the average normal stress developed at points A, B, and C: 0.5in ● A TP₂ Iin. ↓ ● B 0.5in ● P3 ↑ C P4 P₁ ↑ The diameter of each Segment is indicated in the figure above. Take P₁ = 3 kip, P2 = 9 kip, P3 = 8 kip, P4 = 2 kiparrow_forwardA state of stress at a point A is given by σx = -75 MPa, σy = 122 MPa, and τxy = -3.75 MPa. Which of the following is one of the principal stresses for the point A.arrow_forwardFind the stresses acting on the element rotated by ø= 50° from the x-axis. Here, each ø is positive in the counterclockwise direction. Plot these stresses on the plot of the element rotated by each ø.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY