
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
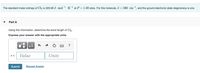
Transcribed Image Text:The standard molar entropy of Cl2 is 223.08 J · mol. K-l at P = 1.00 atm. For this molecule, i = 560 cm=1, and the ground electronic state degeneracy is one.
Part A
Using this information, determine the bond length of Cl2.
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
Value
Units
Submit
Request Answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Their relationship is ALWAYS spontaneous -ΔΗ +ΔΗ +AS -AS +AG -AGarrow_forwardOnly typed solutionarrow_forwardCalculate the number of microstates for each of the following systems. Simplify algebraic expressions or evaluate numerically. a. 4 b. 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 0 0 Wa = W₁ ≈ 1 1 4 1 3 n - 4 I P Enter numeric valuearrow_forward
- How many unique protons are present in the following molecules? CF3 CF 3 OCH3 "CH3arrow_forwardConsider a container with a frictionless piston that contains a given amount of CO₂- Assume that the behavior of this gas can be described by the van der Waals equation of state. For carbon dioxide gas (CO₂), the constants in the van der Waals equation are a=0.364 J- m³/mol and b=4.27 x 10 m³/mol. -5 Let's assume that initially the external pressure is 22.0 bar, which is the sum of a 1 bar atmospheric pressure and the pressure created by a very large number of very small pebbles that rest on top of the piston. The initial volume of gas is 0.5 L and the initial temperature is 25°C. Now, you will increase the volume of the gas by changing the external pressure slowly in a way that guarantees that the temperature of the system remains constant throughout the process. To do this, imagine you remove the pebbles one by one slowly to increase the volume by an infinitesimal amount. Every time you remove a weight you allow the system to equilibrate. Your cylinder is immersed in a water bath at…arrow_forward4) Use data for AG°f to calculate equilibrium constants for each reaction at 25C: a) C(s - graphite) C (s-diamond) J b) 4 Ag + O₂ = 2 Ag₂O R=631 Mal Rarrow_forward
- Answer the following questions with complete/step-by-step solutions: (Note: The following problems are interconnected to each other.) Problem 1. A quantity of an ideal gas in an isolated system is expanded isothermally and reversibly at 400 degrees Kelvin from a volume V1 to V2. During the expansion the gas absorbs 200 calories of heat from the reservoir in contact with it. Find (a) the entropy change of the gas, (b) the entropy change of the reservoir and (c) the entropy change of the whole system. Problem 2. If the gas in problem 1 is expanded from V1 to V2 isothermally but irreversibly at 400 degrees Kelvin with an absorption of 100 calories of heat, what will be the entropy changes for (a) the gas, (b) the reservoir, (c) the complete system? Problem 3. Suppose the gas in problem 1 expands freely from V1 to V2 at 400 degrees Kelvin. What will be the entropy changes for (a) the gas, (b) the reservoir, and (c) the entire system?arrow_forwardthe probabilities of states of independent systems X and Y are given by tables: xi x1 x2 pi 0,3 0,7 yi y1 y2 pi 0,4 0,6 find the entropy of the combined system (X, Y).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY