
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
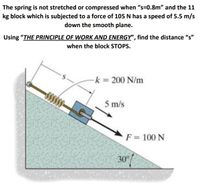
Transcribed Image Text:The spring is not stretched or compressed when “s=0.8m" and the 11
kg block which is subjected to a force of 105 N has a speed of 5.5 m/s
down the smooth plane.
Using "THE PRINCIPLE OF WORK AND ENERGY", find the distance "s"
when the block STOPS.
k = 200 N/m
5 m/s
F = 100 N
30°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- T= m Amr = 3195 kg truck starts at rest and beings to pull a mRv = 2035 kg RV behind it with a cable. Determine the velocity of the truck at time t = 5 s and the tension in the cord, T. Assume the tires provide a force of Ff = 9kN and positive direction is to the right. S T N Fr ⒸDarrow_forwardA 100 pound pipe is at rest vertically, when the cable is connected to B at the force of P=50 pounds. Find the pipes angular velocity and acceleration at A. Please include FBD is necessary. Thank you. 4 ft A 3 ft P = 50 lb В 3 ftarrow_forwardQ1 The slider of mass 1 kg attached to a spring of stiffness 400 N/m and unstretched length of 0.5 m is released from A. Determine the velocity of the slider as it passes through B and C. Also compute the distance beyond C where the slider will come to the rest. (Neglect friction and Use the concept of potential energy) 0.5 m 0.5 m do A www mmmmmmmmmmm 0.5 m B Darrow_forward
- M = A frisbee is thrown such that its final angular velocity is w = 9 after being in flight for t = 2 s. As it rad S flies, the wind applies a constant moment, causing the frisbee to rotate faster. If the frisbee was initially at rest, determine the moment of the wind and the work done by said moment. Assume the frisbee can be modelled as a disk with mass m = = 0.15 kg and that it rotates about its center of gravity G. The frisbee has a radius of r = 0.12 m. UM = N.m r J G Marrow_forwardThe spool, which has a mass of 2 kg, slides along the smooth horizontal spiral rod, r = (0.400) m, where is in radians, as shown in (Figure 1). Figure 8= 6 rad/s 1 of 1 Part A If its angular rate of rotation is constant and equals = 6 rad/s, determine the horizontal tangential force P needed to cause the motion, and the horizontal normal force component that the spool exerts on the rod at the instant 0 = 45°. Express your answers in newtons using three significant figures separated by a comma. P, N = Submit Provide Feedback VE ΑΣΦ Request Answer ↓vec ? Next >arrow_forwardThe 4-lb collar is compressed against a spring a distance of 6 inches and then releasedfrom rest. The spring can be considered elastic and has a constant of k = 10 lb/in. Thespring is not adhered to the collar, and can be considered massless, so it will notextend into tension. Plot the acceleration of the collar as a function of x for x = 0 to 7 inches.What is the velocity as the collar leaves the spring?arrow_forward
- A mass that weighs 8 lb stretches a spring 24 inches. The system is acted on by an external force of 4 sin(4t) lb. If the mass is pulled down 6 inches and then released, determine the position of the mass at any time t. Assume that the u-axis is directed downwards and ft = g 32 Express your answer as a linear combination of sin(at) $² and cos(at), where u is in feet and t is in seconds. u(t) = Determine the first four times at which the velocity of the mass is zero. Exclude t = 0 as trivial, and enter exact answers. First zero: t = Third zero: t = Second zero: t = Fourth zero: t =arrow_forwardThe collar has a mass of 28-kg and slides along the smooth rod. Two springs are attached to it and the ends of the rod as shown. S kA kB: 12 0.25 m Each spring has an uncompressed length of I1=2-m and l2=3-m and stiffnesses k1=51-N/m and k2=176-N/m respectively. Determine the velocity that must be subjected to the collar to generate a compression of 0.7 marrow_forwardA spring with spring constant k=70 kN/m is used to stop the box of mass m with initial velocity V1= 7 m/s. The spring is initially compressed 100 mm with cables. Since the box produces a maximum compression x=60 mm in the spring. m= 60 kg. s=750mm(a) Find the kinetic coefficient of friction between the surface and the box.(b) Find the velocity of the box as it moves back from its original position.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY