
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
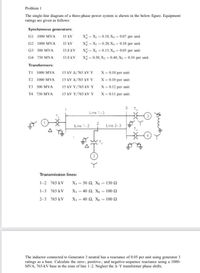
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 1
The single-line diagram of a three-phase power system is shown in the below figure. Equipment
ratings are given as follows:
Synchronous generators:
GI 1000 MVA
15 kV
X - X2 - 0.18, Xo = 0.07 per unit
G2 1000 MVA
15 kV
X = X = 0.20, Xo = 0.10 per unit
G3 500 MVA
13.8 kV
x = X, = 0.15, X, = 0.05 per unit
G4 750 MVA
13.8 kV
X = 0.30, X2 = 0.40, X, = 0.10 per unit
Transformers:
TI 1000 MVA
15 kV A/765 kV Y
X = 0.10 per unit
T2 1000 MVA
15 kV A/765 kVY
X= 0.10 per unit
T3 500 MVA
15 kV Y/765 kV Y
X = 0.12 per unit
T4 750 MVA
15 kV Y/765 kVY
X = 0.11 per unit
T3
Line 1-3
Line 1-2
2
Line 2-3
Transmission lines:
1-2 765 kV
X¡ = 50 Q, X, = 150 N
1-3 765 kV
X = 40 N, X, = 100 .
2-3 765 kV
X1 = 40 Q, X, = 100 N
The inductor connected to Generator 3 neutral has a reactance of 0.05 per unit using generator 3
ratings as a base. Calculate the zero-, positive-, and negative-sequence reactance using a 1000-
MVA, 765-kV base in the zone of line 1-2. Neglect the A-Y transformer phase shifts.
石。
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two single phase transformers A and B with equal turns ratio have reactance of j3.2 and j19.2 referred to secondary. When operated in parallel, the load sharing of 100 kW at 0.8 pf lag between A and B transformers would respectively be a) 75 kw and 25kw b) 60 kw and 40 kw c) 20 kw and 80 kw d) 25 kw and 75 kwarrow_forward5.5 kW, 1450 rpm. L-type equivalent circuit and parameters for a continuous sinusoidal phase of a star connected 3-phase ASM with line voltage 220 V and frequency 50 Hz are given as follows, ignoring core (iron) losses: R1=0.21 Ohm, R2=-0.18 Ohm, X1=X2-0.66 Ohm and Xm = 9.9 Ohm How many times the inrush current will be the rated current when the ASM is started directly? Answer options group 8.0815 2.6455 4.3763 7.1534 1.2558 6.3414 5.2280 3.7473arrow_forward1. A single-phase power system as shown in Figure 1 consists of a 240 V, 60 Hz generator supplying a load, Zod = 8 + j6 Q through a transmission line of impedance, Zne = 0.08 + j0.14 Q. Answer the following questions: (1) transformer, T; and T2. Determine the voltage at the load and transmission line losses without the (ii) Determine the voltage at the load and transmission line losses with the transformer, T, and T2. T1 T2 1:10 10:1 IG Zaine Zioad source Figure 1arrow_forward
- Number 17arrow_forward2) The power system consists of generators, motors, transformers, and transmission lines. The ratings are as follows: G1: 3-phase generator 25 MVA, 11 KV, X = 20% M1: 3-phase motor M2: 3-phase motor T1:3 single phase transformers T2: 3-phase transformer Line: 15 MVA, 13 KV, X = 25% 7.5 MVA, 13 KV, X = 25% Single phase transformer rating 30 MVA, 6.9/69 KV X = 10% Three phase transformer rating 30 MVA, 13.8/69 KV X = 10% Χ - 50 Ω = Τι G₁ 2. Line Figure 1. 3 T2 Σ M₁ Δι M2 Find the reactance (X) in p.u. units, given the base value of 25 MVA, 11 KV.arrow_forwardA synchronous generator is rated 645 MVA, 24 kV, 0.9 pf lagging. It has a synchronous reactance 1.2 . The generator is feeding full load at 0.9 pf lagging at rated voltage. Calculate: (a) Excitation emf (E,) and power angle 8 (b) Reactive power drawn by the load Carry out calculations in pu form and convert the result to actual values.arrow_forward
- In the following power system M ilio YA T₂ L47 YA 5 ΔΥ synchronous generators G₁,G₂ and synchronous motor M all have the same per-unit impedances Xo=0.05, X₁=X₂=0.7 The three transformers T₁, T₂, T3 are identical with X=0.1pu. Finally, the three transmission lines L47, L57, L67 are identical with per-unit impedances X₁=0.2, X₁=X₂=0.1 Pre-fault all voltages are 1 pu. Then the a phase at bus 6 faults to ground (through zero impedance). What is the magnitude of the per-unit fault current? उह 4 7 L 67 L 57 Yarrow_forwardIf the load draws a current of 2727 A, in phase, from a generator, which of the following statement is true? O A. The reactive power is flowing from generator to the load and the real power is flowing from the load to the generator. O B. Since the current is in phase with the generator voltage, both the real and reactive power is flowing from the generator to the load. O .Since the current is leading the generator, both the real and reactive power is flowing from the load to the generator. O D. The real power is flowing from generator to the load and the reactive power is flowing from the load to the generator. O E. None of the other choices are correctarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,