
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780470458365
Author: Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
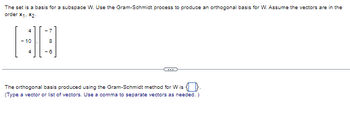
Transcribed Image Text:The set is a basis for a subspace W. Use the Gram-Schmidt process to produce an orthogonal basis for W. Assume the vectors are in the
order *1-*2-
-7
8
-6
The orthogonal basis produced using the Gram-Schmidt method for W is
(Type a vector or list of vectors. Use a comma to separate vectors as needed.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Determine whether the vectors (1,2,3), (5,6,7), (9,10, 11), and (4,8, 12) are linearly independent.arrow_forwarda = Let 9₁ 4 2 92 4 = || b = 93 = 6 0 b, and c. Use the Gram-Schmidt procedure to determine an orthonormal basis {9₁, 92, 93} for the subspace of R³ spanned by the vectors a, 3 C = 3 -3 3arrow_forwardUsing the Gram-Schmidt process, construct an orthogonal basis for V con- sisting of vectors with integer components, where -({··]}) V = Spanarrow_forward
- Express v = (-i, 2 + i, -1) as a linear combination of the following basis vectors given below. Justify your answer. (see image)arrow_forwardFind the value of K that lets the vectors form a basisarrow_forwardUse the Gram-Schmidt process to convert the given set of vectors to an orthogonal basis with respect to the given inner product. (Apply the Gram-Schmidt process in the order the vectors are given and do not normalize.) The set {2x + 1,x², 9} with respect to the inner product (p, q) = p(−1)q(-1) + p(0)q(0) + p(2)q(2).arrow_forward
- in terms of linear algrebraarrow_forwardplease dont provide hand written solution K If B is the standard basis of the space P3 of polynomials, then let B = {1, t, t², t³). Use coordinate vectors to test the linear independence of the set of polynomials below. Explain your work. (-3-t)³, (-2-t)², 31+31t+10² +³ Write the coordinate vector for the polynomial (-3-t)³, denoted p₁.arrow_forwardFind the scalar and vector projections of b onto a. a = −3, −6, 2 , b = 2, 1, 1arrow_forward
- Please show clear workarrow_forward2- Verify that the set of vectors (-0.6, 0.8, 0), (0.8, 0.6, 0), (0, 0, 1) form an orthonormal basis for R³, then obtain an orthonormal basis from them. Express (3,7,-4) as a linear combination of the orthonormal basis. 3- Determine whether the following sets of vectors are linearly dependent or linearly independent. a) (1,1,0), (0,0,1), (0,1,1) in R³ b) (1,0,0), (2,2,0), (3,3,3) in R³arrow_forwardCreate a basis of R¹ containing vectors (1,-1,3, 2) and (2,1,3, 4) by adding basis vectors of the orthogonal comlement to their span.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780073397924
Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781118141809
Author:Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781337798310
Author:Peterson, John.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

