
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
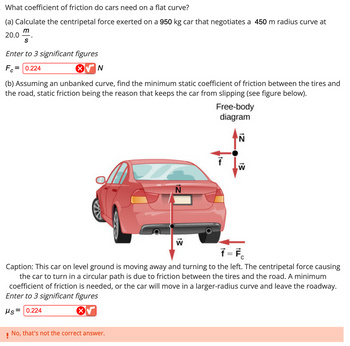
Transcribed Image Text:What coefficient of friction do cars need on a flat curve?
(a) Calculate the centripetal force exerted on a 950 kg car that negotiates a 450 m radius curve at
m
20.0
S
Enter to 3 significant figures
Fo 0.224
N
(b) Assuming an unbanked curve, find the minimum static coefficient of friction between the tires and
the road, static friction being the reason that keeps the car from slipping (see figure below).
W
!
No, that's not the correct answer.
Free-body
diagram
f
N
W
ƒ = F
Caption: This car on level ground is moving away and turning to the left. The centripetal force causing
the car to turn in a circular path is due to friction between the tires and the road. A minimum
coefficient of friction is needed, or the car will move in a larger-radius curve and leave the roadway.
Enter to 3 significant figures
Hs= 0.224
√
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
the second part is inc
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
the second part is inc
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Merry-go-round Fir for maximum a Consider the father pushing a playground merry-go-round as pictured above. He exerts a force of 302N on the 50.0-kg merry-go-round, which has a 1.48m radius. Consider the merry-go- round itself to be a uniform disk with negligible retarding friction. a) How long does it take the father to give the merry-go-round and his 18.0-kg child sitting at the outer edge an angular velocity of 1.6 rad/s? b) How many revolutions must he go through to generate this velocity? rev c) If he exerts a slowing force of the same magnitude, how long would it take him to stop them?arrow_forwarde Calculate the centripetal force on the end of a 122-m (radius) wind turbine blade that is rotating at 0.5 rev/s. Assume the mass is 6 kg. F₁ = Question Help: Submit Question Read 1 Hint 1 Read 2arrow_forwardA. A 1800 kg car's tires have a coefficient of friction equal to 0.25 on wet asphalt. What is the fastest that this car can drive along a flat turn with a radius of 200 m without slipping? B. How would this speed change if the car had a mass of 3600 kg instead? C. How would this speed change if the road were slanted? Would the possible speed be higher or lower?arrow_forward
- practice problemarrow_forwardA bucket of water with a mass of 2.36 kg is attached to a rope that is wound around a cylinder. The cylinder has a mass of 3.00 kg and is mounted horizontally on frictionless bearings. The bucket is released from rest. A) Find the speed of the bucket after it has fallen through a distance of 0.800 m. in m/s B) What is the tension in the rope? in N C) What is the acceleration of the bucket? Enter a positive value if the acceleration of the bucket is upward and enter a negative value if the acceleration of the bucket is downward. in m/s^2arrow_forwardCar A uses tires for which the coefficient of static friction is 0.281 on a particular unbanked curve. The maximum speed at which the car can negotiate this curve is 11.0 m/s. Car B uses tires for which the coefficient of static friction is 0.812 on the same curve. What is the maximum speed at which car B can negotiate the curve?arrow_forward
- Suppose you use an ideal pulley of the type shown in image (a) in the figure below to support a car engine of mass 145 kg. MA-2 MA-3 MA-4 Ο (b) (c) (a) What would be the tension in newtons in the rope? N (b) What force in newtons must the ceiling supply, assuming you pull straight down on the rope? Neglect the pulley system's mass. Narrow_forwardA car of mass M = 900 kg traveling at 60.0 km/hour enters a banked turn covered with ice. The road is banked at an angle 0, and there is no friction between the road and the car's tires as shown in (Figure 1). Use g = 9.80 m/s throughout this problem. Figure (arrow_forwarda The deflection of the needle would decrease. b The deflection of the needle would increase. c The needle would return to its rest position. d The needle would deflect in the opposite direction.arrow_forward
- A small block with mass 0.0450 kg slides in a vertical circle of radius 0.0710 m on the inside of a circular track. There is no friction between the track and the block. At the bottom of the block's path, the normal force the track exerts on the block has magnitude 3.70 N Part A What is the magnitude of the normal force that the track exerts on the block when it is at the top of its path?arrow_forwardI Revie A racetrack curve has radius 80.0 m and is banked at an angle of 15.0°. The coefficient of static friction between the tires and the roadway is 0.400. A race car with mass 1200 kg rounds the curve with the maximum speed to avoid skidding. Part A As the car rounds the curve, what is the normal force exerted on it by the road? Express your answer with the appropriate units. ? n = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B What is the car's radial acceleration? Express your answer with the appropriate units. Arad = Value Units Submit Request Answerarrow_forwardA certain spacecraft measures 60 m in length when it is at rest. The spacecraft then travels at 75% of the speed of light. Determine the length of the spacecraft (a) according to a passenger onboard the ship. (b) according to an Earthbound observer. Explain your answersarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON