
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
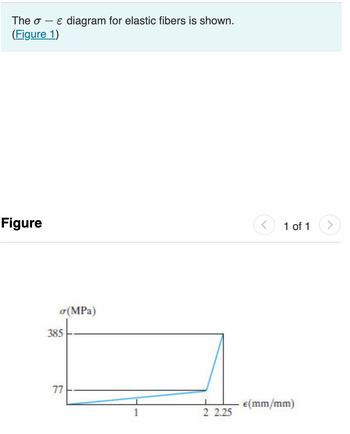
Transcribed Image Text:The σ - ε diagram for elastic fibers is shown.
(Figure 1)
Figure
385
σ(MPa)
77
<
1 of 1
€(mm/mm)
1
2 2.25

Transcribed Image Text:Part A
Determine the modulus of elasticity of the fibers.
Express your answer using three significant figures.
Part B
Estimate their modulus of toughness.
Express your answer using three significant figures.
Part C
Estimate their modulus of resilience.
Express your answer using three significant figures.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A 0 degree lamina of glass fiber-epoxy 3501 composite with fiber arranged withmax. volume fraction of fiber in a square array is subjected to a stress σx = 50MPa at theta =20 degrees. What are the resulting lamina strains [ε]xy and strains[ε]12? (Apply the Halpin-Tsai correction to transverse moduli and shear moduli)arrow_forwardConsider a graphite-reinforced polymer composite lamina. Plot the graph of each elastic constant (E1, V12, E2, and G₁2) versus the fiber volume fraction V. Use all values of V, ranging from 0 to 1 (in increments of 0.1). Assume the following material properties for the matrix and fibers. Em 4.62 GPa, E{ = 233 GPa, E = 23.1 GPa, G₁₂ = = 8.96 GPa = vm = 0.360 v2 = 0.200 123 = 0.400 G₁3 = 8.27 GPaarrow_forwardWhich of these models would best give a description of viscoelastic behavior for polymers? Explain your answerarrow_forward
- Rigid bar ABCD is loaded and supported. Steel [E=30,000 ksi] bars (1) and (2) are unstressed before the load P is applied. Bar (1) has a cross-sectional area of 0.625 in.2 and bar (2) has a cross-sectional area of 1.25 in. 2. After load P is applied, the strain in bar (2) is found to be 900 με. If there is a clearance of 0.05 in. in the pin connection at C, determine: (a) the stresses in bars (1) and (2).(b) the vertical deflection of point D.(c) the load P.arrow_forward1. Arectangular plate 50 mm x 10 mm with a hole 10 mm diameter is subjected to an axial load of 10KN. Taking stress concentration into account, find the maximum stress induced. [Ans. 50 MPa]arrow_forwardCompute the modulus of elasticity for a composite which uses High Modulus Carbon fibers and Polyester matrix. The volume fraction of fibers is 45 % and matrix is 55 %. Note-use chart in imagearrow_forward
- Mechanics of materials Iarrow_forwardI need to calculate the tensile stiffness along the fibre which have a length of 250um below are the values ive been given Matrix Stiffness Em = 6 GPaMatrix Strength (sigma)m = 50 MPaFibre Volume Fraction 0.41Fibre Stiffness Ef = 49 GPaFibre Strength (sigma)f = 103 MPaFibre Shear Stiffness Gf = 23 GPaMatrix Shear Stiffness Gm = 2 GPaInterface Strength ti = 7 MPaFibre Diameter = 7um poissons ratio of matrix = 0.32Poissons ratio of fibre = 0.23tensile stress of 190 MPa applied at an angle of 60 degrees. it is a unidirectional composite.arrow_forwardQ2/ At constant strain, about 7.6 Mpa of stress is used to a polymer. After 960 h, the stress reduced to 4.8 Mpa at 30 °C. When the same polymer is heated to 50 °C the relaxation time is 1200 h. 1- Estimate the relaxation time at 30 °C? 2- Estimate the stress after 1440 h and 30 °C? 3- Estimate the stress relaxation activation energy using the equation below: !=Cexp ) Where R = 8.314 j/mol. K, and C: constant %3D RTarrow_forward
- My answer is displayed and incorrect. Please give answer in ksi.arrow_forwardThe diameter (d) of a solid rod (i.e., with a circular cross-section) is 16 mm and is made from a homogeneous material. The length (L) of the rod is 1.75 m and Young’s Modulus for the material (E) is 250 GPa. When the rod is placed under tension it experiences deformation and a stress (?) of 650 MPa. Calculate the following:(1) Strain energy (U) to 2 decimal places in Joules.(2) Strain energy per unit volume (U/V) in J/m3(3) The change in length ∆L to 2 decimal places in mm.(4) The strain (?) due to deformation to 2 significant figures. (show all work)arrow_forwardThis is a Important Problem, Please solve carefully Include all the steps (diagram, formula) Handwritten Solution Recommendedarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY