
- The ROT-13
algorithm encrypts a string one character at a time by adding 13 to the value of the internal representation of the character. We want our encryption scheme to cover the entire printable ASCII range. After examining the ASCII character set and their internal representations, we see that characters 0 through 32 and character 127 are control characters. Technically, characters 32 (space) and 127 (DEL) are printable, but we don’t want to include them in our encryption routine. Therefore, we want our encrypted string to only contain characters in the range of 33 through 126. As an example:
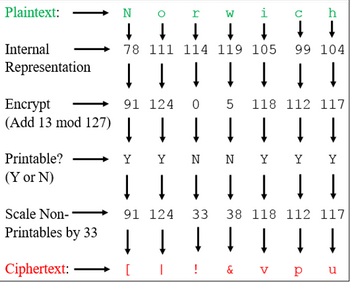
Plaintext: Norwich
Ciphertext: [|!&vpu
The internal representation of ‘N’ is 78. 78 plus 13 is 91, which is the character ‘[‘. The internal representation of ‘o’ is 111. 111 plus 13 is 124, which is the character ‘|’. The internal representation of ‘r’ is 114. 114 plus 13 is 127. Since 126 is our maximum value for our desired printable range, we must use modular arithmetic. Therefore, we get (114+13)%127=0. The character for 0 on the ASCII chart is NULL, which is still not within our desired range. So we have to shift any values less than 33. Therefore, ‘r’ encrypts to ‘!’ which is value 33. Character ‘s’ would be encrypted as ‘"’, which is value 34. The image below helps explain the encryption process.
Write a C++ program that prompts the user to enter a password. The program then calls an encryption function that returns a string as the encrypted password. Print the encrypted password to the screen. Note that the printing of the encrypted password should occur inside of main() and not inside of your encryption function. Show your source code and a screenshot of your program output.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

- Encrypt Encrypt the animal name pangolin using the letter to number correspondence abcdet ghijk 1 m nopqrstuvM x y z e 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 18 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 28 21 22 23 24 25 and the encrypton function f (n) = (n + 20) mod 26 The answer will be a nonsense word (no numbers). Decrypt An animal name was encrypted with the scheme described above. The encrypted animal name is urifinf . What is the animal name?arrow_forwardBob sent Alice an encrypted message. The message consists of 3 words. In each word, Bob encoded the letters as follows: A = 01, B = 02, C = 03, ..., Z = 26. The he wrote the codes next to each other to form a number that represent the word. For example, the word "WE" is encoded as: 2305 since it consists of 2 letters W=23 and E=05. After encoding, Bob encrypted each encoded word with RSA using Alice public key(pq, e) where p=100000007, q=10000019, e=13. Alice received the following 3 encrypted words from Bob: 451095483713115 570203572152011 762324289903198 She used here RSA private key (d) to decrypt the message. The first word of the message that Bob sent was: WE.arrow_forwardSolving this problem in the Java languagearrow_forward
- Can someone explain to me each step and why it would be the respective answers?arrow_forwardThe binary string 11001111101001 is a floating-point number expressed using the 14-bit simple model given in your text. What is its decimal equivalent? Note: in the 14-bit simple model, the left-most bit is the sign, followed by 5 bits for the exponent, followed by 8 bits for the mantissa (There are no implied bits). The exponent is in Excess 15 notation.arrow_forwardwrite an encoder and a decoder for a modified "book cipher." A book cipher uses a document or book as the cipher key, and the cipher itself uses numbers that reference the words within the text. For example, one of the Beale ciphers used an edition of The Declaration of Independence as the cipher key. The cipher you will write will use a pair of numbers corresponding to each letter in the text. The first number denotes the position of a word in the key text (starting at 0), and the second number denotes the position of the letter in the word (also starting at 0). For instance, given the following key text (the numbers correspond to the index of the first word in the line) [0] 'Twas brillig, and the slithy toves Did gyre and gimble in the wabe; [13] All mimsy were the borogoves, And the mome raths outgrabe. [23] "Beware the Jabberwock, my son! The jaws that bite, the claws that catch! [36] Beware the Jubjub bird, and shun The frumious Bandersnatch!" [45] He took his vorpal sword in…arrow_forward
- Write a program to handle a user's rolodex entries. (A rolodex is a system with tagged cards each representing a contact. It would contain a name, address, and phone number. In this day and age, it would probably have an email address as well.) Typical operations people want to do to a rolodex entry are: 1) Add entry 2) Edit entry 3) Delete entry 4) Find entry 5) Print all entries 6) Quit You can decide what the maximum number of rolodex entries is and how long each part of an entry is (name, address, etc.). When they choose to edit an entry, give them the option of selecting from the current rolodex entries or returning to the main menu — don't force them to edit someone just because they chose that option. Similarly for deleting an entry. Also don't forget that when deleting an entry, you must move all following entries down to fill in the gap. If they want to add an entry and the rolodex is full, offer them the choice to return to the main menu or select a person to overwrite. When…arrow_forwardConvert the decimal number -43.68 to a floating-point number expressed in the 14-bit simple model given in your textbook. Note: in the 14-bit simple model, the left-most bit is the sign, followed by 5 bits for the exponent, followed by 8 bits for the mantissa (There are no implied bits). The exponent is in Excess 15 notation. 101011.1010arrow_forwardWrite a Java program to perform basic string compression using the counts of repeated characters. For example, the string "aabcccccaaa" would become "a2b1c5a3".arrow_forward
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





