
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
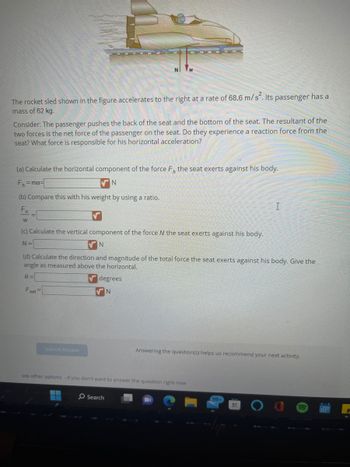
Transcribed Image Text:The rocket sled shown in the figure accelerates to the right at a rate of 68.6 m/s². Its passenger has a
mass of 62 kg.
Consider: The passenger pushes the back of the seat and the bottom of the seat. The resultant of the
two forces is the net force of the passenger on the seat. Do they experience a reaction force from the
seat? What force is responsible for his horizontal acceleration?
(a) Calculate the horizontal component of the force F, the seat exerts against his body.
F₁=ma=
N
(b) Compare this with his weight by using a ratio.
F₁
W
(c) Calculate the vertical component of the force N the seat exerts against his body.
N=
N
(d) Calculate the direction and magnitude of the total force the seat exerts against his body. Give the
angle as measured above the horizontal.
0=
Fet=
Submit Answer
degrees
N
see other options - If you don't want to answer the question right now
O Search
Answering the question(s) helps us recommend your next activity.
99+
I
H
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The rocket sled shown in the figure decelerates at a rate of 155 m/s2 . Its passenger has a mass of 75 kg. Use a coordinate system in which the sled is moving in the positive direction, and assume the contact forces with the seat are the only forces acting on the passenger.(a) Calculate the horizontal component of the force that the seat exerts against his body, in newtons. What is the ratio of the magnitude of the horizontal force to the magnitude of the force of gravity? Find the angle of the total force that the seat exerts against his body. Give your answer in degrees from the negative horizontal direction, with positive being clockwise.arrow_forwardConsider 2 forces acting on a mass of 2.37 kg. F1 = 10 N @ 19.3 degrees and F2 = 7.97 N @ 67.9 degrees where the angles are measured relative to the +x direction. What is the magnitude of the acceleration produced considering only these 2 forces acting?arrow_forwardConsider two blocks connected . Block A has mass 2.00 kg, and block B has mass 5.00 kg. The table on which B sits is frictionless, the cord connecting the blocks is light and flexible, and the pulley is light and frictionless. The horizontal force F S has magnitude F = 20.0 N, and block B moves to the left with an acceleration of 1.50 m/s2. What is the tension in the cord that connects the two blocks?arrow_forward
- There are two forces on the 2.26 kg box in the overhead view of the figure but only one is shown. For F₁ = 12.6 N, a = 11.5 m/s², and 0 = 24.4°, find the second force (a) in unit-vector notation and as (b) a magnitude and (c) a direction. (State the direction as a negative angle measured from the +x direction.) (a) Number i (b) Number i (c) Number i + i Units Units F x Ĵ Units î îarrow_forwardTwo objects are connected by a massless cable passing over a frictionless pulley. Object A is positioned on a table, while object B hangs freely. The coefficient of kinetic friction between object A and the table is 0.09950. If the mass of object A is 150 kg, and the mass of object B is 238 kg, what is the acceleration of the objects?arrow_forwardTwo teams of nine members each engage in a tug of war. Each of the first team's members has an average mass of 72 kg and exerts an average force of 1350 N horizontally. Each of the second team's members has an average mass of 77 kg and exerts an average force of 1373 N horizontally. (a) What is the acceleration (in m/s2 in the direction the heavy team is pulling) of the two teams?arrow_forward
- Two blocks are connected by a massless rope. The rope passes over an ideal frictionless and massless pulley such that one block with mass m1= 12.25 kg is on a horizontal table and the other block with mass m2=7.5 kg Thanks vertically. Both blocks experience gravity in the tension fourth, T. Used to coordinate system specified in the diagram.(A) assuming friction forces are negligible, write an expression, using only the variables provided come up for the acceleration at the block of mass M one expresses an X direction. Your answer should involve the tension, T. (B) under the same assumptions, written expression for the magnitude of the acceleration, a2, the block of mass into experiences in the Y direction. Your answer should be in terms of attention, T and M2.  (c) carefully consider how the accelerations a1 and a2 are related. So for the magnitude of the acceleration, a1, of the block of mass m1, in meters per square second. (D) find the magnitude of the tension in the rope , T…arrow_forwardA block of mass m1 = 40 kg on a horizontal surface is connected to a mass m2 = 16.0 kg that hangs vertically as shown in the figure below. The two blocks are connected by a string of negligible mass passing over a frictionless pulley. The coefficient of kinetic friction between m1 and the horizontal surface is 0.23. (a) What is the magnitude of the acceleration (in m/s2) of the hanging mass? (b) Determine the magnitude of the tension (in N) in the cord above the hanging mass.arrow_forwardAn SUV containing 5 passengers has a mass of 3500 kg. It has a driving force of 2500 N directed west on a perfectly horizontal road. The surface of the road exerts a resistive force of 500 N due east. At the same time, a strong wind is blowing a force of 500 N due east in the opposite direction of the car's drive force. Does the car have any acceleration? If yes, then what is the magnitude and direction of the car's acceleration?arrow_forward
- An ideal massless rope passes over a massless, frictionless pulley. Block A with mass mA=7.2 kg, and block B with mass mB=4.9 kg, are suspended from opposite ends of the rope, as shown. (This contraption is known as an Atwood's machine.) Consider the motion of the blocks after they are released from rest. Let "a" be the magnitude of their acceleration, and let FT be the tension in the rope. Let upward be the positive y direction for block B, and let downward be the positive y direction for block A. What is the numerical value, in newtons, of the tension in the rope?arrow_forwardThe figure shows two blocks connected by a cord (of negligible mass) that passes over a frictionless pulley (also of negligible mass). The arrangement is known as Atwood's machine. Block 1 has mass m1 = 1.2 kg; block 2 has mass m2 = 1.7 kg. What are (a) the magnitude of the blocks’ acceleration and (b) the tension in the cord?arrow_forwardThree blocks are connected over two frictionless, massless pulleys by two inextensible, massless cords as shown in the figure. There is friction between block m2 and the horizontal surface of the table. If the block m₁ moves downward after being released from rest, then what is the magnitude of the acceleration of the blocks and the magnitude of the tension in the cords in terms of the masses of the blocks m₁, m2, and m3, the coefficient of kinetic friction between block m₂ and the table, uk, and the acceleration due to gravity, g. Include a force diagram or free-body diagram of the situation. m1 mq m3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON