Question
thumb_up100%
Practice
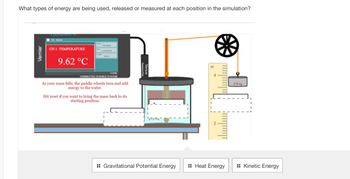
Transcribed Image Text:### Energy Simulation Explanation
This diagram represents a simulation demonstrating the transformation of different types of energy.
#### Components:
1. **Temperature Display**
- Located on the left, a Vernier interface shows the current temperature, which is 9.62°C. This indicates the heat energy involved in the system.
2. **Mass and Pulley System**
- To the right, a mass (270 g) is suspended by a rope over a pulley. This system is crucial for demonstrating gravitational potential energy as the mass is elevated.
3. **Paddle Wheel and Beaker**
- As the mass falls, it drives a paddle wheel submerged in the beaker below, transferring energy to the water. The movement of the paddle wheel illustrates kinetic energy.
4. **Energy Transitions**
- **Gravitational Potential Energy**: The elevated mass holds potential energy, preparing to be released as it descends.
- **Kinetic Energy**: As the mass falls, it converts its potential energy to kinetic energy, rotating the paddle wheel.
- **Heat Energy**: The rotation stirs the water, transferring kinetic energy into heat energy, resulting in a temperature increase.
5. **Measurement Ruler**
- Positioned beside the mass, it measures the height of the mass related to gravitational potential energy.
#### Interactive Elements:
- The simulation allows users to observe energy conversion and offers a reset function to bring the mass back to its starting point.
- Below the diagram, options exist to identify the types of energy involved: Gravitational Potential Energy, Heat Energy, and Kinetic Energy.
This educational tool aids in understanding how energy transforms from one form to another within a physical system.
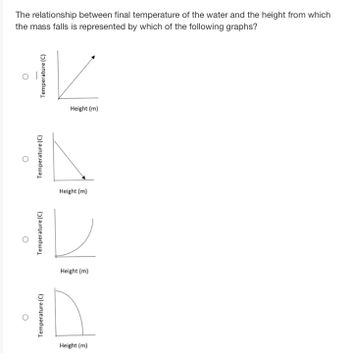
Transcribed Image Text:The question asks about the relationship between the final temperature of water and the height from which a mass falls.
Several graphs are provided as options:
1. **Graph 1:** Shows a linear increase where the temperature (°C) increases as the height (m) increases.
2. **Graph 2:** Shows a linear decrease where the temperature (°C) decreases as the height (m) increases.
3. **Graph 3:** Displays an upward curve indicating that the temperature (°C) increases at an increasing rate with height (m).
4. **Graph 4:** Displays a downward curve indicating that the temperature (°C) decreases at an increasing rate with height (m).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Question in picturesarrow_forwardTwo identical magnitude point charges Q are located on the x-axis both a distance d away from the z-axis as shown. The charges have opposite sign. Using Coulomb's Law, Ē = çî, find the electric field for point P on the z-axis.arrow_forwardNeed help with part 4arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios