
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
On an uncomfortable summer day, the air is at 87 °F and 80 % relative humidity. A laboratory air conditioner is to deliver 1.0 x 103 ft3/min of air at 55 °F in order to maintain the interior air at an average temperature of 75°F and a relative humidity of 40%.
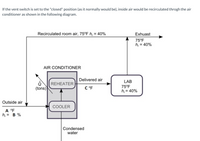
Transcribed Image Text:If the vent switch is set to the "closed" position (as it normally would be), inside air would be recirculated through the air conditioner as shown in the following diagram.
### Diagram Explanation:
The diagram represents the air circulation process within a closed system air conditioner, specifically illustrating the flow of air through the system.
1. **Air Conditioner Components**:
- **Reheater**: A component within the air conditioner that reheats the air before it's delivered.
- **Cooler**: A component that cools the air, and during this process, condensed water is produced.
2. **Airflow Process**:
- **Recirculated Room Air**: The process starts with recirculated room air at a temperature of 75°F and a relative humidity of 40%.
- **Delivering Air**: After passing through the air conditioner, the air is delivered to the lab at a specified temperature (C °F).
- **Exhaust Air**: Some air is exhausted out of the system at 75°F and 40% relative humidity.
3. **External Air Interaction**:
- **Outside Air**: There is an intake of outside air with unspecified temperature (A °F) and relative humidity (B %).
- **Ventilation and Heat Exchange**: The interaction between indoor and outside air within the air conditioner contributes to the overall cooling and reheating process.
The diagram helps visualize how air is conditioned and circulated within a controlled environment, maintaining specific temperature and humidity levels in the lab space.
![Assume A = 87 °F, B = 80%, C = 55 °F.
The recycle ratio (ft³ recirculated/ft³ exhausted) is 2:1.
Calculate the condensation rate and the overall cooling requirement in tons if conditioned air is delivered at the same rate, temperature, and relative humidity as in the first part.
What percentage of the cooling load on the air conditioner is saved by recirculating the air?
- **Condensation rate:** [Input field] lbₘ/min
- **Cooling load:** [Input field] tons
- **Percentage savings:** [Input field] %
Note: The diagram is an input form for calculating and displaying the condensation rate, cooling load, and percentage savings.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/73303aca-d795-4569-9e8f-a8984c4a41f6/c1121bff-6fb6-4b54-bb9f-24da3fa82666/auevkyf_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:Assume A = 87 °F, B = 80%, C = 55 °F.
The recycle ratio (ft³ recirculated/ft³ exhausted) is 2:1.
Calculate the condensation rate and the overall cooling requirement in tons if conditioned air is delivered at the same rate, temperature, and relative humidity as in the first part.
What percentage of the cooling load on the air conditioner is saved by recirculating the air?
- **Condensation rate:** [Input field] lbₘ/min
- **Cooling load:** [Input field] tons
- **Percentage savings:** [Input field] %
Note: The diagram is an input form for calculating and displaying the condensation rate, cooling load, and percentage savings.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 7 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Estimate the thermal conductivity of tomato juice at 35 ° C. (Water content = 87.0% wet basis). Thermal conductivity of material = AnswerW / m ° Carrow_forwardHeat Conduction The wall (thickness L) of a furnace, with inside temperature 800° C, is comprised of brick material [thermal conductivity = 0.02 W m-¹ K-¹)]. Given that the wall thickness is 12 cm, the atmospheric temperature is 0° C, the density and heat capacity of the brick material are 1.9 gm cm-³ and 6.0 J kg ¹ K¹ respectively, estimate the temperature profile within the brick wall after 2 hours. Solve the partial differential equation ƏT = pc at Ə əx (NOT) k subject to the initial condition TX 2L and = T(x,0) = 800 sin and boundary conditions at the inner (x = L) and outer (x = 0) walls of T = 0 x = 0 = 0 ƏT at x = L əx Find the temperature profile at T = 7200 seconds at = 2 hours.arrow_forwardOne side of a copper block 5 cm thick is maintained at 250°C. The other side is covered with a layer of fiberglass 2.5 cm thick. The outside of the fiberglass is main- tained at 35°C, and the total heat flow through the copper-fiberglass combination is 52 kW. What is the area of the slab?arrow_forward
- 3 A continuous countercurrent adiabatic rotary drier is being designed for the production of 500 lb/h of a product containing 2% moisture from wet crystal containing 30% moisture, wet basis. The air entering the drier will have a dry-bulb temperature of 230°F and a wet-bulb temperature of 102°F. The air leaving the drier will be at a temperature of 115°F. Because of the small size of the crystals, the highest allowable air velocity is 10 lb dry air/ft2-min of drier cross section. Find: a. Dry air required (lb/min) b. Cross-sectional area of the drier c. Length of drier required if the volumetric coefficient of heat transfer is 25 BTU/ft3-h-°Farrow_forwardInsulating material is used to reduce heat loss from the heating furnace walls to the room. The surface temperature of the insulating material is 100 ° C and the other surfaces 25 ° C. Allowable heat loss up to 160 W / m2 from the wall. If the thermal conductivity of the insulation material is 0.05 W / (m ° C), calculate the required thickness of insulation. insulation thickness = Answer cmarrow_forwardA piece of beef steak 7 cm thick will be frozen in the freezer room -30 ° C. This product has a moisture content of 73%, a density of 970 kg / m³, and a thermal conductivity (frozen) of 1.1 W / (m K). Estimate the freezing time. using the Plank equation. This product has an initial freezing temperature of -1.75 ° C, and the movement of air in the freezing room gives a convective heat transfer coefficient of 15 W / (m² K). t f = ... hour.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The