
Essentials Of Investments
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781260013924
Author: Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
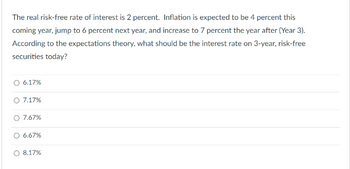
Transcribed Image Text:The real risk-free rate of interest is 2 percent. Inflation is expected to be 4 percent this
coming year, jump to 6 percent next year, and increase to 7 percent the year after (Year 3).
According to the expectations theory, what should be the interest rate on 3-year, risk-free
securities today?
O 6.17%
O 7.17%
O 7.67%
O 6.67%
8.17%
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Treasury securities that matures in 8 years currently have a rate of 11.9 %. Inflation is expected to be 5 percent each of the next 3 years and 6 percent each year after the 3rd year. The maturity risk premium is estimated to be 0.2 (t-1). Where t is the zero. The real risk rate is assumened to be tconsint over time what is the risk free rate of interest. a. 6. 28 b. 4.88 C. 2.51 D. 4.68arrow_forwardCalculating interest rates The real risk-free rate (r*) is 2.8% and is expected to remain constant. Inflation is expected to be 8% per year for each of the next five years and 7% thereafter. The maturity risk premium (MRP) is determined from the formula: 0.1(t – 1)%, where t is the security’s maturity. The liquidity premium (LP) on all Smith and Carter Inc.’s bonds is 1.05%. The following table shows the current relationship between bond ratings and default risk premiums (DRP): Rating Default Risk Premium U.S. Treasury — AAA 0.60% AA 0.80% A 1.05% BBB 1.45% Q1. Smith and Carter Inc. issues fifteen-year, AA-rated bonds. What is the yield on one of these bonds? Disregard cross-product terms; that is, if averaging is required, use the arithmetic average. a. 12.33% b. 13.38% c. 6.05% d. 11.98% Q2. Based on your understanding of the determinants of interest rates, if everything else remains the same, which of the following will be true? Option a. A BBB-rated bond has a…arrow_forwardI need help with this questionarrow_forward
- A 5-year Treasury bond has a 4.35% yield. A 10-year Treasury bond yields 6.5%, and a 10-year corporate bond yields 9.8%. The market expects that inflation will average 2.85% over the next 10 years (IP10 = 2.85%). Assume that there is no maturity risk premium (MRP = 0) and that the annual real risk-free rate, r*, will remain constant over the next 10 years. (Hint: Remember that the default risk premium and the liquidity premium are zero for Treasury securities: DRP = LP = 0.) A 5-year corporate bond has the same default risk premium and liquidity premium as the 10-year corporate bond described. The data has been collected in the Microsoft Excel Online file below. Open the spreadsheet and perform the required analysis to answer the question below. Open spreadsheet What is the yield on this 5-year corporate bond? Round your answer to two decimal places. fill in the blank %arrow_forwardUsing the expectations hypothesis theory for the term structure of interest rates, determine the expected return for securities with maturities of two, three, and four years based on the following data. (Input your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places.) 1-year T-bill at beginning of year 1 1-year T-bill at beginning of year 2 1-year T-bill at beginning of year 3 1-year T-bill at beginning of year 4 2-year security 3-year security 4-year security Expected Return Interest Rate 58 78 10% 128arrow_forward4arrow_forward
- An investor in Treasury securities expects inflation to be 2.0% in Year 1, 2.7% in Year 2, and 3.55% each year thereafter. Assume that the real risk-free rate is 2.35% and that this rate will remain constant. Three-year Treasury securities yield 5.20%, while 5-year Treasury securities yield 6.00%. What is the difference in the maturity risk premiums (MRPs) on the two securities; that is, what is MRP5 - MRP3? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal placesarrow_forwardToday is January 2, 2022, and investors expect the annual nominal risk-free interest rates in 2022 through 2024 to be: Year One-Year Rate (rRF) 2022 2.5 % 2023 2.3 2024 3.3 Assume the bonds have no risks. What is the yield to maturity for Treasury bonds that mature at the end of 2023 (a two-year bond)? Round your answer to one decimal place. % What is the yield to maturity for Treasury bonds that mature at the end of 2024 (a three-year bond)? Round your answer to one decimal place. %arrow_forwardA 5-year Treasury bond has a 4.25% yield. A 10-year Treasury bond yields 6%, and a 10-year corporate bond yields 8.9%. The market expects that inflation will average 2.7% over the next 10 years (IP10 = 2.7%). Assume that there is no maturity risk premium (MRP = 0) and that the annual real risk-free rate, r*, will remain constant over the next 10 years. (Hint: Remember that the default risk premium and the liquidity premium are zero for Treasury securities: DRP = LP = 0.) A 5-year corporate bond has the same default risk premium and liquidity premium as the 10-year corporate bond described. The data has been collected in the Microsoft Excel Online file below. Open the spreadsheet and perform the required analysis to answer the question below. Open spreadsheet What is the yield on this 5-year corporate bond? Round your answer to two decimal places. % Check My Work Reset Problemarrow_forward
- 3. Calculating interest rates The real risk-free rate (r*) is 2.8% and is expected to remain constant. Inflation is expected to be 7% per year for each of the next two years and 6% thereafter. The maturity risk premium (MRP) is determined from the formula: 0.1(t – 1)%, where t is the security’s maturity. The liquidity premium (LP) on all Smith and Carter Inc.’s bonds is 1.05%. The following table shows the current relationship between bond ratings and default risk premiums (DRP): Rating Default Risk Premium U.S. Treasury — AAA 0.60% AA 0.80% A 1.05% BBB 1.45% Smith and Carter Inc. issues 7-year, AA-rated bonds. What is the yield on one of these bonds? Disregard cross-product terms; that is, if averaging is required, use the arithmetic average. 11.54% 10.94% 10.49% 5.25% Based on your understanding of the determinants of interest rates, if everything else remains the same, which of the following will be true? In…arrow_forwardShow complete stepsarrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Essentials Of Investments
Finance
ISBN:9781260013924
Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,



Foundations Of Finance
Finance
ISBN:9780134897264
Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. William
Publisher:Pearson,

Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395250
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...
Finance
ISBN:9780077861759
Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education