
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
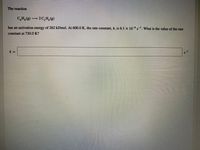
Transcribed Image Text:The reaction
C,H, (g) 2C,H,(
has an activation energy of 262 kJ/mol. At 600.0 K, the rate constant, k, is 6.1 x 10-8 s-1. What is the value of the rate
constant at 730.0 K?
k =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the following reaction mechanism: Step 1: 2NO (g) + 1.50,(g) --> N,Og(s) Step 2: 2NO,(g) --> 2NO(g) + O2 (g) Write the overall reaction and identify any reaction intermediates.arrow_forwardThe reaction C 4 H 8 (g) longrightarrow2C 2 H 4 (g) has an activation energy of 262kJ / m * o * l . At 600.0 K, the rate constant, k, is 6.1 * 10 ^ - 8 * s ^ - 1 What is the value of the rate constant at 800.0 K? k=arrow_forwardGeneral Chemistry 4th Edition McQuarrie • Rock • Gallogly dUniversity Science Books presented by Macmillan Learning The reaction C,H¿ (g) → 2 C,H¿(g) has an activation energy of 262 kJ/mol. At 600.0 K, the rate constant, k, is 6.1 × 10-8 s-!. What is the value of the rate constant at 840.0 K? k =arrow_forward
- For the reaction A + B ---> C, the rate constant at 215°C is 5.0x10-3 M-1s-1and 1.2x10-1 M-1s-1at 452 °C. What is the activation energy for the reaction? [R=8.314 x 10-3kJ/mol.K]arrow_forwardThe rate constant for the reaction is 0.200 M-! · s-! at 200 °C. A products If the initial concentration of A is 0.00780 M, what will be the concentration after 105 s? [A] = M * TOOLS x10arrow_forward8. Dinitrogen tetraoxide (N2O4) decomposes spontaneously at room temperature in the gas phase: N2O4 (g) → 2 NO2(g) The rate law governing the disappearance of N2O4 with time is A[N,O4] = k N2O4]. At At 30°C, k = 5.1 x 106 s-1 and the activation energy for the reaction is 54.0 kJ/mol. Calculate the time (in seconds) required for the partial pressure of N2O4(g) to decrease from а. 0.10 atm to 0.010 atm at 30°C. b. Calculate the value of the rate constant at 300K. Repeat the calculation for the reaction in a) at the new temperature (300K). С. d. Write an observation about how the rate of reaction changed upon increasing the temperature.arrow_forward
- Please don't provide hand writtin solution....arrow_forwardConsider the following general reaction for which gases A and B are mixed in a constant volume container: A(g) + B(g) -> C(g) + D(g) Match what happens to the rate of the reaction under the following changes: (consider each change separately) v all of gas B is removed from the container more gas A is added to the container the temperature of the container is increased there is no change to the reaction rate ya catalyst is added to the container I. the reaction proceeds at a faster rate v gas D is also added to the container the reaction proceeds at a slower rate II. some of gas B is removed from the container Iy the reaction does not proceed at all the volume of the container is increasedarrow_forwardThe reaction C₂H₂(g) → 2C₂H₂(g) - has an activation energy of 262 kJ/mol. At 600.0 K, the rate constant, k, is 6.1 x 10-8 s-1. What is the value of the rate constant at 820.0 K? k = 9.42 X10-26 Incorrect S-1arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY