
The owner of a small factory has installed a new well to supply process water.
The well is 0.3 m in diameter and is fully screened for the entire 12 m depth of the aquifer, which is composed of coarse sand having a bulk density of 2 g/cm3, K of 0.1 cm/sec, porosity of 0.25 and organic content of 0.5%.
The radius of influence of this well can be taken as 3,000 m. What is the steady state drawdown of the well, if the average water use by the factory is 360 L/min.
A plume of TCE-contaminated groundwater lies 800 m from the well. How fast is the TCE plume moving towards the well? Neglect any movement that may be due to regional groundwater flow and consider only the influence of well pumping at hydraulic steady state.
Please only use the equation I have provided to answer this question. Thank you
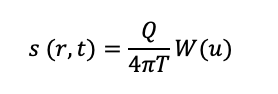
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

- Assume a chemical solvent, which is denser than water is spilled into the reservoir. How many days will it take for the contaminant to reach the observation well assuming only advection occurs in the aquifer? The stratum has a hydraulic conductivity of 4 x 10-² cm/sec The silty sand in the aquifer has a void ratio of 0.75. Observation well↓ el. 167.3 m Reservoir Clay Silty sand Clay 256 m el. 165.0 m 3.2 marrow_forwardCould you help me answer the following question? Thank you A fully penetrating pumping well extracts groundwater from a confined aquifer with a pumping rate of 750 m3/day. The hydraulic conductivity of the aquifer is 10 m/day and the saturated thickness is 50 m. The drawdown of the aquifer from this pumping well is insignificant at a distance of 1000 m from the pumping well. At what distance from the pumping well is the drawdown 10 cm? Assume the hydraulic gradient is negligible in the local area. Transmissivity T = 1746.76 gal/min/ft Hydraulic conductivity = 11.645 gal/min/ft2 Storativity = 0.809 The drawdown on Jenny’s Well by the end of August. =0.6902 ft. Observation well situated is 69.7 ft away from the pumping well (which is pumping at the rate of 305 gal/min). The aquifer is confined, and the depth has been measured from well logs and is 150 ft. The data for time (t) and drawdown (s) is given below: t (min) s (ft) 0.072 0.003 0.105 0.006 0.155 0.012…arrow_forwardA confined aquifer has a thickness of 30m (m) and is fully penetrated by well where the aquifer is pumped at the rate of 500 litres per second. The groundwater thickness (H₁) is 50 m. The drawdown measured in two observation wells located at distance of 10 m and 100 m from the well are 7.5 m and 0.5m respectively. Determine the average hydraulic conductivity of the aquifer. At what distance from the well the drawdown is insignificant i.e. is zero (R).arrow_forward
- In a confined aquifer, a 50-cm diameter well fully penetrates the aquifer. The hydraulic conductivity of the aquifer was approximately 0.8 m/day. Originally the piezometric head was 300 m above the top of the aquifer, which is 30 m. thick. If 0.8 m³ / min. is pumped from the well, what should be the depth of water in the well? What will the height of the piezometric head be ( above the top of the aquifer ) at a distance of 50 m. from the well? Assume the radius of influence to be 1000 ft.arrow_forwardA site consists of a homogenous dense silty sand layerof 8m thickness which is underlain by an imprevious stiff clau stratum. The initial water table was at 3m depth below the ground level. A pumping test was carrier out by pumping water at the rate of 0.7 m^3/min. Onservation wells were dug into the ground at 25m and 50m distances from the center line of the well. At steady state (i.e., when there was no change in water levels in the observation wells), the water levels in the two wells dropped by 500mm and 150mm, respectively. Determine the hydraulic conductivity of the clay sand layer.arrow_forwardA well penetrates an unconfined aquifer, with undisturbed water level (ho) equal to 21m. After pumping the well at a constant rate of Q = 0.07 m/s, the steady-state drawdown at distances of 45 m and 110 m from the well are 3 m and 1 m. respectively. Assume the void ratio as 0.2. Compute the hydraulic conductivity of the aquifer. 215.0 m/day what is the porosity 0.16 find the darcy velocity in m/day 69.4 m/dayarrow_forward
- Which of the following are characteristics of an unconfined aquifer. Select all that apply. Pore spaces are 100% filled with water. An artesian well results from digging into this aquifer. This aquifer is sandwiched between two impermeable layers. This aquifer can reach the ground surface if the water table depth is already shallow.arrow_forwardThe permeability of sand in horizontal and vertical directions are 3 × 10- 3 cm/sec and 1 x 10-3 cm/sec and the permeability of clay in horizontal and vertical directions are 9 x 10-7 cm/sec and 3 × 10-9 cm/sec, then the ratio of X seepage Loss per meter length of dam in sand to clay is:arrow_forwardIn a field testing, the hydraulic gradient between two peizometers is 1.11, the area of flow is 4.08 m2 and the hydraulic conductivity of the aquifer material is 0.94 m/day, calculate the discharge in m3/day. Note that discharge cannot be negativearrow_forward
- A well 0.5 m in diameter penetrates 33 m below the static water table. After a long period of pumping at a rate of 80 m³/hr, the drawdowns in wells 18 and 48 m from the pumped well were found to be 1.8 and 1.1 respectively. (1) What is the transmissivity of the aquifer? (2) What is the approximate drawdown in the pumped well? (3) Determine the radius of influence of the pumping well.arrow_forwardA field pumping test was conducted from an aquifer of sandy soil of 4 m thickness confined between two impervious strata. When equilibrium was established, 105 liters of water was pumped out per hour. The water elevation in an observation well 3.50 m away from the test well was 2.1 m and another 6.0 m away was 2.7 m from the roof level of the impervious stratum of the aquifer. Find the value of k of the soil in m/sec.arrow_forwardA well in an unconfined aquifer is pumped at the rate of 50 L/s ( 800 gal/min.). The thickness of the aquifer is 30 m. and the elevation of the phreatic surface is 25 m. above the underlying aquiclude at an observation of well 20 m away from the well and 34.6 m above at a well 50 m. away. What is the value of K for this aquifer?arrow_forward

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning





