
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781285199047
Author: John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
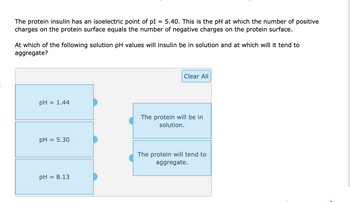
Transcribed Image Text:The protein insulin has an isoelectric point of pl 5.40. This is the pH at which the number of positive
charges on the protein surface equals the number of negative charges on the protein surface.
At which of the following solution pH values will insulin be in solution and at which will it tend to
aggregate?
pH
= 1.44
pH = 5.30
pH
= 8.13
Clear All
The protein will be in
solution.
The protein will tend to
aggregate.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- β‑Galactosidase (β‑gal) is a hydrolase enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of β‑galactosides into monosaccharides. A 0.395 gsample of β‑galactosidase is dissolved in water to make 0.138 L of solution, and the osmotic pressure of the solution at 25 ∘Cis found to be 0.609 mbar. Calculate the molecular mass of β‑galactosidase.arrow_forwardChoose any amino acid and show, by diagrams of your own creation, how pH will modify the charge distribution of the molecule. Which form is present at the isoelectric point?arrow_forwardAt room temperature, the equation for Gibbs free energy change of an uncharged solute moving into the cell is this [C ] AG = 1.4 kcal/mol * log10 [C,] %3D Imagine that a concentration of an uncharged solute outside the cell is 1 M, and inside the cell 10 M. The movement of this solute into the cell will be Thermodynamically favorable (negative G) Thermodynamically unfavorable (positive G) Thermodynamically neutral (G = 0) %D O O Oarrow_forward
- write out the equilibrium expression for the solvation of Ag2CrO4 in water please explain step by steparrow_forwardAccording to Henry’s law the atmospheric partial pressure of CO2 dictates the concentration of aqueous CO2 according to the following equilibrium expression where k is the Henry’s law constant for CO2. CO2 (g) <-> CO2 (aq) k=1x10^-1.5 The acid dissociation constant Ka for carbonic acid applies to CO2 (aq). Given pKa1=6.35 and pKa2=10.33 and the fact that the partial pressure of CO2 in the atmosphere is 10^-3.5 atm, find the pH of water in equilibrium with the atmosphere.arrow_forwardWhat is the symbolic expression for the equillibrium constant for the reaction: 2C2H6(g) + 7 O2(g) = 4CO2(g)+6H2O(g)?arrow_forward
- Calculate AG° for H20(g) + 02(g) = H2O2 (g) at 595 K, using the following data: H2 (9) + O2 (9) = H2O2(g) K = 3.7 x 1037 at 595 K 2H2 (9) + O2 (9) = 2H2O(g) K = 2.6 × 10® at 595 K AG kJ/molarrow_forwardWrite the equilibrium constant expression (Kc) for the reaction below 2P2O5(g) + 10Cl2(g) ⇌ 4PCl5(aq) + 5O2(g)arrow_forwardWhat is the freezing point of a 0.400 m solution of sucrose in ethanol? The freezing point depression constant forethanol is 1.99oC/m and the freezing point of ethanol is -114.1oC.arrow_forward
- Type your answer... 20 Consider the reaction: N2(g) + 3H2 (g)2NH3 (g) AG°F (NH3) = -17.65kJ/mol Determine the equilibrium constant for this reaction at 298.15K. (Hint: Check the stoichiometry of the reaction when you use the Gibbs energy of formation) %3D Report your answer as a whole number (no places past the decimal point). Do not use scientific notation. Type your answer...arrow_forwardArrange the following bases in increasing base strength. There Strongest base Methylamine (CH3NH2), K, = 4.4 x 104 I Pyridine (C5H5N), K 1.7x 109 Aniline (C,H5NH2), K = 3.9 x 10 10 Dimethylamine (CH3)2NH), Kp = 5.1x 104 | Hydrazine (N2H4), Kg = 1.3 x 106 Weakest base 1. 2) 3. 4) 5.arrow_forwardCoral structures found in the Great Barrier Reef are composed of calcium carbonate, CaCO3, and are under threat of dissolution due to ocean acidification. Consider the following equilibrium reaction equation. CaCO3(s) + CO2(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ Ca2+(aq) + 2HCO3–(aq) Write the expression for the equilibrium constant, Kc for this reaction. Predict whether the pH of the ocean will increase or decrease as a result of a decrease in the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere (circle your answer). Calculate the molar solubility (s) of calcium carbonate in water at 25 °C when Ksp = 4.5 ´ 10–9.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning