
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
thumb_up100%
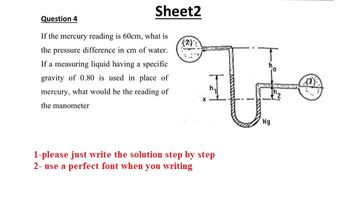
Transcribed Image Text:Sheet2
Question 4
If the mercury reading is 60cm, what is
the pressure difference in cm of water.
If a measuring liquid having a specific
gravity of 0.80 is used in place of
mercury, what would be the reading of
the manometer
مشيرا
1-please just write the solution step by step
2- use a perfect font when you writing
Hg
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (3) The pressure difference between two points as measured with a manometer is gven as P2 P1 pgh The following figure shows a single U-tube manometer for measuring pressure difference between ponts "A" and "E". Air Water The U-tube manometer. By determining the prestre at point "a" through the left leg and then through the right leg, show that the difference in pressure between point "A" PA and "B Ps is approximately given by PA- Pg = g (hz -h, )(Puzo) 21Page |曾目 底 の 10:44 PM 2/8/2021 Y MD 23 24 25 26 22 16 11 A ins prt sc home no + backspace unu lock 80 COarrow_forwardAn hydrogen vapour container is mounted with a pressure gauge which shows 86 bar. Then its absolute pressure is bar Pressure in bararrow_forwardThe specific gravity of steel is 8.89. What is the volume in ft of a steel ingot weighing 8650 kg?arrow_forward
- In the Figure shown, find the Pressure difference between A and B. Given: Specific Gravity of Oil, SGoil = 0.85, Specific Gravity of Mercury, SGmercury = 13.6, Specific Gravity of Kerosene, SGkerosene = 0.81, Specific Weight of Water, Ywater= 9790 N/m², Specific Weight of Air, yair = Also, hi = 20.0 cm, h2 = 14.0 cm, h3 = 10.0 cm, h4= 8.0 cm, h5 = 4.0 cm. 12 N/m³. Show all calculations. Kerosene Air IB A oil hay hi Water Mercuryarrow_forward1. A manometer is connected to a pipe containing a liquid with a specific gravity of 0.95. Find the pressure in the pipe, in Pascal. 25cm www יויויויידי Hg 45cm זיװיויויו اااا ➜arrow_forwardAn open tube mercury manometer is used to measure the pressure in an oxygen tank. When the atmospheric pressure is 1040 mbar, what is the absolute pressure (in Pascal) in the tank if the height of the mercury in the open tube is 28 cm higher? (density of mercury = 13.6 X 10° kg/m³) * O 1.41 X10 pa O 2.34 X105 pa O 1.82 X105 pa O 2.12 X105 paarrow_forward
- Determine the pressure if the reading in a barometer shows 2.5 inches of Mercury. 8.65 kPa 1.23 psi 60 mmHg O 65 torrarrow_forwardWhat is the absolute temperature reading in degree Rankine(°R), if the arbitrary temperature °C reading is thrice to the arbitrary temperature °F reading.arrow_forwardThree different liquids are used in the manometer shown below. www P₁ P2 T Pc Suppose fluid A is methanol, B is water, and C is a manometer fluid with a specific gravity of 1.37; P2 = 103 kPa, h1 = 31.4 cm and h2 = 25.4 cm, calculate P1 in kPa. The specific gravity of methanol is 0.792. PA- 5+24 h₂ -PBarrow_forward
- 1. A pressure gage 6 m above the bottom of the tank containing a liquid reads 90 kPa. Another gage 4 m above the bottom reads 103 kPa. What is the specific weight of the fluid?arrow_forwardThe pressure a car tire measured to be 200 kPa (gauge) before a trip to Welkom from Bloemfontein. On arrival at Welkon, the mesured presure was 219 kPa (gauge) after the trip. The atmospheric pressure of both places are given as 85 kPa. If the temperature of air in the tire before the trip is 16 ° C, determine the air temperature after the trip ( ° C to 2 decimal place). NB: the degree sign may not be included in the answer unit.=arrow_forwardA / An empty cold room has a volume of 27 m³, If the pressure inside is 1.2 bar and the temperature is -8 °C. If the temperature rise to 15 °C, and no change in the mass of air. what would be the pressure inside? 1arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY