Question
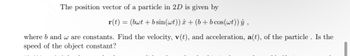
Transcribed Image Text:The position vector of a particle in 2D is given by
r(t) = (bwt + b sin(wt)) â + (b + bcos (wt)) ŷ,
where b and w are constants. Find the velocity, v(t), and acceleration, a(t), of the particle. Is the
speed of the object constant?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Suppose the position vector for a particle is given as a function of time by r(t) = x(t)î + y(t)ĵ, with x(t) : c = 0.120 m/s², and d = 1.02 m. (a) Calculate the average velocity during the time interval from t = 2.10 s to t = 3.85 s. V = m/s (b) Determine the velocity at t = 2.10 s. m/s = at + b and y(t) = ct² + d, where a = 1.80 m/s, b = Determine the speed at t = 2.10 s. m/s 1.20 m,arrow_forwardThe figure shows thes initial position i and the final position f of a particle. 4 m i 3 m 3 m 4 m 4m 3 m 5m 3m 2 m 1m What is the initial position vector in unit-vector notation? n 2 m/ Xy 1m! 4m 5m 3 m x .i 3m m î+ i m + i mkarrow_forwardA plane flies 493 km east from city A to city B in 45.0 min and then 983 km south from city B to city C in 1.30 h. For the total trip, what are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction of the plane's displacement, the (c) magnitude and (d) direction of its average velocity, and (e) its average speed? Give your angles as positive or negative values of magnitude less than 180 degrees, measured from the +x direction (east). (a) Number i Units (b) Number Units (c) Number i Units (d) Number i Units (e) Number Units IIarrow_forward
- Please asaparrow_forwardSuppose the position vector for a particle is given as a function of time by , with x(t) = at + b and y(t) =ct2 + d, where a = 1.00 m/s, b = 1.00 m, c= 0.125 m/s2, and d = 1.00 m. (a) Calculate the average velocity during the time interval from t = 1.00 s to t = 4.00 s. (b) Determine the velocity and the speed at t = 3.00 s. (c) Determine the acceleration at t = 3.00 s.arrow_forwardA particle has a constant acceleration of à = (6.7 m/s2)î + (3.8 m/s2)ĵ . At time t = 0, the velocity is zero and the position vector is ro = (9.3 m)î. (a) Find the velocity and position vectors as functions of time t. m/s m (b) Find the equation of the particle's path in the xy plane. (Use the following as necessary: x.) y = m Sketch the path. Choose File No file chosen This answer has not been graded yet. еВokarrow_forward
- You hit a golf ball from the (level) ground, with an initial speed and an initial angle. Ignore air resistance. (This is very unrealistic.) The initial speed is v0 = 23.7 m/s, and the angle the ball is hit at is θ = 46o. Calculate vx0, the initial horizontal component of velocity (in m/s). What equations describe the trajectory of the golf ball?arrow_forwardUse the given acceleration function and initial conditions to find the velocity vector v(t), and position vector r(t). Then find the position at time t = 3. a(t) = 8i + 4k v(0) = 5j, r(0) = 0 v(t) = r(t) = r(3) =arrow_forwardThe position vector 4.70t|i+ [et + ft2 locates a particle as a function of time t. Vector is in meters, t is in seconds, and factors e and f are constants. The figure gives the angle e of the particle's direction of travel as a function of time (0 is measured from the positive direction of the x axis). What are (a) factor e and (b) factor f, including units? 20° 0° 10 20 -20° t (s) (a) Number Units (b) Number Unitsarrow_forward
- Suppose that a dove is flying so that its acceleration vector at time t is given by a(t)=<t^4, t^3, t^2>, its initial velocity is v(0)=<1,2,3> and its initial displacement is s(0)=<7,6,5>. Find the position vector s(t) at time t.arrow_forwardA snowmobile is originally at the point with position vector 30.5 m at 95.0° counterclockwise from the x-axis, moving with velocity 4.89 m/s at 40.0°. It moves with a constant acceleration 1.72 m/s2 at 200°. After 5.00 s have elapsed, find the following. (Express your answers in vector form.) (a) its velocity vector. (b) its position vector.arrow_forwardA particle initially located at the origin has an acceleration of = 4.00ĵ m/s2 and an initial velocity of i = 6.00î m/s. (a) Find the vector position of the particle at any time t (where t is measured in seconds).( t î + t2 ĵ) m(b) Find the velocity of the particle at any time t.( î + t ĵ) m/s(c) Find the coordinates of the particle at t = 7.00 s.x = my = m(d) Find the speed of the particle at t = 7.00 s.m/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios