
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:The pH of an acid solution is 5.70. Calculate the K for the monoprotic acid. The initial acid concentration is 0.010 M. Be sure your answer has the correct
number of significant digits.
K
0
x10
X
5
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
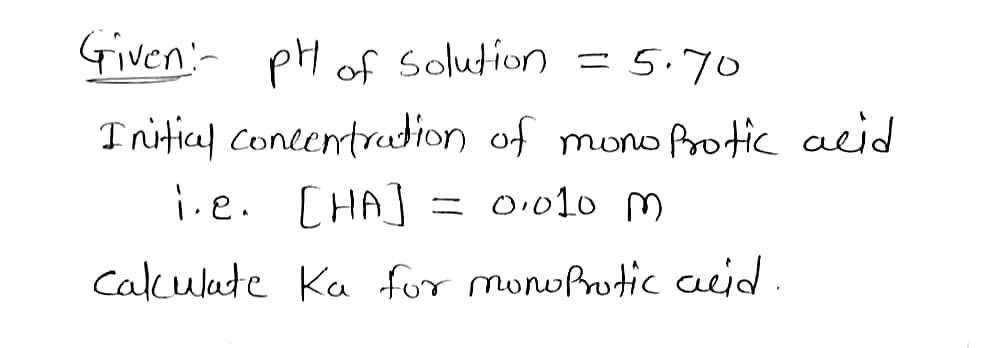
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- < Interconverting pH and hydronium ion concentration 1:23 solution A B Each row of the table below describes an aqueous solution at about 25 °C. Complete the table. That is, fill in any missing entries in the second and third columns. Be sure each entry you write ind correct number of significant digits. с H₂O*] PH 5.9 x 10-12 mol/L mol/L 6.1 x 10 mol/LO 1.22 Today 1:22 AM 317 .5G → Edit رت Eparrow_forwardThe neutralization of an acid with a base yields a salt and usually water in aqueous solution. Calculate the pH when 53.0 mL of 0.217 M hydrochloric acid is mixed with 53.0 mL of 0.217 M sodium hydroxide solution at 25 °C. pH = Calculate the pH when 53.0 mL of 0.217 M of a monoprotic weak acid, HA, is mixed with 53.0 mL of 0.217 M sodium hydroxide solution at 25 °C. The Ka for HA is 4.5 x 10-3. pH =arrow_forwardA chemist dissolves 172. mg of pure barium hydroxide in enough water to make up 120. mL of solution. Calculate the pH of the solution. (The temperature of the solution is 25 °C.) Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. x10 ?arrow_forward
- You find a mysterious solution. You add universal indicator to it and the solution turns Yellow! What kind of solution is it and why? A base, because it has a concentration of H+ ions less than 1 x 10^-7. An acid, because it has a concentration of H+ ions less than 1 x 10^-7. An acid, because it has a concentration of H+ ions greater than 1 x 10^-7. A base, because it has a concentration of H+ ions greater than 1 x 10^-7arrow_forwardThe quality assurance lab just received a shipment of three solutions. The lab manager asks you to verify the stock solutions and label each bottle with the solution's hydrogen ion concentration, [H*]. You first use the pH meter to determine the pH of each solution. Calculate the hydrogen ion concentration of solution #1, which has pH 2.25. Calculate the hydrogen ion concentration of solution #2, pH 7.25. which Calculate the hydrogen ion concentration of solution #3, which has pH 10.75. [H*] = I [H*] = [H] = M M Marrow_forwardAn engineer wants to determine whether a certain pH meter is working correctly. She uses the meter to measure the pH in 14 neutral substances (pH = 7.0) and obtains the data shown in the following table. 7.01 7.04 6.97 7.00 6.99 6.97 7.04 7.04 7.01 7.00 6.99 7.04 7.07 6.97 Is there sufficient evidence that the meter is not correctly measuring the pH?arrow_forward
- Please don't provide handwritten solution ....arrow_forwardIn an aqueous solution of a certain acid the acid is 0.083% dissociated and the pH is 4.20. Calculate the acid dissociation constant K of the acid. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K= x10 $ ? Xarrow_forwardA solution of sodium cyanide, NaCN, has a pH of 11.30. How many grams of NaCN are in 865 mL of a solution with the same pH? Kb (CN–) = 1.7 × 10–5 mass = ___________ g *I asked this prevously and 1.81 x 10^-12 is the wrong anwser for this question, if you get that.arrow_forward
- Some chemical compounds are listed in the first column of the table below. Each compound is soluble in water. Imagine that a few tenths of a mole of each compound is dissolved in a liter of water. The important chemical speci written in the second column of the table. Use the checkboxes to classify each compound. type of compound (check all that apply) important species present when dissolved in water lonic molecular strong weak strong weak base compound acid acid base C,H,NH, c,H,NH, OH , C,H,NH,, H,0 HC,H,0, H,0", C,H,0,, HC,H,0,, H,0 КОН к", он , н,о H BrO4 H,0", Bro,, H,0arrow_forwardFour solutions of an acid dissolved in water are sketched below, as if under a microscope so powerful individual atoms could be seen. The same volume of solution is shown in each sketch. Rank the solutions by the strength of the dissolved acid. That is, select 1 under the solution of the strongest acid, 2 under the solution of the next strongest acid, and so on. Note: =H,0 Solution 1 Solution 2 (Choose one) (Choose one) Solution 3 Solution 4 Submit Assignment Continue 2021 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility MacBook Air DII DD 吕0 F10 FB FO F6 F7 F3 F4 F5 F2 %23 $4 1. 3. 4. 7 8.arrow_forward1.00 mL of 0.345 M HCI -Solution A. To this solution you add 123.00 mL of H2O -Solution B. i) Solution A, determine the hydronium (H^ + ) and hydroxide (OH^-) concentrations And the pH and pOH ii) Solution B determine the hydronium (H ^+ ) and hydroxide (OH) concentrations and the pH and pOHarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY